What's inside the Curiosity Mars Rover
On August 6, 2012, a Curiosity unit landed on the surface of Mars. In the next 23 months, the rover will study the surface of the planet, its mineralogical composition and radiation spectrum, look for traces of life, and also evaluate the possibility of landing a person.
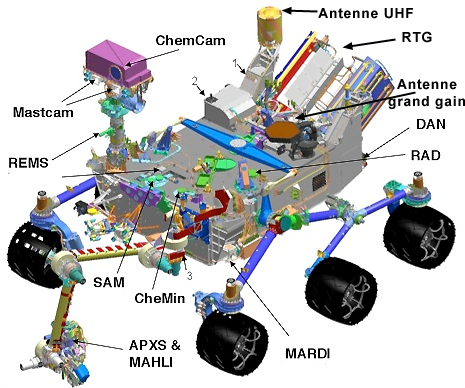
The main research tactic is to search for interesting breeds with high-resolution cameras. If they appear, then the rover from afar irradiates the studied rock with a laser. The result of the spectral analysis determines whether it is necessary to reach the manipulator with a microscope and an X-ray spectrometer. Further, Curiosity can extract and load a sample into one of the 74 cups of the internal laboratory for further analysis.
')
With all its great weight and external lightness, the device has a mass of a passenger car (900 kg) and weighs 340 kg on the surface of Mars. For powering the entire equipment, the decay energy of plutonium-238 from the Boeing radioisotope thermoelectric generator, which has a life span of at least 14 years, is used. At the moment, it produces 2.5 kWh of thermal energy and 125 W of electrical energy, over time, the output of electricity will decrease to 100 watts.
On the rover installed several different types of cameras . Mast Camera is a system of two unequal cameras of normal color rendering, which can take pictures (including stereoscopic) with a resolution of 1600 × 1200 pixels and, which is new for rovers, record a 720p video stream (1280 × 720) in hardware. To store the received material, the system has 8 gigabytes of flash memory for each of the cameras - this is enough to fit several thousand pictures and a couple of hours of video recording. Photographs and videos are processed without any load on the control electronics of Curiosity. Despite the manufacturer’s configuration with a zoom lens, the cameras do not have a zoom, since there was no time to test.

Illustration of images from MastCam. Colorful panoramas of the surface of Mars are obtained by gluing together several images. The MastCam cameras will be used not only for entertaining the public with the weather of the red planet, but also as an aid when retrieving samples with a manipulator and when moving.
 Also on the mast is fixed part of the ChemCam system. This is a laser-spark emission spectrometer and an imaging unit that work in pairs: after a tiny amount of the studied rock is evaporated by a 5-nanosecond laser pulse, the spectrum of the plasma radiation obtained is analyzed, which will determine the elemental composition of the sample. You do not need to push the manipulator.
Also on the mast is fixed part of the ChemCam system. This is a laser-spark emission spectrometer and an imaging unit that work in pairs: after a tiny amount of the studied rock is evaporated by a 5-nanosecond laser pulse, the spectrum of the plasma radiation obtained is analyzed, which will determine the elemental composition of the sample. You do not need to push the manipulator.The resolution of the equipment is 5-10 times higher than that of the one installed on previous Mars rovers. From 7 meters, ChemCam can determine the type of rock under study (for example, volcanic or sedimentary), the structure of the soil and stones, track the predominant elements, recognize ice and minerals with water molecules in the crystal structure, measure traces of erosion on the stones and visually assist in the study of rocks using a manipulator.

