SAP security in numbers
Notes
According to the partnership agreement with SAP, we do not have the right to publish detailed information about the vulnerabilities found before the patch is released. Therefore, in this report, only those vulnerabilities are described in detail, information about which we have the right to disclose at the moment. However, examples of exploitation of all the mentioned vulnerabilities, proving that they really exist, can be found on conference videos, as well as on erpscan.ru and dsec.ru.
It should also be noted that our research in the field of SAP security in general and statistics collection in particular does not end with this report. We plan to publish new statistics at least annually or as new methods of attack appear. The latest statistics updates from SAP systems present on the Internet can be found on sapscan.com.
1. Introduction
The core of every large company is an ERP system; It includes all business-critical processes, ranging from purchasing, payment and delivery, to the management of human resources, products and financial planning. All information stored in ERP-systems is of great importance, and any unauthorized access to it can incur enormous losses, including stopping a business. According to the Theft and Fraud Investigation Association (ACFE) report, from 2006 to 2010, the loss of organizations from internal fraud amounted to about 7 percent of annual revenue (!). That is why we decided to conduct a detailed study on SAP security using ERPScan - the Digital Security security monitoring system developed by SAP systems.
')
The common myth that ERP security is just the SOD matrix has exhausted itself over the last 5 years and already seems like a long history of days gone by. Over the past 5 years, SAP security experts have presented many reports detailing various attacks on SAP's internal subsystems, such as the RFC data exchange protocol, the access control system SAP ROUTER, SAP web applications and client workers. stations running SAP GUI . Each year, interest in the topic increases exponentially: if in 2007 at specialized technical conferences on hacking and protection there was only 1 report about SAP, then in 2011 there were more than 20. Recently, a number of hacking tools have been released, confirming the possibility SAP attacks.
According to the statistics of vulnerabilities in business applications, in 2009 more than 100 vulnerabilities in SAP products were eliminated, whereas in 2010 there were already more than 500. In total, in March 2012 there are more than 2000 SAP security notes other SAP components.
Most of these vulnerabilities allow an unauthorized user to gain access to all of the company's critical business data, which makes it necessary to think about the use of certain solutions aimed at protecting SAP systems.
1.1. New corporate security trends
The trends in the development of the infrastructure of companies have recently moved from a decentralized model to the integration of all business processes into unified systems. If earlier the company had many servers, such as mail, file, domain controller and others, now all these functions are integrated into a single business application, which provides, on the one hand, ease of access, and on the other, a single point of failure. Business applications and ERP systems store all critical company data, ranging from financial statements and personal data, to lists of counterparties and corporate secrets. For an external attacker or insider, such a system is the main target, and its ultimate goal is not the administrator’s rights on the domain controller.
However, many security experts are now unfortunately extremely superficially aware of the protection of business applications such as SAP. The problem also lies in the fact that the security functions do not lie with the CISO, but with the owners of the system, who actually control themselves. As a result, no one is responsible for the security of the most critical elements of the system.
Of the less global problems, it is also worth noting:
• Lack of qualified specialists. In most companies, SAP security is perceived by SAP specialists only as an SOD problem, but by security services, understanding SAP threats is, at best, superficial, not to mention fine-tuning.
• A huge number of fine settings. In the standard settings of the system there are more than 1000 parameters, as well as a huge mass of fine-tuning, not to mention the differentiation of rights to various objects, such as transactions, tables, RFC-procedures and others - for example, web interfaces for accessing the system maybe a few thousand. In all this mass of settings, the task of ensuring the security of even one system can be a daunting task.
• Customizable settings. It is unlikely that there will be two identical SAP systems, since most of the settings are somehow sharpened for the customer, and in addition, their own programs are being developed, the safety of which should also be taken into account in the integrated assessment.
• Automation. Having a large number of systems with constantly changing configurations also introduces additional problems.
Our goal is to bring this problem from a theoretical level to a practical one, based on real data and measurements: ranging from information on the number of problems detected and their popularity to the number of vulnerable systems. To this end, we have implemented a global project to scan SAP systems available from the Internet.
