Compaq Descpro and NetBSD 1.6.1
In mid-August 2003, I first met this computer. I then worked in a small provider, went all day with a twisted pair bay, a ladder and full pockets of network cards on RTL8139 (there were built-in drivers in Win2k) and RTL8029 (yes, we had network segments on BNC!).
Through my acquaintances, the owner of a small company asked me to configure him with a router so that it is inexpensive, safe and secure. It should be noted that in those days, 80% of all the offices I connected managed to install Win2k and the second network card to the computer of a secretary or another employee (Ho-ho! They shared the interface and forth, on the Internet!). The remaining 15% set for this purpose a special computer running any * nix-like OS and only 5% had a router or firewall in the classic sense.
And so, what was this car? It was a company Compaq Descpro, with a processor PIII, carrying on board as many as 512MB of memory, but without a built-in network card. The usual office workaholic of those years. The stamp on the cover indicated the date of production - November 2, 2000. In general, that was not a pity.

')
The choice of OS was not even in front of me - I was experiencing a period of NetBSD passion.

The procedure for installing this operating system is not much more difficult than a similar process for FreeBSD (sysinstall) and certainly much more convenient than OpenBSD.
The set of functions required by the customer is fairly common - packet filtering, NAT, a proxy server for caching traffic (unlimited tariffs then was not only for legal entities, but also for physicists, as far as I know) and caching DNS. Everything I needed was put from the packages, since the build from pkgsrc would take too much time, and I didn’t see any sense in it.
Although the claimed support for a large number of platforms and architectures for this OS is rather conditional (I know what I’m talking about using the example of sun4v and hppa ports), for 386 the range of supported peripherals was quite wide at that time.
After putting the computer to the customer, I saw him a few more times, but mostly for preventive purposes. And then - years went by, the gateway obviously worked without failures, contacts were lost, the company grew, they took an administrator, but he understood more about 1C than NetBSD, and there was no need to change anything.
And so, a month ago, I found a letter in the mail asking if I wanted to take this computer myself? Out of small vanity, I left an autograph under the cover with the name of my site and the date of installation, so it worked. As a reason for the replacement, it was indicated that after changing the provider and expanding the channel, the network settings changed, which were corrected, but the speed of work with the Internet did not exceed 1 Mb / s.
So, let's look into the inner world of this representative of the computer world. I’ll say right away that the DVD drive was installed now, the way I had it, but it wasn’t in Compaq.
Yes, one network card is quite good, it was used as an internal interface. The second - frank consumer goods RTL8139.
From the GENERIC kernel, so small (6254651 bytes for 1.6.1), the extra drivers were removed, which made it possible to further reduce its size to 2602114 bytes. Of particular note is the compilation speed of the kernel - this is a fairly fast process, even by modern standards (if the compile / directory is not empty, then things will go much faster).
#config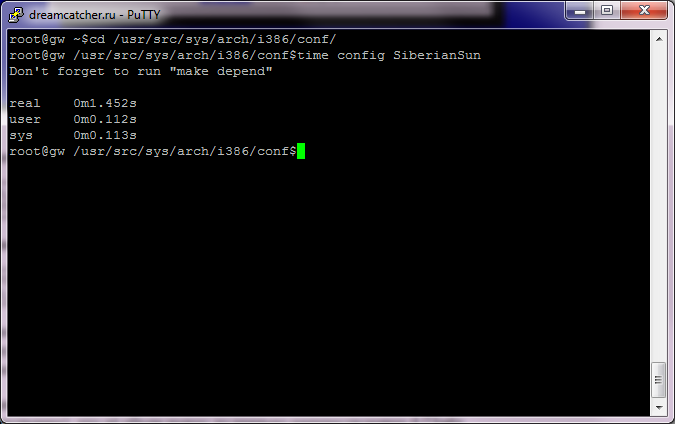
#make depend

#make

DHCP still works (dynamic update of the internal DNS zone), the DNS server works as a caching server, although the response time is rather long. The proxy server is running. The software is very old, with a huge number of vulnerabilities.
BIND9 was shipped from packages, since the BIND8 supplied as part of the system was considered obsolete even in 2003.

