Localization of ASP.NET MVC applications
On the topic of localization, there have already been several articles on Habré, for example Localization of an ASP.NET MVC application using a database or MVC 2: A complete guide to localization , but still the problem is still relevant.
Most recently, we had the task of localizing (translating) the site interface into another language. Our project is developed on ASP.NET MVC and there is a lot of client code in JavaScript and jQuery templates in the project. Another important point for us is the possibility of interactive work of translators, actually translating the site on the fly.
Basically, all articles related to this topic prescribe using resource files, but the solution is not flexible, cumbersome, and besides, the problem of translating scripts and templates, which are a significant part of any modern web project, is not taken into account. In the end, we decided to write our own Knoema.Localization library, which we recently posted openly. Our code is based on the remarkable development of Griffin , but has been significantly improved, includes an interactive translation tool, as well as the means of naturally localizing JS code and patterns.
The library allows you to localize:
The basic idea is that all localized strings are determined by the file name or class, and then presented in the form in which they are in the project.

')
To connect the library to the project, simply install the Nuget package Knoema.Localization.Mvc. To store localized data, you will also need a repository implementation. In the simplest case, it is enough to connect a ready implementation for EF by installing the Knoema.Localization.EFProvider package. An alternative option is to develop your provider by implementing a fairly simple ILocalizationRepository interface.
In Global.asax in Application_Start (), initialize the created repository:
and register in the RegisterRoutes method:
If you use Nuget, then when adding assemblies to web.config, the following values will be added automatically:
If not, then you need to add these settings manually.
The initial configuration is ready, now I will write in more detail about the details of use.
To localize the views in web.config, you need to specify that LocalizedWebViewPage will be used as the base class for the pages:
After that, the Html helper will be available in the presentation code:
Text can be parameterized:
The lines in the code are localized using the extension:
or, if the method is static, where there is no this object, you can use:
To localize models, it is necessary to override the standard validation provider and the metadata provider. To do this, in Application_Start () in Global.asax add:
All models that can be localized should be labeled with the Localized attribute.
Properties and attributes are not necessary to localize separately. All metadata will be added automatically; all that remains is to add an appropriate translation for them.
String constants in javascript code are localized using the jQuery extension:
The extension can be connected anywhere in the page using a helper, better for the entire application at once:
In addition, RenderLocalizationIncludes will embed a widget on the site (provided that you are an administrator), where you can translate everything that has been localized.
It seemed to us inconvenient that every time it is necessary to specify the file name. In our project we use Cassette resource minifiers, where there is an opportunity to add a resource handler before they are compiled. Simple configuration example:
Now the long call to $ .localize ("Layout options", "~ / js / shared / site.js") can be replaced by:
LocalizationResourceProcessor will replace __R with $ .localize and add the file name with the second parameter.
Translation can be added directly to the site using the widget that appears in the lower left corner of the screen.
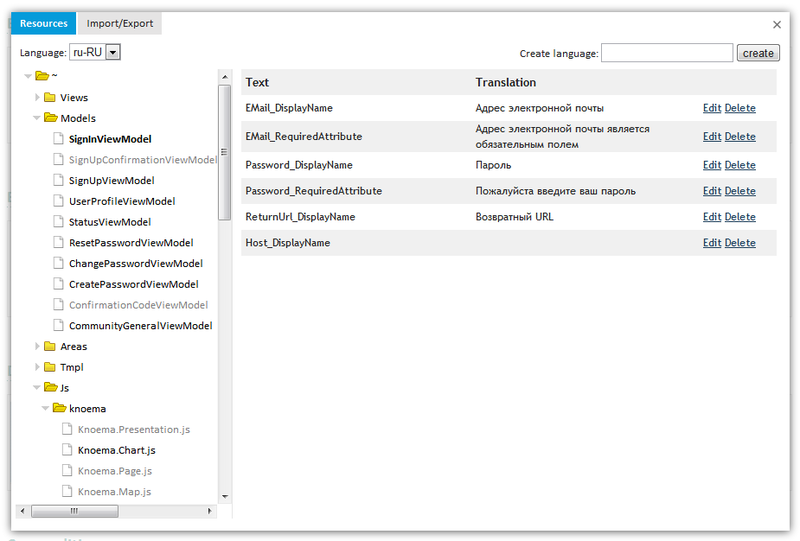
Those representations or models that are fully translated are highlighted in gray.
Editing:
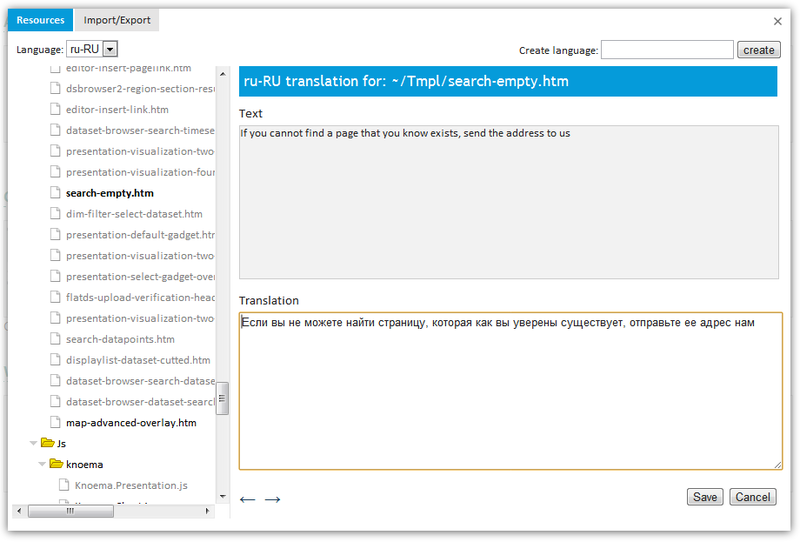
You can add a new language, export / import an existing one.