2. Vulnerability statistics
2.1. The number of SAP security notifications
From time to time, SAP issues an internal document called a “ Security Notice ” (SAP Security note). It typically stores information about one or more vulnerabilities in SAP products or configuration errors that pose a risk to SAP systems. The first such notice was published in 2001. Since 2007, their number has been growing exponentially.
As of April 26, 2012, more than 2000 SAP security notices have been published.
During 2011, on Critical Patches Day (every second Tuesday), approximately 65 SAP security notifications were usually posted. When compared with other manufacturers, it is more than that of Microsoft, Oracle and Cisco. It is worth noting that only 3 years ago there were much fewer of them.

Number of SAP security notifications by year
2.2. SAP Criticality Security Notifications
SAP uses 5 levels of severity for its notifications:
1 - Sensation
2 - High priority
3 - Medium priority
4 - Low priority
5 - Recommendations / additional information
Most of the problems (69%) have a high priority, which means that about 2/3 of the published vulnerabilities need to be fixed quickly.
2.3. SAP Security Notifications by Type
We analyzed all published SAP security notices by type. The most popular problems are presented on the chart:
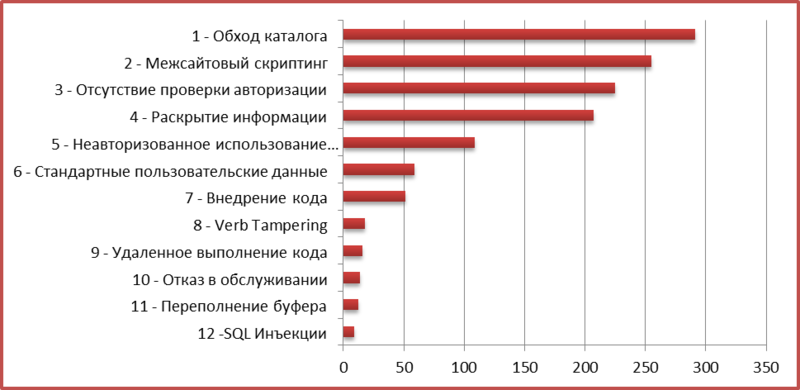
It is worth noting that the new type of vulnerability, which is called Verb Tampering , has become one of the most popular. This “authentication bypass” vulnerability was first discovered by Digital Security, and later as many as 18 problems of this type were found.
About 20% of vulnerabilities were not included in this rating, since a significant number of unique problems are present in SAP systems. Some of them are described in our presentation “ Top 10 most interesting vulnerabilities in SAP ”.
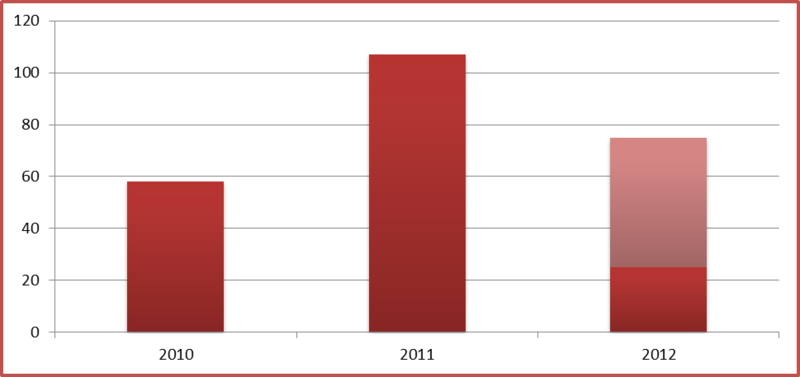
2.4. Number of thanks to outside researchers
In 2010, SAP decided to thank third-party security researchers for the vulnerabilities found in their products. The diagram shows the number of vulnerabilities discovered by third-party researchers since 2010. Half of the vulnerabilities were found and successfully fixed by SAP using Digital Security (50 vulnerabilities and 26% of the total) and VirtualForge (44 vulnerabilities, that is 23%). The second half was discovered by dozens of other companies, and their number is growing, which proves the growing popularity of this area.