The cost of ChemCam was $ 10 million (less than half the percentage point of the entire cost of the expedition). The system consists of a laser on a mast and three spectrographs inside the housing, the radiation to which is fed through a fiber-optic light guide.
The Mars Rover manipulator is mounted on a Mars Hand Lens Imager, capable of taking pictures of 1600 × 1200 pixels in size, on which parts of 12.5 micrometers can be seen. The camera has a white backlight for work both day and night. Ultraviolet illumination is necessary to invoke the emission of carbonate and evaporite minerals, the presence of which suggests that water was involved in the formation of the surface of Mars.
 For mapping purposes, the Mars Descent Imager (MARDI) camera was used, which, during the descent of the vehicle, recorded images of 1600 × 1200 pixels per 8 gigabytes of flash memory. As soon as there were several kilometers to the surface, the camera began to take five color photographs per second. The data obtained will allow you to map the habitat of "Curiosity".
For mapping purposes, the Mars Descent Imager (MARDI) camera was used, which, during the descent of the vehicle, recorded images of 1600 × 1200 pixels per 8 gigabytes of flash memory. As soon as there were several kilometers to the surface, the camera began to take five color photographs per second. The data obtained will allow you to map the habitat of "Curiosity". On the sides of the rover installed two pairs of black and white cameras with a viewing angle of 120 degrees. Hazcams system is used when performing maneuvers and extending the manipulator. On the mast is located the Navcams system, which are two black and white cameras with a viewing angle of 45 degrees. Rover programs constantly build a wedge-shaped 3D map based on data from these cameras, which allows you to avoid collisions with unexpected obstacles. One of the first shots of Curiosity is a picture from the Hazcam camera.
On the sides of the rover installed two pairs of black and white cameras with a viewing angle of 120 degrees. Hazcams system is used when performing maneuvers and extending the manipulator. On the mast is located the Navcams system, which are two black and white cameras with a viewing angle of 45 degrees. Rover programs constantly build a wedge-shaped 3D map based on data from these cameras, which allows you to avoid collisions with unexpected obstacles. One of the first shots of Curiosity is a picture from the Hazcam camera.To measure the weather conditions on the rover, an environmental monitoring station ( Rover Environmental Monitoring Station ) is installed, which measures pressure, atmospheric and surface temperatures, wind speed and ultraviolet radiation. REMS is protected from Martian dust.
CheMin ( Chemistry and Mineralogy ) is a device for studying chemical and mineralogical composition using X-ray fluorescence instrument and X-ray diffraction. Roughly speaking, it will help to find the minerals with which Mars is rich, which will show what the conditions on the planet were.

The main tool for studying the obtained samples is Sample Analysis at Mars , whose mass is half the mass of all scientific equipment. SAM includes a mass spectrometer, a gas chromatograph and an adjustable laser spectrometer. Also in work the x-ray spectrometer of alpha particles is used . The samples will be irradiated with alpha particles, and in two or three hours their complete elemental composition will be obtained, and ten minutes will be enough to review the main components.
A radiation detector is installed inside the rover to assess the possibility of humans visiting Mars and a hydrogen detection device . It is interesting that scientific equipment was developed not only in the USA, these are projects of organizations from France, Canada, Russia and a number of other countries.
All this hardware is controlled by a small duplicated computer with 256 MB of RAM, 2 GB of ROM in the form of flash memory and a RAD750 processor, which is capable of performing 400 million operations per second, which, roughly speaking, is comparable to a regular smartphone. The system capacity is enough to generate 15-40 thousand 3D-points from a stereo image. Memory "Curiosity" is about eight times more productive than the memory of rovers of previous generations. Although the configuration of the system is similar to the filling of a cheap single board computer, it is necessary to take into account the operating conditions of the electronics and the radiation it experiences, from which Raspberry Pi clones do not have protection.
The operating system used is VxWorks. This is a proprietary real-time operating system that controlled the three previous rovers - Spirit, Opportunity and Mars Pathfinder, as well as the SpaceX ship Dragon . In addition to the VxWorks spacecraft, it is used in airliners, robotics, medical technology and other embedded highly reliable systems (for example, Apple has the same operating system as the Mars rovers).
The control programs are divided into 150 modules, each of which is responsible for a separate function. Related modules are combined into components that organize the joint work of the modules included in them. In total there are less than 10 high level components. Most of the code is generated automatically or inherited from previous rovers.
But in these 2.5 million lines of C code , autonomous control of multiple systems is implemented with only rare human interventions - a signal from the Earth takes several minutes. Based on the readings of several cameras and sensors, the computer itself controls the driving of the device, photographing and videotaping, the cooling system, sample extraction and the work of scientific equipment.
The code, of course, is not available to the public, and the data on the software of the rover is scarce. But who knows what to expect from NASA: they have a Github account for a long time.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/149168/
All Articles