NIST adopts standard to protect BIOS
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has paid attention to the security of the BIOS system, in order to protect it against viruses such as Mebromi and Niwa! Mem . The topic is quite specific: by now there are several such malicious programs, a few anti-virus companies understand the BIOS intrusion techniques. All the more surprising is a similar initiative on the part of the state American organization. Probably, this problem worries them greatly in the light of the threat of total BIOS infection on computers assembled in China.
One way or another, NIST has proposed new BIOS security rules for servers ( draft standard, pdf ). Previously, they have already released a similar standard to protect the BIOS on desktop computers ( pdf ).
')
The new document is a guide for manufacturers of server hardware and server administrators with a description of techniques that will help avoid getting the malicious code in the BIOS.
NIST names four key BIOS security features:
- Authentication when updating the BIOS using digital signatures to verify the authenticity of the new firmware.
- Optional secure local update mechanism, which requires the mandatory physical presence of the administrator near the machine to update the BIOS without a digital signature.
- Protection of the integrity of the firmware to prevent it from changing in a way that does not correspond to the above two.
- Security features that ensure that there is no mechanism for a processor or other system component to bypass BIOS security.
According to NIST experts, unauthorized BIOS modification by malware is a serious threat, since the BIOS occupies a privileged position in the system and allows the malware to remain functional even after reinstalling the operating system.
Recall that Windows 8 supports the special option "Secure Boot" (UEFI) ( http://blogs.msdn.com/b/b8/archive/2011/09/22/protecting-the-pre-os-environment-with- uefi.aspx ) to protect against unauthorized operating systems and software.
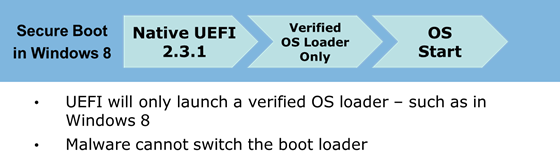
A special certificate will be placed in UEFI, while UEFI will check the bootloader before it starts. If any malware program replaces the bootloader, UEFI will prevent the system from starting.

One way or another, NIST has proposed new BIOS security rules for servers ( draft standard, pdf ). Previously, they have already released a similar standard to protect the BIOS on desktop computers ( pdf ).
')
The new document is a guide for manufacturers of server hardware and server administrators with a description of techniques that will help avoid getting the malicious code in the BIOS.
NIST names four key BIOS security features:
- Authentication when updating the BIOS using digital signatures to verify the authenticity of the new firmware.
- Optional secure local update mechanism, which requires the mandatory physical presence of the administrator near the machine to update the BIOS without a digital signature.
- Protection of the integrity of the firmware to prevent it from changing in a way that does not correspond to the above two.
- Security features that ensure that there is no mechanism for a processor or other system component to bypass BIOS security.
According to NIST experts, unauthorized BIOS modification by malware is a serious threat, since the BIOS occupies a privileged position in the system and allows the malware to remain functional even after reinstalling the operating system.
Recall that Windows 8 supports the special option "Secure Boot" (UEFI) ( http://blogs.msdn.com/b/b8/archive/2011/09/22/protecting-the-pre-os-environment-with- uefi.aspx ) to protect against unauthorized operating systems and software.

A special certificate will be placed in UEFI, while UEFI will check the bootloader before it starts. If any malware program replaces the bootloader, UEFI will prevent the system from starting.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/150218/
All Articles