2.5. Amount of publicly available information
The most dangerous are vulnerabilities, information about exploitation of which (detailed description of vulnerability, PoC-exploits or full-fledged exploits) is available online. We have gathered information from the following popular sources:
SecurityFocus - here you can find a detailed description, sometimes a PoC-exploit. All vulnerabilities in this database have a high probability of exploitation. Details about 123 vulnerabilities were found here (6% of the total).
Exploit-DB - here are ready-made exploits that can be used without making changes and without having any knowledge about the operation of the corresponding system. All vulnerabilities in this database have a critical exploitation probability. 24 exploits were found here (1% of the total number of vulnerabilities).
2.6. Top 5 most important vulnerabilities in 2011
Of the many vulnerabilities published, we selected the top 5 issues that pose the greatest threat:
• Authentication bypass with Verb Tampering
• Bypass authentication using Invoker Servlet
• Buffer overflow in ABAP kernel call
• Remote code execution through TH_GREP
• Extend JSESSIONID using the SAP Management console
1. Bypass authentication using Verb Tampering
This vulnerability was discovered in the SAP NetWeaver J2EE engine. It allows an anonymous hacker to completely compromise the SAP system. It was found about 40 applications vulnerable to this attack. In the most critical case, it was possible to create any user, assign him any role in the system and execute any command in the OS.
| Spying Risk : | Critical |
| The risk of sabotage : | Critical |
| Fraud Risk : | Critical |
| Availability : | Anonymously over the Internet |
| Ease of operation : | High |
| CVSSv2: | ten |
| Description : | http://erpscan.com/advisories/dsecrg-11-041-sap-netweaver-authentication-bypass-verb-tampering/ |
| Patch : | SAP Security Notices: 1589525, 1624450 |
| Author : | Alexander Polyakov (Digital Security) |
2. Bypass authentication using Invoker Servlet
This vulnerability was discovered in the SAP NetWeaver J2EE engine. It allows an anonymous hacker to bypass the security restrictions of SAP web services and directly invoke critical functions by the names of their classes. About 30 applications are vulnerable to this attack. Depending on the specific application, you can add new users to the system, read system files, including database files, or reveal critical information.
| Spying Risk : | Critical |
| The risk of sabotage : | Critical |
| Fraud Risk : | Critical |
| Availability : | Anonymously over the Internet |
| Ease of operation : | High |
| CVSSv2: | ten |
| Description : | http://help.sap.com/saphelp_nw70ehp2/helpdata/en/bb/f2b9d88ba4e8459 e5a69cb513597ec / frameset.htm |
| Patch : | SAP Security Notice: 1585527 |
| Author : | SAP |
3. Buffer overflow in ABAP kernel call
A buffer overflow vulnerability was discovered in an ABAP kernel call. It can be exploited by invoking an ABAP report that uses a vulnerable kernel call and passes the data entered by the user into it. This vulnerability allows a user with BASIS rights to compromise the OS and execute any commands with the rights of the user adm. Now only the PoC-exploit is publicly available, but there is also a working exploit created in our laboratory.
| Spying Risk : | Critical |
| The risk of sabotage : | Critical |
| Fraud Risk : | Critical |
| Availability : | Requires a user with BASIS rights. |
| Ease of operation : | Average. It is necessary to know well the technology of writing exploits for various platforms. |
| CVSSv2: | 4.8 |
| Description : | http://virtualforge.com/tl_files/Theme/whitepapers/BlackHat_EU_ 2011_Wiegenstein_The_ABAP_Underverse-WP.pdf |
| Patch : | SAP Security Notices: 1487330, 1529807 |
| Author : | Andreas Wiegenstein (Andreas Wiegenstein) |
4. Remote code execution through TH_GREP
ABAP remote command execution vulnerabilities became popular in 2011. One of the most known such vulnerabilities was found in the function module TH_GREP. Interestingly, Joris found this vulnerability back in 2010, it was fixed, but our researcher Alexey Tyurin analyzed the patch and found that it did not completely solve the problem: in Windows, the patch could be bypassed. And only then this vulnerability was finally fixed. It allows an authorized user with BASIS rights to compromise the OS and execute any commands with the rights of the user adm.