The reason for slow work was found rather quickly - ALTQ, apparently the administrator did not look at his settings. ALTQ is configured on the internal interface (3Com network card - em0), as it is designed to handle outgoing traffic. That is, the stream from the external network to the internal interface cannot exceed 95% of 1 Mb / s. ALTQ, in this version of NetBSD, is not supported for rtl8139 network cards, so the width of the incoming channel is not adjustable at all. Yes, it does not look very nice, but that was my knowledge about network technologies at that time and I did not have a second network card supported by ALTQ.

The main packet filter for NetBSD is IPF, written by Darren Reed. NetBSD 1.6.1 uses version v3.4.29, the current version of the packet filter is 5.1.1. On the net you can find a lot of documentation on how to configure IP Filter, including in Russian.

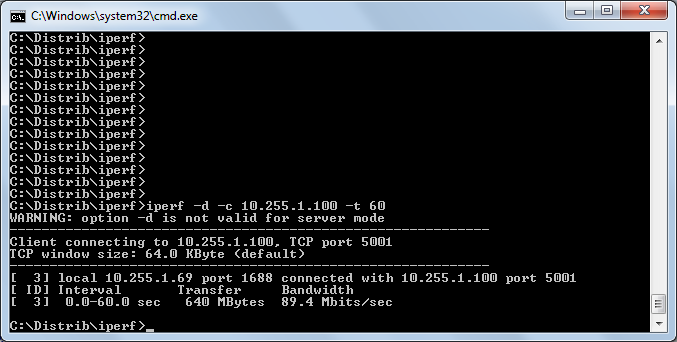
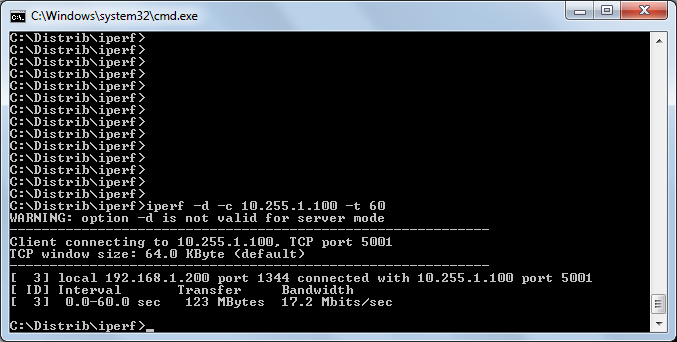
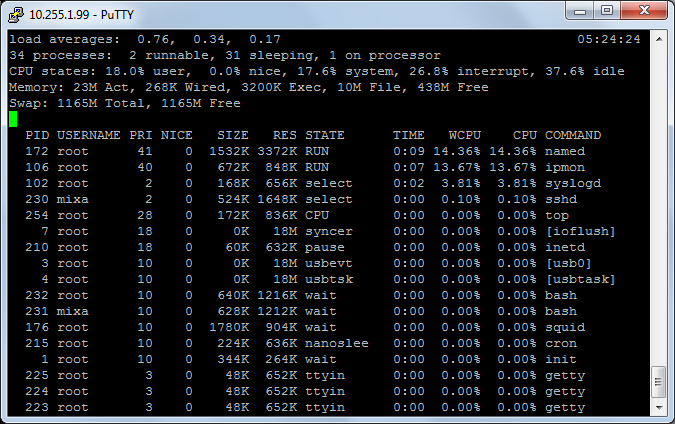
The iperf tests showed that rtk0 is not the most worthy network card, as can be seen on the screenshots below in a large number of interrupts. I also discovered a large resource consumption by the ipmon utility - the reason was simple - I forgot to remove the extra “log” in the rule set.
"Reference" testing: LAN 100mb / s on not very good network cards, bypassing the router:
Through the router, with ALTQ disabled:
Load on the server with ALTQ disabled and “log” in the IPF rules:
The load on the server with ALTQ enabled, “log” in the IPF rules are removed:
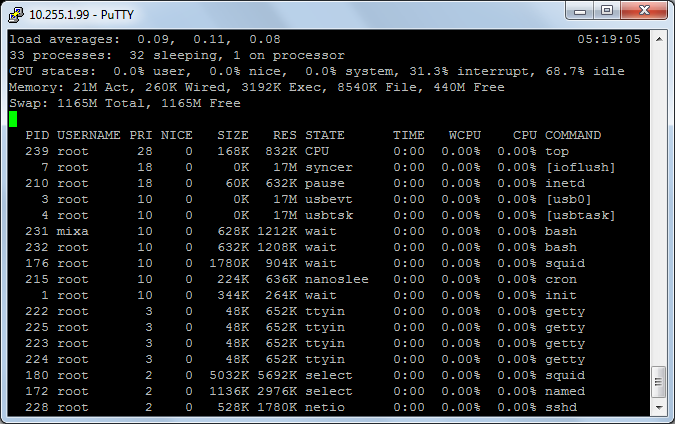
The load on the server with disabled ALTQ, “log” in the IPF rules is removed:

ALTQ work:

Summing up, I would like to say that after so many years the router is operational, although to work with a high-speed channel, it is necessary to replace the rtl0 network card.
More than sure, there are still quite a few machines that continue their hard work of transferring packages in the most difficult conditions - in dusty, dirty, attic and under flower pots on window sills, from which no one remembers passwords and which are terrible to turn off.

And what meetings with the past did you have,%% username?
Disclaimer: external and local addresses, the domain name of the equipment is changed and all matches are random and not intended.
Through my acquaintances, the owner of a small company asked me to configure him with a router so that it is inexpensive, safe and secure. It should be noted that in those days, 80% of all the offices I connected managed to install Win2k and the second network card to the computer of a secretary or another employee (Ho-ho! They shared the interface and forth, on the Internet!). The remaining 15% set for this purpose a special computer running any * nix-like OS and only 5% had a router or firewall in the classic sense.
And so, what was this car? It was a company Compaq Descpro, with a processor PIII, carrying on board as many as 512MB of memory, but without a built-in network card. The usual office workaholic of those years. The stamp on the cover indicated the date of production - November 2, 2000. In general, that was not a pity.

')
The choice of OS was not even in front of me - I was experiencing a period of NetBSD passion.

The procedure for installing this operating system is not much more difficult than a similar process for FreeBSD (sysinstall) and certainly much more convenient than OpenBSD.
The set of functions required by the customer is fairly common - packet filtering, NAT, a proxy server for caching traffic (unlimited tariffs then was not only for legal entities, but also for physicists, as far as I know) and caching DNS. Everything I needed was put from the packages, since the build from pkgsrc would take too much time, and I didn’t see any sense in it.
Although the claimed support for a large number of platforms and architectures for this OS is rather conditional (I know what I’m talking about using the example of sun4v and hppa ports), for 386 the range of supported peripherals was quite wide at that time.
After putting the computer to the customer, I saw him a few more times, but mostly for preventive purposes. And then - years went by, the gateway obviously worked without failures, contacts were lost, the company grew, they took an administrator, but he understood more about 1C than NetBSD, and there was no need to change anything.
And so, a month ago, I found a letter in the mail asking if I wanted to take this computer myself? Out of small vanity, I left an autograph under the cover with the name of my site and the date of installation, so it worked. As a reason for the replacement, it was indicated that after changing the provider and expanding the channel, the network settings changed, which were corrected, but the speed of work with the Internet did not exceed 1 Mb / s.
So, let's look into the inner world of this representative of the computer world. I’ll say right away that the DVD drive was installed now, the way I had it, but it wasn’t in Compaq.
NetBSD 1.6.1 (Siberian Sun) # 0: Wed Aug 20 21:17:36 MSD 2003
root@gw.siberiansun.net: / usr / src / sys / arch / i386 / compile / SiberianSun
cpu0: Intel Pentium III (Coppermine) (686-class), 863.89 MHz
cpu0: I-cache 16 KB 32b / line 4-way, D-cache 16 KB 32b / line 2-way
cpu0: L2 cache 256 KB 32b / line 8-way
cpu0: features 383fbff <FPU, VME, DE, PSE, TSC, MSR, PAE, MCE, CX8, APIC, SEP, MTRR>
cpu0: features 383fbff <PGE, MCA, CMOV, FGPAT, PSE36, MMX>
cpu0: features 383fbff <FXSR, SSE>
total memory = 510 MB
avail memory = 470 MB
using 6144 buffers containing 26236 KB of memory
BIOS32 rev. 0 found at 0xe7300
mainbus0 (root)
pci0 at mainbus0 bus 0: configuration mode 1
