Elements of interaction experience - my brief retelling of the book.
I begin to lay out the abstract of the book "Elements of Interaction Experience", which is mandatory for everyone who is involved in designing web systems to read with which users interact.
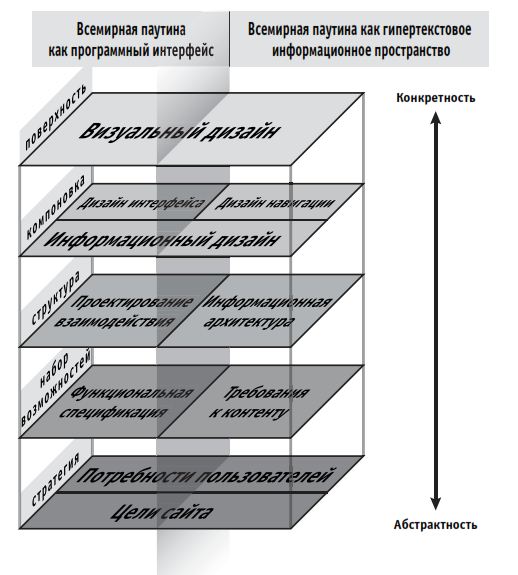
Synopsis spiced with my thoughts, I will lay out the levels, all of them 5:
1. Strategy level
2. Level of feature set
3. Level of structure
4. Layout Level
5. Level surface
')
The Internet is now both a content space and software. That is why the design of interaction experience must take into account an integrated approach.
5 elements of interaction allow to design experience at levels from abstract to concrete.

At this level, we need to understand what we need from the project, and what future users need.
- must reflect the essence of the company's business processes
- not too abstract for us to understand what decisions to take - the site should be beautiful, it is very abstract.
- not too specific for us to evaluate the effect - the buttons on the site should be black. very specific.
- it is best to form goals according to the principles of SMART
Initially, you need to segment potential users:
- through research - demographic and psychographic
- using the methods of characters - I use this technique, exposing it to the analysis of the site owner, as well as possible representatives of the potential audience
The next step is to determine the need of users and divide it into groups.
For example:
A1 Find information about classes
A2 Register for classes
B3 Find information about the opportunity to conduct classes
B4 Register as a teacher
An important part of the collection of information at this design stage, communication with the staff of the company's customer site. At this stage, every need and its source is discussed. And even more so every goal of the company. The objectives are approved by the main person of the company, with full understanding that this is important.

At this level, we need to understand what we need to do, and importantly, what not to do.
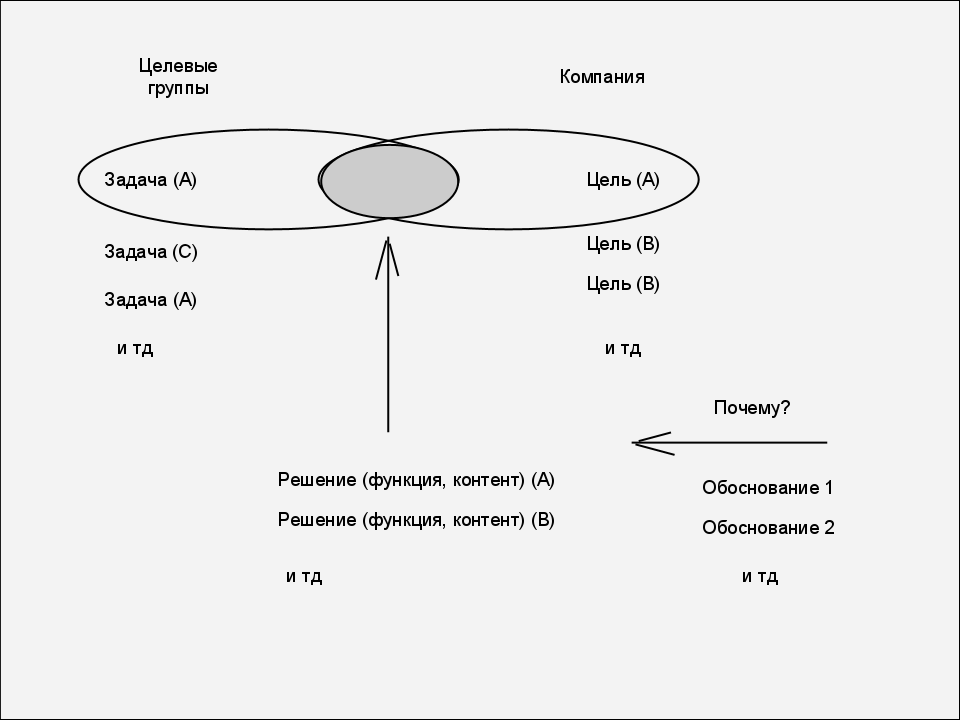
All functional specifications and content requirements are formed at the junction of user needs and company goals, and are in harmony between them.
- Purpose and need define several possibilities.
- Opportunity serves multiple purposes needs
- Describe why
- To give an example, it is better to refer to a similar element.
- Describe the scenario:
- The user presses the button
- The system destroys the world
- User dies
- Be positive:
- no - the system does not allow the user to perform actions 1 without action 0
- yes - the system after the user has done data 1 and redirects it to step 0
- Be objective
- no - the site must be productive
- yes - the site should withstand a load of 1000 visits per 1 minute
- Use conceptual models - solutions often used by developers, to whom the user is already used
- Use mental models - solutions similar to solutions that are used in real life (basket)
- Format - text, sound, video, photo
- Appointment - answer questions, convince
- Who is responsible for creating
- How often to update
At this level, we need to obtain from the obtained solutions a holistic picture of what all these decisions will apply.
- Top-down approach to the development of architecture- we divide all content and functional solutions into categories based on the goals of the site and the user's needs:
Choose product
Order product
Deliver the goods
Cons of this approach - you can miss the details
- Ascending approach to the development of architecture - based on the content and functional solutions we define categories:
Catalog
Service Catalog
Addresses of shops
Disadvantages of this approach are not flexible for new content and solutions.
The truth, as always, is between 2 approaches, that is, the categories of the right level are defined by the downward approach, and the category of the low ones is ascending.
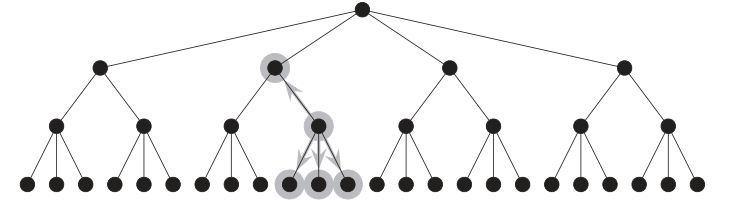
1. Hierarchical system
Each parent has a node except the topmost level.