| Spying Risk : | Critical |
| The risk of sabotage : | Critical |
| Fraud Risk : | Critical |
| Availability : | Requires a user with BASIS rights. |
| Ease of operation : | High. |
| CVSSv2: | 6 |
| Description : | http://erpscan.ru/advisories/dsecrg-11-039-sap-netweaver-th_grep-module-code-injection-vulnerability-new/ |
| Patch : | SAP Security Notice: 1620632 |
| Author : | Joris van de Wiz and Alexei Tyurin (Digital Security) |
5. Extend JSESSIONID using the SAP Management console
Mariano Nunez discovered a vulnerability in SAP MMC that allowed anonymous reading of any log file in the SAP system. In turn, during the testing of SAP penetration systems, we found that the JSESSIONID value is sometimes stored in the log files, if the maximum trace level is set. And access to JSESSIONID means the ability to insert its value into a cookie and enter the SAP system under the guise of an existing user.
| Spying Risk : | Tall |
| The risk of sabotage : | Average |
| Fraud Risk : | Tall |
| Availability : | Average. Remote MMC access required |
| Ease of operation: | Average. Tracing must be enabled. |
| CVSSv2: | 5.6 |
| Description : | http://erpscan.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/06/Top-10-most-interesting-vulnerabilities-and-attacks-in-SAP-2012-InfoSecurity-Kuwait.pdf |
| Patch : | SAP Security Notice: 1439348 |
| Author : | First discovered by Mariano Nunes (Mariano Nunez); new vector found by Alexei Tyurin (Digital Security) |
3. Increasing interest
Information security trends currently focus mainly on mobile applications, cloud services, social networks, and critical infrastructure facilities that may be targeted by attackers in the near future. However, there is such an area as the security of ERP-systems, and these systems are under threat now. Therefore, a growing number of companies that are engaged in the security of ERP-systems and develop software to audit their security. At the same time, new companies are constantly appearing that offer specialized consulting services in the field of ERP system security.
3.1. Number of safety reports at technical conferences
Since 2006, SAP security has received increasing attention at technical security conferences such as BlackHat, HITB, etc. Since 2010, this trend has spread to other conferences. More and more companies and researchers are publishing SAP security research. From 2006 to 2009, most of the reports were devoted to the classic IS threats in the SAP landscape: SAP web application security, SAP client security, backdoors, and trojans under SAP. Last year, the focus shifted to highly specialized studies of various types of vulnerabilities in SAP, in the ABAP code and in SAP Kernel, such as SQL injection , buffer overflow , vulnerabilities in the J2EE engine. The most striking examples are Verb Tampering , Session Fixation , Invoker Servlet , as well as vulnerabilities in their own SAP protocols - DIAG and P4 .

The number of SAP security reports presented at various conferences each year is shown on the graph. For 2012, an approximate amount is calculated based on data for the first 4 months.
4. SAP on the Internet
Among the many people working with SAP, there is a myth that SAP systems are isolated from the Internet, so all vulnerabilities in SAP can only be exploited by insiders.
From an interview with Saccar Paulus (Sachar Paulus, senior vice president of product protection and security at SAP) for CIO magazine:
CIO : What, in your opinion, are the most important SAP security threats? What aspects of SAP security do you consider the most difficult?
Sakkar : Another threat is people who connect their SAP systems to the Internet in order to increase support for the supply chain in the system or to add new functionality to make life easier for employees. The problem here is that the classic, well-studied network threats are poorly understood by the ERP community. People who are in charge of ERP systems understand the threat of an insider attack, because they have been dealing with it for many years, but when business requirements dictate the need to connect the system to the Internet, these people do not think about such threats as cross-site scripting . Viruses or worms may appear under the ERP platform, while these people do not understand the importance of patches. This is the hardest challenge for organizations. To accept this challenge, cooperation is needed between people who understand the security of ERP systems, and people who understand the security of the Internet, email and web services .