pci0: i / o space, memory space enabled, rd / line, rd / mult, wr / inv ok
pchb0 at pci0 dev 0 function 0
pchb0: Intel 82815 Hub (rev. 0x02)
agp0 at pchb0: aperture at 0x44000000, size 0x4000000
vga1 at pci0 dev 2 function 0: Intel 82815 Graphics (rev. 0x02)
wsdisplay0 at vga1 kbdmux 1: console (80x25, vt100 emulation)
wsmux1: connecting to wsdisplay0
ppb0 at pci0 dev 30 function 0: Intel 82801AA Hub-to-PCI Bridge (rev. 0x02)
pci1 at ppb0 bus 2
pci1: i / o space, memory space enabled
rtk0 at pci1 dev 9 function 0: RealTek 8139 10 / 100BaseTX
rtk0: interrupting at irq 5
rtk0: Ethernet address 00: 80: 48: 18: 01: 70
ukphy0 at rtk0 phy 7: Generic IEEE 802.3u media interface
ukphy0: OUI 0x000000, model 0x0000, rev. 0
ukphy0: 10baseT, 10baseT-FDX, 100baseTX, 100baseTX-FDX, auto
ep0 at pci1 dev 10 function 0: 3Com 3c595-TX 10/100 Ethernet
ep0: interrupting at irq 9
ep0: address 00: 20: af: d2: 0d: 6a, 64KB word-wide FIFO, 3: 1 Rx: Tx split
ep0: 10baseT, 10baseT-FDX, 100baseTX, 100baseTX-FDX (default 100baseTX)
pcib0 at pci0 dev 31 function 0
pcib0: Intel 82801AA LPC Interface Bridge (rev. 0x02)
pciide0 at pci0 dev 31 function 1: Intel 82801AA IDE Controller (ICH) (rev. 0x02)
pciide0: bus-master DMA support present
pciide0: primary channel wired to compatibility mode
wd0 at pciide0 channel 0 drive 0: <ST340014A>
wd0: drive supports 16-sector PIO transfers, LBA48 addressing
wd0: 38165 MB, 16383 cyl, 16 head, 63 sec, 512 bytes / sect x 78163247 sectors
wd0: 32-bit data port
wd0: drive supports PIO mode 4, DMA mode 2, Ultra-DMA mode 5 (Ultra / 100)
pciide0: primary channel interrupting at irq 14
wd0 (pciide0: 0: 0): using PIO mode 4, Ultra-DMA mode 4 (Ultra / 66) (using DMA data transfers)
pciide0: secondary channel wired to compatibility mode
atapibus0 at pciide0 channel 1: 2 targets
cd0 at atapibus0 drive 1: <_NEC DVD_RW ND-4550A,, 1.07> type 5 cdrom removable
cd0: 32-bit data port
cd0: drive supports PIO mode 4, DMA mode 2, Ultra-DMA mode 2 (Ultra / 33)
pciide0: secondary channel interrupting at irq 15
cd0 (pciide0: 1: 1): using PIO mode 4, Ultra-DMA mode 2 (Ultra / 33) (using DMA data transfers)
uhci0 at pci0 dev 31 function 2: Intel 82801AA USB Controller (rev. 0x02)
uhci0: interrupting at irq 11
usb0 at uhci0: usb revision 1.0
uhub0 at usb0
uhub0: Intel UHCI root hub, class 9/0, rev 1.00 / 1.00, addr 1
uhub0: 2 ports with 2 removable, self powered
auich0 at pci0 dev 31 function 5: i82801AA (ICH) AC-97 Audio
auich0: interrupting at irq 5
auich0: ADS96 codec; headphone, Analog Devices Phat Stereo
audio0 at auich0: full duplex, mmap, independent
isa0 at pcib0
com0 at isa0 port 0x3f8-0x3ff irq 4: ns16550a, working fifo
com1 at isa0 port 0x2f8-0x2ff irq 3: ns16550a, working fifo
pckbc0 at isa0 port 0x60-0x64
pckbd0 at pckbc0 (kbd slot)
pckbc0: using irq 1 for kbd slot
wskbd0 at pckbd0: console keyboard, using wsdisplay0
lpt0 at isa0 port 0x378-0x37b irq 7
pcppi0 at isa0 port 0x61
sysbeep0 at pcppi0
isapnp0 at isa0 port 0x279: ISA Plug 'n Play device support
npx0 at isa0 port 0xf0-0xff: using exception 16
fdc0 at isa0 port 0x3f0-0x3f7 irq 6 drq 2
isapnp0: no ISA Plug 'n Play devices found
biomask fd45 netmask ff65 ttymask ffe7
Kernelized RAIDframe activated
boot device: wd0
root on wd0a dumps on wd0b
root file system type: ffs
IP Filter: v3.4.29 initialized. Default = pass all, Logging = enabled
wsdisplay0: screen 1 added (80x25, vt100 emulation)
wsdisplay0: screen 2 added (80x25, vt100 emulation)
wsdisplay0: screen 3 added (80x25, vt100 emulation)
wsdisplay0: screen 4 added (80x25, vt100 emulation)
Yes, one network card is quite good, it was used as an internal interface. The second - frank consumer goods RTL8139.
From the GENERIC kernel, so small (6254651 bytes for 1.6.1), the extra drivers were removed, which made it possible to further reduce its size to 2602114 bytes. Of particular note is the compilation speed of the kernel - this is a fairly fast process, even by modern standards (if the compile / directory is not empty, then things will go much faster).
#config