2. Matrix
Allows you to build navigation on the same content to different users (filters).

3. Organic
Randomly connects nodes, suitable for content links in which are not clear.

4. Sequential structure
Nodes one after another, for articles and separate sections.

Create a vocabulary of regulatory vocabulary, where all the terms used on the site are understandable to both users and developers. To avoid productive thinking.

At this level, we concentrate on individual pages and functional blocks.
- If the user performs an action - interface design.
- If the user moves - navigation design.
- If the user performs an action - information design.
A good interface is one in which important information is immediately visible, and not important secondary.
Interface design is reduced to the selection of suitable items, taking into account the tasks facing the user, and placing them in such a way that it is easy how and why to use them.
Interface design elements:
Checkboxes

Buttons

Text fields

Drop down lists

Drop down lists

Radio batons - allow you to make a choice dependent on each other

3 main navigation functions:
1. Allow the user to move from one point of the site to another
2. Reflects the relationship between pages (hierarchy)
3. Reflects the relationship between navigation and page content.
! The most important question of the user is where I am and where I can go.
Global navigation
Allows you to go from one end of the site to another, To any place of the site, to any level

Local navigation
Provides access to the parent page, pages to descendants and pages to neighbors
Additional navigation
Gives access to content related to the page.
Contextual navigation
Built into the content, allows you to move to the section based on the need to study the context.

Service navigation
Sections with information that can always be useful (contacts, order a call)

Portable navigation
- site map - probably everyone knows what it is)
- index - all links alphabetically
This is about how to present information in such a way that it is easier for people to perceive and use it.
For the description of information design, prototypes of the page are used which refer to:
- Content requirements
- Interaction Schemes
- Technical Specifications

At this level we:
- reflect the brand's visual communication style
- we draw attention to important elements - it is important that some elements attract more attention and others less, otherwise either nothing will attract attention, or it will be too hard to focus on something
One element can be distinguished by:
- Contrast
- Uniformity of elements
2 problems:
- External - a different design approach in comparison with other products and communications of the company.
- Internal - different approaches to design in different parts of the site.
Solutions:
Use on the site and in other communications an identity that produces the same effect.
Design items outside the page context so that it can be reused.
All design decisions are in the corporate identity manual - so as not to get away from the sequence at the tactical level, as well as when leaving employees
- Use different fonts to attract attention
- Do not overload through changeable number of fonts
- There should be no noise in the font.
Synopsis spiced with my thoughts, I will lay out the levels, all of them 5:
1. Strategy level
2. Level of feature set
3. Level of structure
4. Layout Level
5. Level surface

')
The Internet is now both a content space and software. That is why the design of interaction experience must take into account an integrated approach.
5 elements of interaction allow to design experience at levels from abstract to concrete.
Strategy level