As a conclusion I want to say that the library was first written for internal use, it turned out quite well and therefore we decided to publish it and write an article.
References:
GitHub source code
Knoema.Localization.Core
Knoema.Localization.MVC
Knoema.Localization.Cassette
Most recently, we had the task of localizing (translating) the site interface into another language. Our project is developed on ASP.NET MVC and there is a lot of client code in JavaScript and jQuery templates in the project. Another important point for us is the possibility of interactive work of translators, actually translating the site on the fly.
Basically, all articles related to this topic prescribe using resource files, but the solution is not flexible, cumbersome, and besides, the problem of translating scripts and templates, which are a significant part of any modern web project, is not taken into account. In the end, we decided to write our own Knoema.Localization library, which we recently posted openly. Our code is based on the remarkable development of Griffin , but has been significantly improved, includes an interactive translation tool, as well as the means of naturally localizing JS code and patterns.
Opportunities
The library allows you to localize:
- Views
- String constants in the code
- Models and text in data validation attributes
- Text in javascript code
- JQuery templates
The basic idea is that all localized strings are determined by the file name or class, and then presented in the form in which they are in the project.

')
Connection and configuration
To connect the library to the project, simply install the Nuget package Knoema.Localization.Mvc. To store localized data, you will also need a repository implementation. In the simplest case, it is enough to connect a ready implementation for EF by installing the Knoema.Localization.EFProvider package. An alternative option is to develop your provider by implementing a fairly simple ILocalizationRepository interface.
In Global.asax in Application_Start (), initialize the created repository:
Knoema.Localization.LocalizationManager.Repository = new Knoema.Localization.EFProvider.LocalizationRepository(); and register in the RegisterRoutes method:
routes.IgnoreRoute("_localization/{*route}"); If you use Nuget, then when adding assemblies to web.config, the following values will be added automatically:
<system.webServer> <modules> <add name="Knoema.Localization" type="Knoema.Localization.Web.LocalizationModule"/> </modules> <handlers> <add name="Knoema.Localization" verb="*" path="_localization/*" type="Knoema.Localization.Web.LocalizationHandler" allowPathInfo="true" resourceType="Unspecified" /> </handlers> </system.webServer> If not, then you need to add these settings manually.
The initial configuration is ready, now I will write in more detail about the details of use.
View localization
To localize the views in web.config, you need to specify that LocalizedWebViewPage will be used as the base class for the pages:
<system.web.webPages.razor> ... <pages pageBaseType="Knoema.Localization.Mvc.LocalizedWebViewPage"> <namespaces> <add namespace="System.Web.Mvc" /> ... </namespaces> </pages> </system.web.webPages.razor> After that, the Html helper will be available in the presentation code:
public string R(string text, params object[] formatterArguments); Example
<p>@R("Hello world!")</p> Text can be parameterized:
<p>@R("Hello {0}!", username)</p> Localization of string constants in the code
The lines in the code are localized using the extension:
public static string Resource(this string value, object obj) or, if the method is static, where there is no this object, you can use:
public static string Resource(this string value, Type type) Example
"The given input does not refer to a valid Search.".Resource(this) Model localization
To localize models, it is necessary to override the standard validation provider and the metadata provider. To do this, in Application_Start () in Global.asax add:
ModelValidatorProviders.Providers.Clear(); ModelValidatorProviders.Providers.Add(new ValidationLocalizer()); ModelMetadataProviders.Current = new MetadataLocalizer(); All models that can be localized should be labeled with the Localized attribute.
Example
[Localized] public class SignInViewModel { [Required(ErrorMessage = "Please provide your e-mail")] [Display(Name = "E-mail")] public string EMail { get; set; } [Required(ErrorMessage = "Please type your password")] public string Password { get; set; } } Properties and attributes are not necessary to localize separately. All metadata will be added automatically; all that remains is to add an appropriate translation for them.
Javascript and html templates
String constants in javascript code are localized using the jQuery extension:
$.localize(text, scriptSource); The extension can be connected anywhere in the page using a helper, better for the entire application at once:
@RenderLocalizationIncludes(User.IsInRole("Admin")) In addition, RenderLocalizationIncludes will embed a widget on the site (provided that you are an administrator), where you can translate everything that has been localized.
Example
$.localize("Layout options", "~/js/shared/site.js"); Note
It seemed to us inconvenient that every time it is necessary to specify the file name. In our project we use Cassette resource minifiers, where there is an opportunity to add a resource handler before they are compiled. Simple configuration example:
public class CassetteConfiguration : ICassetteConfiguration { private void CustomizeScript(ScriptBundle bundle) { bundle.Processor = new ScriptPipeline().Prepend(new LocalizationResourceProcessor()); } public void Configure(BundleCollection bundles, CassetteSettings settings) { bundles.AddPerIndividualFile<ScriptBundle>("js/shared/site.js", customizeBundle: CustomizeScript); } } Now the long call to $ .localize ("Layout options", "~ / js / shared / site.js") can be replaced by:
__R("Layout options"); LocalizationResourceProcessor will replace __R with $ .localize and add the file name with the second parameter.
Add translation
Translation can be added directly to the site using the widget that appears in the lower left corner of the screen.

Those representations or models that are fully translated are highlighted in gray.
Editing:

You can add a new language, export / import an existing one.

As a conclusion I want to say that the library was first written for internal use, it turned out quite well and therefore we decided to publish it and write an article.
References:
GitHub source code
Knoema.Localization.Core
Knoema.Localization.MVC
Knoema.Localization.Cassette
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/149802/
All Articles