Business applications are not only accessible from the internal network; This is a myth that was a reality ten years ago, when all information about a company was usually stored on one server. Business is changing, and companies need network connections between different applications. They need to have a connection with branches all over the world, exchange data with clients through web portals, SRM and CRM systems, and have access to information from anywhere in the world through mobile solutions. Almost all business applications now have access to the Internet.
To destroy this myth, we will demonstrate which services are remotely accessible, which companies they belong to and in what respect these services are vulnerable to modern threats.
4.1. Google search results by country
These statistics were collected using simple queries in the well-known search engine Google.
| Application Server Type | Search query |
| SAP NetWeaver ABAP | Inurl: / SAP / BC / BSP |
| SAP NetWeaver J2EE | Inurl: / irj / portal |
| SAP BusinessObjects | inurl: infoviewapp |
The scan revealed about 610 unique servers with various SAP web applications. Obviously, the most popular platform is J2EE. Unfortunately, such servers are more vulnerable than the ABAP engine, since this platform has at least 3 different vulnerabilities that can be exploited anonymously and provide full access to the system. On the other hand, in the ABAP engine, many predefined user accounts with standard logins and passwords can be used by hackers. SAP BusinessObjects has both of these problems.
| Apps server | amount | % |
| SAP NetWeaver J2EE | 268 | 44% |
| SAP Web Application Server | 163 | 27% |
| SAP BusinessObjects | 106 | 17% |
| SAP NetWeaver ABAP | 73 | 12% |
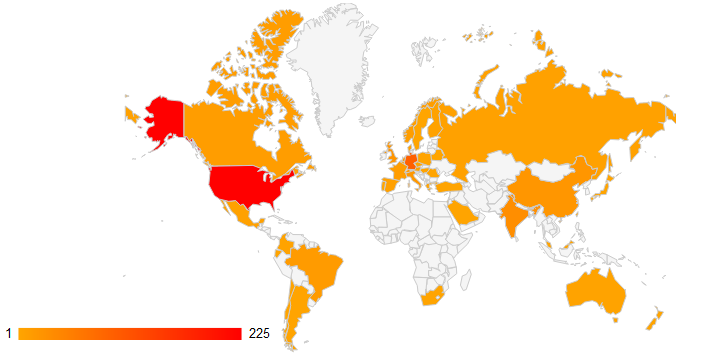
Application Servers by Country
4.2. Search results for Shodan by country
Www.shodanhq.com was chosen as the second resource for searching SAP web interfaces on the Internet. The peculiarity of this service is that it not only finds applications that have been indexed by search robots, but scans the entire Internet for the presence of the open 80th port (and others), so it was used for an additional search for SAP systems.
In general, we found 2677 servers with a variety of SAP web applications. This is 4.5 times more than with Google.