At this level, we need to understand what we need from the project, and what future users need.
Definition of site objectives
- must reflect the essence of the company's business processes
- not too abstract for us to understand what decisions to take - the site should be beautiful, it is very abstract.
- not too specific for us to evaluate the effect - the buttons on the site should be black. very specific.
- it is best to form goals according to the principles of SMART
Determine user needs
Initially, you need to segment potential users:
- through research - demographic and psychographic
- using the methods of characters - I use this technique, exposing it to the analysis of the site owner, as well as possible representatives of the potential audience
The next step is to determine the need of users and divide it into groups.
For example:
A1 Find information about classes
A2 Register for classes
B3 Find information about the opportunity to conduct classes
B4 Register as a teacher
Collection of information
An important part of the collection of information at this design stage, communication with the staff of the company's customer site. At this stage, every need and its source is discussed. And even more so every goal of the company. The objectives are approved by the main person of the company, with full understanding that this is important.
Capability Level

At this level, we need to understand what we need to do, and importantly, what not to do.

All functional specifications and content requirements are formed at the junction of user needs and company goals, and are in harmony between them.
How to rank opportunities
- Purpose and need define several possibilities.
- Opportunity serves multiple purposes needs
How to describe functional specifications
- Describe why
- To give an example, it is better to refer to a similar element.
- Describe the scenario:
- The user presses the button
- The system destroys the world
- User dies
- Be positive:
- no - the system does not allow the user to perform actions 1 without action 0
- yes - the system after the user has done data 1 and redirects it to step 0
- Be objective
- no - the site must be productive
- yes - the site should withstand a load of 1000 visits per 1 minute
- Use conceptual models - solutions often used by developers, to whom the user is already used
- Use mental models - solutions similar to solutions that are used in real life (basket)
How to determine content requirements
- Format - text, sound, video, photo
- Appointment - answer questions, convince
- Who is responsible for creating
- How often to update
Structure level

At this level, we need to obtain from the obtained solutions a holistic picture of what all these decisions will apply.
Information architecture
- Top-down approach to the development of architecture- we divide all content and functional solutions into categories based on the goals of the site and the user's needs:
Choose product
Order product
Deliver the goods
Cons of this approach - you can miss the details
- Ascending approach to the development of architecture - based on the content and functional solutions we define categories:
Catalog
Service Catalog
Addresses of shops
Disadvantages of this approach are not flexible for new content and solutions.
The truth, as always, is between 2 approaches, that is, the categories of the right level are defined by the downward approach, and the category of the low ones is ascending.
Possible architectural solutions
1. Hierarchical system
Each parent has a node except the topmost level.

2. Matrix
Allows you to build navigation on the same content to different users (filters).

3. Organic
Randomly connects nodes, suitable for content links in which are not clear.

4. Sequential structure
Nodes one after another, for articles and separate sections.

Language and Methodology
Create a vocabulary of regulatory vocabulary, where all the terms used on the site are understandable to both users and developers. To avoid productive thinking.
Layout Level

At this level, we concentrate on individual pages and functional blocks.
- If the user performs an action - interface design.
- If the user moves - navigation design.
- If the user performs an action - information design.
Interface design
A good interface is one in which important information is immediately visible, and not important secondary.
Interface design is reduced to the selection of suitable items, taking into account the tasks facing the user, and placing them in such a way that it is easy how and why to use them.
Interface design elements:
Checkboxes

Buttons

Text fields

Drop down lists

Drop down lists

Radio batons - allow you to make a choice dependent on each other

Navigation design
3 main navigation functions:
1. Allow the user to move from one point of the site to another
2. Reflects the relationship between pages (hierarchy)
3. Reflects the relationship between navigation and page content.
! The most important question of the user is where I am and where I can go.
Types of navigation
Global navigation
Allows you to go from one end of the site to another, To any place of the site, to any level

Local navigation
Provides access to the parent page, pages to descendants and pages to neighbors

Additional navigation
Gives access to content related to the page.

Contextual navigation
Built into the content, allows you to move to the section based on the need to study the context.

Service navigation
Sections with information that can always be useful (contacts, order a call)

Portable navigation
- site map - probably everyone knows what it is)
- index - all links alphabetically
Information Design
This is about how to present information in such a way that it is easier for people to perceive and use it.
For the description of information design, prototypes of the page are used which refer to:
- Content requirements
- Interaction Schemes
- Technical Specifications
Surface level

At this level we:
- reflect the brand's visual communication style
- we draw attention to important elements - it is important that some elements attract more attention and others less, otherwise either nothing will attract attention, or it will be too hard to focus on something
One element can be distinguished by:
- Contrast
- Uniformity of elements
Possible design problems in the company
2 problems:
- External - a different design approach in comparison with other products and communications of the company.
- Internal - different approaches to design in different parts of the site.
Solutions:
Use on the site and in other communications an identity that produces the same effect.
Design items outside the page context so that it can be reused.
All design decisions are in the corporate identity manual - so as not to get away from the sequence at the tactical level, as well as when leaving employees
Font usage
- Use different fonts to attract attention
- Do not overload through changeable number of fonts
- There should be no noise in the font.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/145518/
All Articles