Cloud databases: who makes them and what they are capable of
 Remember, before there were only two or three cloud platforms and about the same cloud databases? Today, clouds have become much more popular, and, in connection with this, the number of database services built on them has also increased significantly. To be honest, it is already becoming difficult to keep track of their development and distribution! In this article we will present to your attention the main cloud databases available and briefly describe what they are and where they are going.
Remember, before there were only two or three cloud platforms and about the same cloud databases? Today, clouds have become much more popular, and, in connection with this, the number of database services built on them has also increased significantly. To be honest, it is already becoming difficult to keep track of their development and distribution! In this article we will present to your attention the main cloud databases available and briefly describe what they are and where they are going.Note: we are talking only about automated databases, not including those that require user administration.
SQL Services
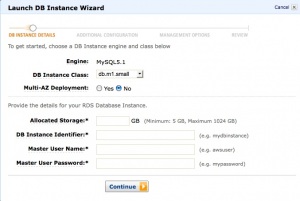
- Amazon Relational Database Service: Being one of the first cloud databases, Amazon Web Services' RDS , however, is also one of the most "completed" cloud databases. Like most AWS products, it is connected to the AWS management interface and is compatible with a huge number of other cloud services of the company. Moreover, if earlier RDS provided the ability to manage databases located only on AWS hosting, now users can also manage databases located on Microsoft SQL Server and Oracle Database.
- Clustrix Database as a Service: Clustrix entered the cloud market quite recently, but immediately made an impression of a strong player. Its service, which runs on Rackspace Cloud, provides the user with high-performance hardware and scalable MySQL features . The company claims that their equipment is suitable for both OLTP and OLAP applications, and that it monitors the state of the system immediately by 2500 indicators.
- EnterpriseDB Postgres Plus Cloud Database: A PostgreSQL database and its Postgres Plus cloud version. Focusing more on corporate developers than on self-taught hackers, Postgres Plus Cloud includes features such as high availability of clusters, a large number of connections, and compatibility with Oracle environments.
- FathomDB: For those who do not yet know: FathomDB still exists, but the company has made its original open-source technology to help developers do at least something-as-a-service . Now the company does not provide any hosting and database, but its representatives claim that the development of a new generation database service is underway.
- Google Cloud SQL: is not the most functional database, but it has its advantages. For example, it easily integrates with all other Google cloud services. In addition, Cloud SQL is geographically replicated for maximum availability. Currently, however, it only supports Java and Pythom applications, and has a limit of 10 gigabytes.
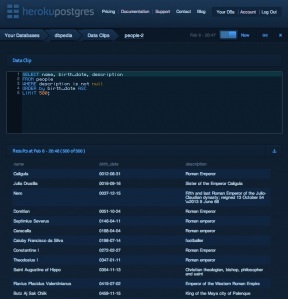 Heroku Postgres: this database is designed for reliability and information protection - Heroku claims that 99.99% of the development time was spent on achieving 99, (9)% of reliability. - and trying to bring their experience to those developers who can not use their PaaS. One of the most interesting features of this database is Data Clips, which allows users to send the results of SQL queries to someone else via a url.
Heroku Postgres: this database is designed for reliability and information protection - Heroku claims that 99.99% of the development time was spent on achieving 99, (9)% of reliability. - and trying to bring their experience to those developers who can not use their PaaS. One of the most interesting features of this database is Data Clips, which allows users to send the results of SQL queries to someone else via a url.- HP Cloud Relational Database for MySQL: What else can you say about this service ? His name is clearly speaking. To begin with, it should be noted that it is still in the beta stage, which means that there is still a lot to do and add. It should also be noted that it was developed on OpenStack, which, theoretically, should facilitate the process of transferring the database from one cloud to another.
- IBM SmartCloud Application Services: As with HP, IBM cloud database development is still incomplete. What are the special features is also unclear, except, perhaps, the fact that the service is based on the technology of DB2 Server and is part of the SmartCloud Application Services .
- Microsoft SQL Database: SQL Database is a critical component of the new Microsoft strategy, which focuses on hybrid clouds. Yes, it can work as a standalone cloud database, but it also provides a common Microsoft SQL Server user interface and the ability to exchange data via SQL Server. Also there is the ability to synchronize multiple databases.
- Oracle Database Cloud Service: this service is not for everyone, but for Oracle database users who want to try out cloud hosting. Moreover, Oracle Database Cloud Service provides all the features of Oracle Database 11g Release 2, which are really many. Pricing policy is not very clear, but it is clear that it is built on the basis of the size of the database.
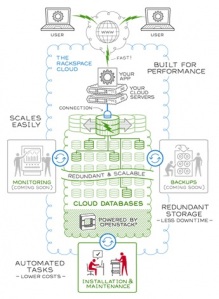 Rackspace Cloud Databases: The latest cloud offer from Rackspace, Cloud Databases is their first platform built on OpenStack. At first, users will not receive SLA or additional host features (such as monitoring or GUI). But users get the promise of high performance and reliability, thanks to container virtualization and special architecture.
Rackspace Cloud Databases: The latest cloud offer from Rackspace, Cloud Databases is their first platform built on OpenStack. At first, users will not receive SLA or additional host features (such as monitoring or GUI). But users get the promise of high performance and reliability, thanks to container virtualization and special architecture.- Xeround: If not for Amazon RDS, Xeround could become the most popular cloud database. It has good flexibility: you can deploy it in almost any cloud. The company claims that automatic scalability is one of the main advantages of their database, that it is a new level of the MySQL interface, which, theoretically, can support many different database parameters.
')
NoSQL Services
- Amazon DynamoDB: DynamoDB is a NoSQL service managed by AWS, based on the original Dynamo key-value system developed several years ago for internal purposes. Designed for web or large applications , DynamoDB has the potential for scalability. DynamoDB is built on the SD architecture and scales automatically when adding information to the system.
- Amazon ElastiCache: Technically, this is not a NoSQL service, but ElastiCache complements the system with good caching, which provides maximum access speed for users.
- Cloudant: Despite the fact that it is based on CouchDB, Cloudant is, rather, not a NoSQL service, but a Data Layer . Designed on the basis of multiple cloud databases, it offers not only scalable NoSQL data storage, but also an analytical MapReduce engine. This is one of the main reasons why the agro-industrial giant Monsanto uses it to support its infrastructure.
 Database.com: The self-contained Salesforse.com database, Database.com , is not exactly NoSQL, but rather a relational database. Its architecture resembles the “multi-unit” architecture of Salesforce.com and Force.com CRM. It supports a wide variety of data types and is designed for applications that support existing Salesforce.com services.
Database.com: The self-contained Salesforse.com database, Database.com , is not exactly NoSQL, but rather a relational database. Its architecture resembles the “multi-unit” architecture of Salesforce.com and Force.com CRM. It supports a wide variety of data types and is designed for applications that support existing Salesforce.com services.- Microsoft Windows Azure Table Storage: This is a NoSQL datastore for Windows Azure , created to easily transfer terabytes of non-relational information. As part of the Windows Azure Storage family, Table Storage provides users with up to 100 terabytes of storage space.
- MongoHQ / MongoLab: MongoDB is the most popular NoSQL database, but it may be too large to be placed in the cloud. As a result, there are several MongoDB services, although MongoHQ and MongoLab are better known. The advantages of both are simple: rapid deployment, careful monitoring and reliability. Both services are trying to appeal to a wide range of users, giving both general and special offers.
And what do you think about the above services? What are the pros and cons can highlight?
Maybe you think that some service forgot to include?
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/148483/
All Articles