| Apps server | amount | % |
| SAP NetWeaver J2EE | 863 | 32% |
| SAP Web Application Server | 734 | 27% |
| SAP BusinessObjects | 686 | 26% |
| SAP NetWeaver ABAP | 394 | 15% |
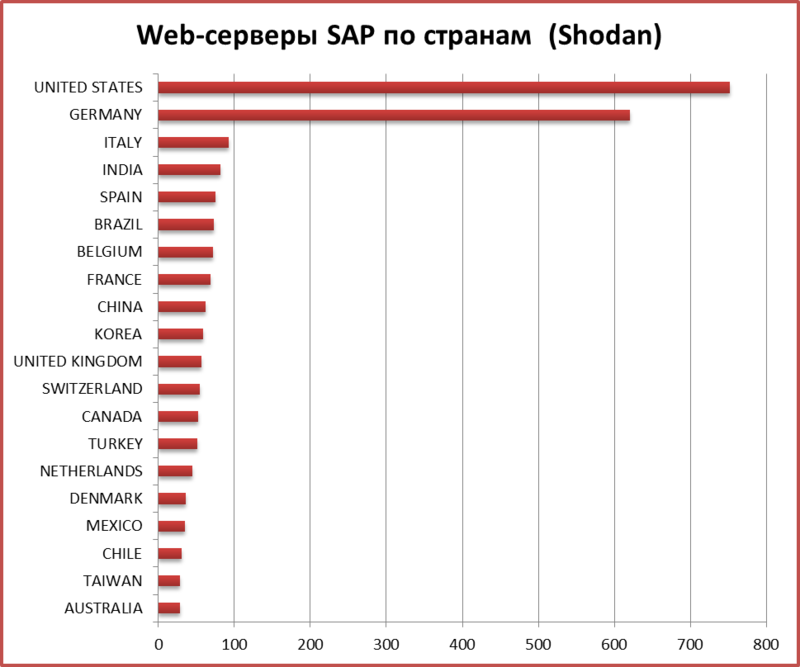
4.3. Port scan results by country
The most interesting and difficult part of the study is scanning the Internet not only for the presence of web services, but also for services that should not be accessible on the Internet at all.
At this stage, this task was performed using a simple algorithm that scanned only the subnets of the servers that were found through Google and Shodanhq (these are about 1,000 subnets). We found a large number of ports that are monitored by SAP services such as Message Server HTTP, SAP Gateway, SAP HostControl. The number of open ports will be updated online at www.sapscan.com - the official project website.
Another project that has not yet been completed is a global scan of the Internet for open ports. At the moment, only a number of the largest countries have been completely scanned.
As an example, below are the results of scanning Russia. A total of 58 SAP routers installed by default on port 3299 were detected. After receiving the list of SAP routers on all subnets where SAP routers were detected, a scan was started for the presence of prohibited external services, such as SAP Hostcontrol, SAP Dispatcher , SAP Message Server, SAP Management console.
10% of Russian companies that use SAP, open access to the Internet bypassing the router for SAP Dispatcher.
The diagram below shows the percentage of companies that provide Internet access to certain critical SAP services.

5. SAP Versions
We checked which versions of the ABAP and J2EE engines are most often present on the Internet in order to understand the life cycle of SAP products and find out which versions of products are currently popular. We also checked which OS and RDBMS are used in conjunction with SAP systems most often.
5.1. ABAP engine versions
To find out the versions of ABAP, we connected to the root of the application server and analyzed HTTP responses. We also took advantage of the information disclosure vulnerability. The SAP NetWeaver version can be easily recognized if the application is configured insecurely and allows an attacker to extract information from / sap / public / info.
After scanning all the available SAP NetWeaver ABAP servers, it was discovered that 59% of them are vulnerable to information disclosure.
The best security settings, such as disabling access to all BSPs, are available by default in the EHP 2 update, but EHP 2 is installed on only 11% of servers. This means that, even though SAP itself is concerned about the security of its systems, without the participation of system administrators, the efforts of developers are useless.
The most popular version (45%) is NetWeaver 7.0, and in fact it was released in 2005!

5.2. J2EE engine versions
J2EE version information can be easily found by reading the HTTP response. However, detailed information about the patch version is available if the application server is configured incorrectly and allows an attacker to view information from certain pages. For example, these two pages reveal information about the J2EE engine: /rep/build_info.jsp and /bcb/bcbadmSystemInfo.js.
After scanning all the available SAP NetWeaver J2EE servers, it turned out that 62% of them are vulnerable to information disclosure through the /rep/build_info.jsp page and 17% through the /bcb/bcbadmSystemInfo.jsp page.
Detailed information on product versions is presented below.