#make depend

#make

DHCP still works (dynamic update of the internal DNS zone), the DNS server works as a caching server, although the response time is rather long. The proxy server is running. The software is very old, with a huge number of vulnerabilities.
BIND9 was shipped from packages, since the BIND8 supplied as part of the system was considered obsolete even in 2003.

The reason for slow work was found rather quickly - ALTQ, apparently the administrator did not look at his settings. ALTQ is configured on the internal interface (3Com network card - em0), as it is designed to handle outgoing traffic. That is, the stream from the external network to the internal interface cannot exceed 95% of 1 Mb / s. ALTQ, in this version of NetBSD, is not supported for rtl8139 network cards, so the width of the incoming channel is not adjustable at all. Yes, it does not look very nice, but that was my knowledge about network technologies at that time and I did not have a second network card supported by ALTQ.

The main packet filter for NetBSD is IPF, written by Darren Reed. NetBSD 1.6.1 uses version v3.4.29, the current version of the packet filter is 5.1.1. On the net you can find a lot of documentation on how to configure IP Filter, including in Russian.

The iperf tests showed that rtk0 is not the most worthy network card, as can be seen on the screenshots below in a large number of interrupts. I also discovered a large resource consumption by the ipmon utility - the reason was simple - I forgot to remove the extra “log” in the rule set.
"Reference" testing: LAN 100mb / s on not very good network cards, bypassing the router:

Through the router, with ALTQ disabled:

Load on the server with ALTQ disabled and “log” in the IPF rules:

The load on the server with ALTQ enabled, “log” in the IPF rules are removed:

The load on the server with disabled ALTQ, “log” in the IPF rules is removed:

ALTQ work:

Summing up, I would like to say that after so many years the router is operational, although to work with a high-speed channel, it is necessary to replace the rtl0 network card.
More than sure, there are still quite a few machines that continue their hard work of transferring packages in the most difficult conditions - in dusty, dirty, attic and under flower pots on window sills, from which no one remembers passwords and which are terrible to turn off.

And what meetings with the past did you have,%% username?
Disclaimer: external and local addresses, the domain name of the equipment is changed and all matches are random and not intended.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/147641/
All Articles