Permissions on files in Win7: changing user in current session
Good afternoon, dear habra-inhabitants!
Preface: from time to time it is necessary to set the rights to separate folders and files for users at work. In XP, this was done easily and simply (the way, if someone does not know, under the cut), but with the release of Vista and Seven - an old proven friend let me down. Let's find out how you can quickly set the rights to individual folders and files in Windows under the current user. Save time!
So, first of all, the way that runs in Windows XP:
Run cmd with administrator rights (this is runas / user: domain \ login cmd if someone suddenly forgot and enter the magic command - explorer / separate .
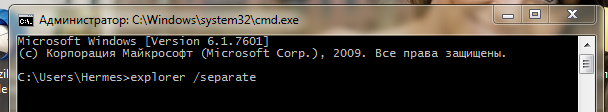
As a result, we will launch an explorer with admin privileges. Expose the right and enjoy their resourcefulness.
')
But the time has come to change and in newer systems this command will launch the explorer from the current user.
You can, of course, set rights through admin balls from your workplace, or launch other file managers from yourself ... But sometimes you need to set rights here and now, and installing an extra program on a computer that will have to be used once a month is wrong.
So, I found two ways to overcome this situation: one is correct and interesting, the second is fast and funny. Let's start with the first.
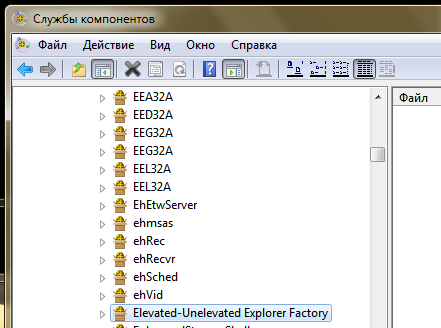
One of the COM objects is responsible for the delineation of explorer rights. Namely - Elevated-Unelevated Explorer Factory .
This miracle is as follows:
Run cmd with administrator privileges - dcomcnfg and then in the DCOM configuration, look for the Elevated-Unelevated Explorer Factory parameter.
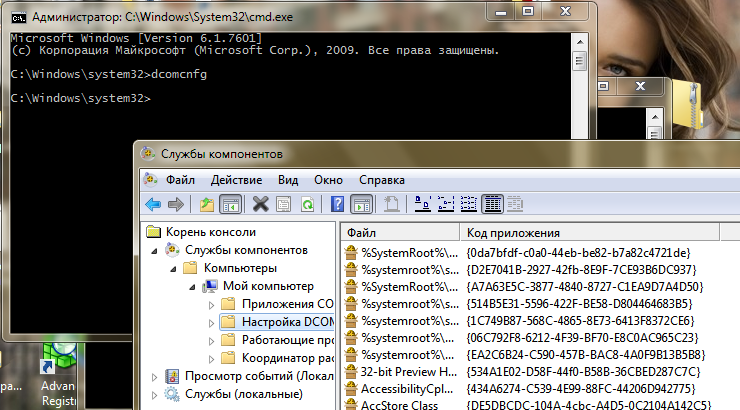
and look for our hidden animal there:
However, you probably won't be able to edit this parameter. No rights to change the registry key HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT \ AppID \ {CDCBCFCA-3CDC-436f-A4E2-0E02075250C2}
When did such trifles stop us? We make ourselves an owner, change permissions and run dcomcnfg again.
HOORAY! We can now set the parameter on the Identity - Starting User tab.
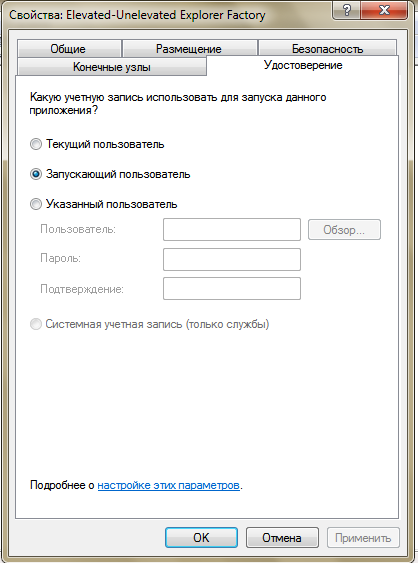
A little chore, huh? You can immediately edit the registry key - HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT \ AppID \ {CDCBCFCA-3CDC-436f-A4E2-0E02075250C2} \ RunAs
It is possible to resolve this issue through politics, but alas, I did not find this, and I don’t apply it at work. Is that comes to mind batch file on the registry key. Well, the first way we mastered ...
And now is the time of magic .
Run cmd as administrator, open notepad, select Open and display all files and quietly change permissions on files and folders.
A picture illustrating my eyes at the time of this wonderful discovery is attached:

Thank you for attention!
UPD
Thanks to the user denis_g and several other Linux users, I remembered that I had read a long time about the console command for managing access rights - CACLS
Once the link to the syntax
Two syntax reference
It turns out that adding a user with change rights is done like this:
cacls PATH: \ To \ FILE / t / e / p username: C
Where variables: / t - subdirectories (for folders), / e - edit ie. change of existing rights, / p - change of pav to the user (if not, add), C - read.
Carefully, practice first, because you can demolish all the rights to the folder to null!
UPD2 didn't work for me
Hold SHIFT and select “Run as a different user” of the Explorer ...
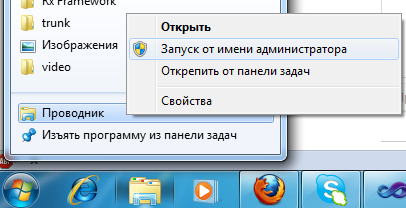
UPD3 from tachidi
1) Kill in the explorer.exe processes
2) Run it on behalf of the admininstrator account
3) Set the necessary parva
4) Do not forget to return everything back!
Preface: from time to time it is necessary to set the rights to separate folders and files for users at work. In XP, this was done easily and simply (the way, if someone does not know, under the cut), but with the release of Vista and Seven - an old proven friend let me down. Let's find out how you can quickly set the rights to individual folders and files in Windows under the current user. Save time!
So, first of all, the way that runs in Windows XP:
Run cmd with administrator rights (this is runas / user: domain \ login cmd if someone suddenly forgot and enter the magic command - explorer / separate .

As a result, we will launch an explorer with admin privileges. Expose the right and enjoy their resourcefulness.
')
But the time has come to change and in newer systems this command will launch the explorer from the current user.
You can, of course, set rights through admin balls from your workplace, or launch other file managers from yourself ... But sometimes you need to set rights here and now, and installing an extra program on a computer that will have to be used once a month is wrong.
So, I found two ways to overcome this situation: one is correct and interesting, the second is fast and funny. Let's start with the first.
Method 1. For the curious and patient
One of the COM objects is responsible for the delineation of explorer rights. Namely - Elevated-Unelevated Explorer Factory .
This miracle is as follows:
Run cmd with administrator privileges - dcomcnfg and then in the DCOM configuration, look for the Elevated-Unelevated Explorer Factory parameter.

and look for our hidden animal there:

However, you probably won't be able to edit this parameter. No rights to change the registry key HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT \ AppID \ {CDCBCFCA-3CDC-436f-A4E2-0E02075250C2}
When did such trifles stop us? We make ourselves an owner, change permissions and run dcomcnfg again.
HOORAY! We can now set the parameter on the Identity - Starting User tab.

A little chore, huh? You can immediately edit the registry key - HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT \ AppID \ {CDCBCFCA-3CDC-436f-A4E2-0E02075250C2} \ RunAs
- Interactive User value for current user
- deletion of this parameter for the launching user
- username to launch explorer from a particular user
It is possible to resolve this issue through politics, but alas, I did not find this, and I don’t apply it at work. Is that comes to mind batch file on the registry key. Well, the first way we mastered ...
And now is the time of magic .
Method 2. Fast and fun
Run cmd as administrator, open notepad, select Open and display all files and quietly change permissions on files and folders.
A picture illustrating my eyes at the time of this wonderful discovery is attached:

Thank you for attention!
UPD
Thanks to the user denis_g and several other Linux users, I remembered that I had read a long time about the console command for managing access rights - CACLS
Once the link to the syntax
Two syntax reference
It turns out that adding a user with change rights is done like this:
cacls PATH: \ To \ FILE / t / e / p username: C
Where variables: / t - subdirectories (for folders), / e - edit ie. change of existing rights, / p - change of pav to the user (if not, add), C - read.
Carefully, practice first, because you can demolish all the rights to the folder to null!
UPD2 didn't work for me
Hold SHIFT and select “Run as a different user” of the Explorer ...

UPD3 from tachidi
1) Kill in the explorer.exe processes
2) Run it on behalf of the admininstrator account
3) Set the necessary parva
4) Do not forget to return everything back!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/146634/
All Articles