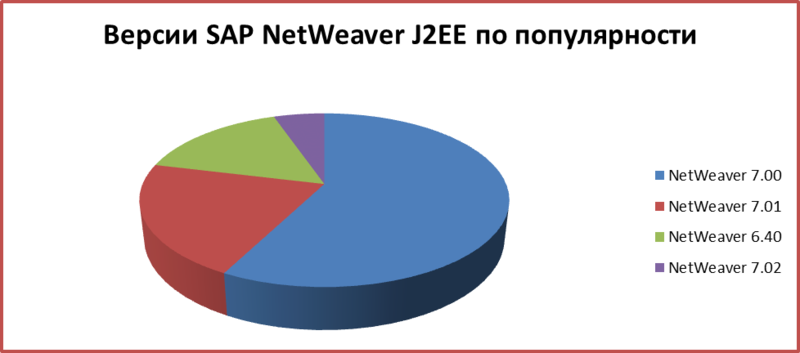
5.3. Popular OS for SAP
Using the page / sap / public / info, you can get information about the OS versions where ABAP is deployed. Analysis of the search results for SAP systems that have access to the Internet showed that the most popular operating systems are Windows NT (28%) and AIX (25%). Our statistics, compiled during the SAP internal auditing process, shows the great popularity of * .NIX systems, although Windows is leading in systems connected to the Internet.

5.4. Popular DBMS for SAP Backend
The most popular DBMS is still Oracle - 59%. Other DBMSs are listed below.
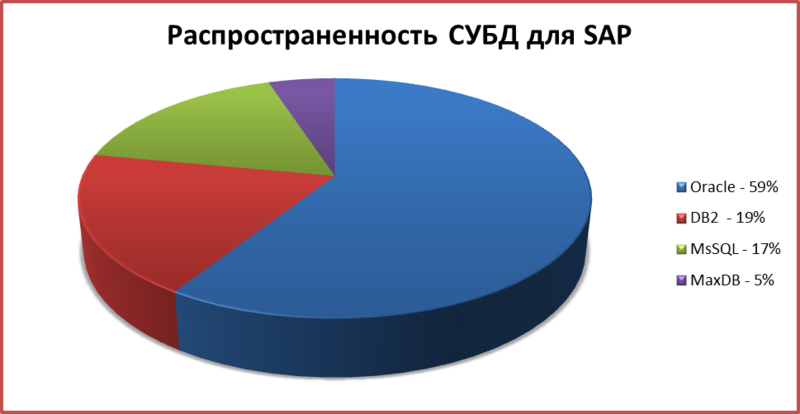
It is worth noting that the Oracle DBMS installed together with SAP is vulnerable to a very dangerous attack , where authorization costs and an unauthorized user gets direct access to the database without any authentication data, due to the incorrect use of the REMOTE_OS_AUTHENT parameter. This is a very old problem, published back in 2002, but it is still relevant.
6. Critical Internet Services
In addition to web interfaces that need to be available on the Internet due to various business requirements, such as SAP Portal solutions, SAP SRM or SAP CRM, there are services that should not be accessible from the outside. They not only carry potential risk, but also have real vulnerabilities and configuration errors, which are well known and well described in public sources. Of course, we do not provide a complete list of critical SAP services, only the most popular ones. About 1000 subnets of companies using SAP were scanned. The graph shows the percentage of companies where critical SAP-services were open for remote access.
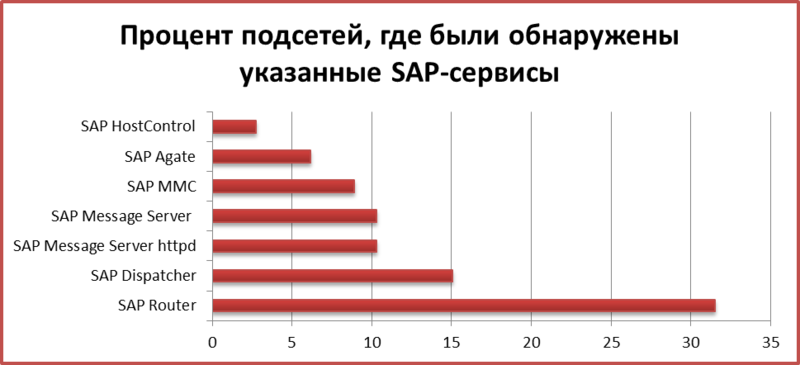
It is easy to notice that the most popular service is SAP Router, and this is normal, because its purpose is to be open to remote connections. But what about the other services? They should not be available via the Internet, however they are available. And the number of them is not as small as we assumed before the start of the project.
6.1. WebRFC service as part of NetWeaver ABAP
WebRFC is a default web service available on the SAP NetWeaver ABAP platform. It allows you to perform dangerous RFC functions using HTTP requests to the NetWeaver ABAP port and to the / sap / bs / web / rfc page. Some of these functions are critical, for example:
• Reading data from SAP tables
• Creating SAP users
• Running OS commands
• Financial transactions, etc.
By default, any user has access to this interface and the ability to execute the RFC_PING command by sending an XML packet. Additional authorizations are required to perform other functions. Thus, there are two main risks:
• If the system has a default user with a pre-set password, an attacker can perform many dangerous RFC functions, because users have fairly dangerous permissions by default.
• If a hacker finds out remotely the authentication data of any existing user, he can execute a denial of service attack by sending an RFC_PING request with a modified XML package.
It was found that the WebRFC service is included in 40% of ABAP systems.
We did not check whether standard passwords are used in these systems, but in accordance with various statistics collected during our research and research of colleagues, one or more accounts have a default account in 95% of the systems.
6.2. CTC service as part of NetWeaver J2EE
CTC, or ConfigTool, is the default web service installed on the NetWeaver J2EE engine. It allows you to remotely control the J2EE engine. This web service can be found through Google, and it is often found in SAP Portal systems. It is possible to perform such functions as:
• Creating users
• Assigning Roles to Users
• Running OS commands
• Remotely enable and disable the J2EE engine
Digital Security researchers have discovered a vulnerability in this service called Verb Tampering . It allows you to bypass authorization checks when accessing the CTC service remotely. This means that anyone can remotely get full unauthorized access to all business-critical information located in the J2EE engine.
It was found that CTC was enabled on 61% of J2EE systems on the Internet.
We did not check whether these systems are vulnerable, but our experience with penetration tests shows that about 50% of the systems are potentially vulnerable.
6.3. SAP Message Server HTTP
The SAP Message Server HTTP is the HTTP port of the SAP Message Server service that allows you to balance the load on SAP application servers. Usually this service is available only within the company, however, in some systems external IP addresses were discovered that, as a rule, are not needed to perform business tasks and at the same time can lead to performing critical actions in the system. By default, the SAP Message Server listens on port 80NN, where NN is the system number. One of the problems of SAP Message Server HTTP is the ability to get the values of the configuration parameters of the SAP system remotely without authorization. They can be used for further attacks.
A scan of a sample of 1000 subnets of companies using SAP found 98 Message Server HTTP open access systems. Approximately every 10th company is vulnerable to unauthorized collection of system parameters remotely via the Internet; most of them are located in China (55%) and India (20%).
6.4. SAP Management Console
SAP HostControl is a service that allows you to remotely monitor SAP systems. Its main functions are remote on and off, to use them you need to know your login and password. , , , . , . (Chris John Riley), .
Digital Security JSESSIONID. JSESSIONID – , HTTP. JSESSIONID cookie - .
, , , 9% SAP Management . 548. 11- , .
6.5. SAP Dispatcher
SAP Dispatcher – - SAP. SAP NetWeaver SAP GUI DIAG. SAP Dispatcher , . : Dispatcher, WEB Dispatcher, , , .
, 1000 , 832 SAP Dispatcher, , 15% . 6- DoS- SAP Dispatcher.
?
-, SAP- SAP GUI, , . SAP , , 95% .
, Core Security, , SAP Dispatcher , « », . 9 , - . , , , DIAG 2 3 – . , .
7.
, SAP . SAP, , , SAP ( APT), «», .
SAP Security Response Team , , . SAP SAP-, . SAP , , , , ABAP .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/146967/
All Articles