Triple Play: how do telephone, TV and Internet get along in a single IP environment?
The term Triple Play itself (3P) was initially purely marketing, reflecting some kind of joint provision of services based on new generation networks. Experience has shown that all modern communication services (of any complexity) are a set of three basic services for a natural person subscriber:
Technologically, all three basic services “live” on different platforms, but in the same environment, so there are many difficulties with billing, working with SORM, blocking services with zero balance (while maintaining the possibility of an emergency call), technical support and anti-fraud.
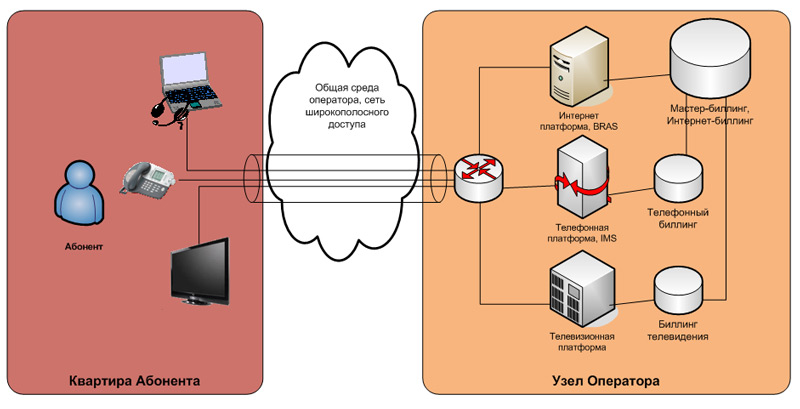
Triple Play services and their IT systems
Platforms:
')
The essential feature of the implementation of the 3P concept is a certain unified environment of the operator, on the basis of which all three services are built. The picture above shows the most widely used to date implementation of such services: the operator creates a broadband access network on the basis of the fiber-optic network and subnets are created on its base to provide telephony and television services.
Historically, the cable television networks and the ADSL network were the first to create 3P environments. And there, and there used analog frequency division for voice, Internet connections and television. Now these technologies make up the bulk of all 3P connections on the planet.
But such solutions are actively being supplanted by optics-based connections. The fiber-optic network used for 3P services in the Russian realities can have both a ring and a star-shaped structure. Almost all operators use one of the FTTx technologies (Fiber to the X - optics to point X):
The main way to connect in the Russian Federation is now FTTB. A typical network usually has a ring structure in the city (to provide reservation for highways) and take-out into quarters, which are reserved by a ring only in the case of a very large number of houses / apartments.
Traffic balancing, of course, is applied across the city - at the level of aggregation nodes, appropriate solutions are used to balance the traffic between the main links. Traffic balancing between quarters or even houses is also used, but usually the scheme is simpler - i.e. balancing between semirings is used and, of course, depends on the volume of subscribers on a specific object.
Further, almost all Russian operators have the same technical design: in the attics or in the basements there are metal cabinets containing Ethernet equipment for connecting end users. At the same time, the design by telephony may differ: it is possible to install VoIP gateways in common metal cabinets (and then the subscriber receives an analog RJ-11 telephone jack), or put the VoIP adapter / VoIP phone immediately in the subscriber’s apartment. The design of IP television is also the same - the set-top box (STB, Set Top Box) is always placed in the subscriber’s apartment, after the Internet router.
Among the most significant organizational and technological problems in this part it is necessary to note the need to configure individual subnets:
Let us describe separately the implementation of calls to emergency services (01, 02, 03, 04, 112 in certain regions). The scheme of implementation of IP-telephony with the requirements of the legislation assumes the presence of a certain switching node in each city providing the service. It is this node that is entrusted with the task of routing emergency calls to specific emergency numbers of each city. The picture 2 shows for comparison the passage of a green normal call (telephone signaling goes through the core of the system, the call is set by an border device) and a red emergency call (control is not used, the call is immediately forwarded to the public telephone network, PSTN).
Boundary devices in telephony are commonly called Session Border Controllers (SBC). Their functions are similar to firewalls in the Internet environment, plus a number of specific functions to ensure the normal operation of VoIP connections.
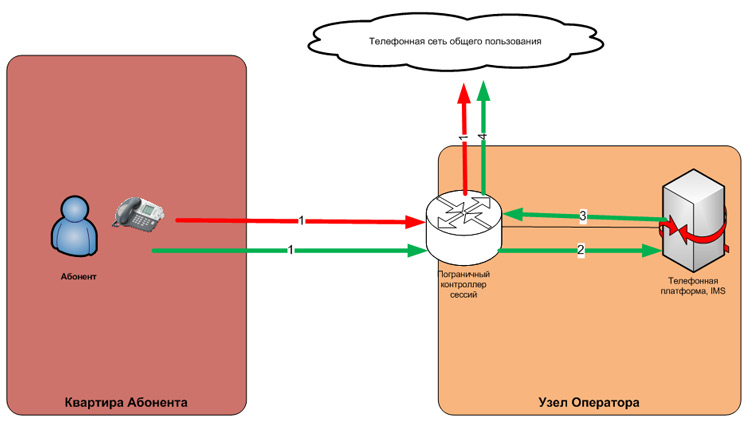
Differences between regular and emergency VoIP calls
Here we also note an interesting Russian peculiarity of the implementation of telephone connections within 3P: the duty of every Russian law-abiding operator to send all calls to SORM. And here a technological problem arises, because All multimedia platforms are configured to provide direct connectivity of all registered users among themselves. And we have two problems:
To solve these problems, again, SBC are used, to which the FSB consoles are connected (well, or SBC are connected to local telephone switches). All calls with SBC numbers are output to such consoles. This solves the problem of telephone SORM. And all calls with logins, nicknames, etc. (i.e., calls over the broadband access network, including video calls) are output to the telematic SORM, which is used to monitor Internet connections.
The bandwidth requirements for traffic for services are different. Telephony is a low bandwidth service. The following voice coding algorithms are mainly used: G.711 A-law / G.711 u-law with a bandwidth (bit rate) of 64 kbit / s, G.729 variants with a band of 8 kbit / s, and a GSM codec with a bitrate of 13 kbit / s with. Taking into account the total volume of IP packet headers, we get the necessary bandwidth from 30 to 90 kbps.
IP television requires significantly more bandwidth (for example, MPEG2 / MPEG4 codecs are often used): so, ordinary SD TV channels require from 2 to 4 Mbps, and high-quality HD channels from 8 to 12 Mbps. It is clear that for such containers smart control of multicast television traffic is required: each channel is fed to the site and / or residential quarter only once, regardless of the number of subscribers watching. It helps statistics - if subscribers in one quarter include all non-overlapping channels, then the operator, providing 100-120 normal channels and 5-20 channels of HD network in this area will fail. But this is not how it happens in life - the distribution of “viewing” usually allows placing requirements on IP TV in the 1-2 Gbit / s band by district / quarter.
Separation by type of traffic to ensure the quality of work of all three services is usually used in the segment of corporate customers and is not used in services for individuals. This is due to the following factors, since residential buildings are quite predictable in terms of consumption.
Depending on which service is more important for the operator, a billing master system is chosen, let's say. For example, account management is organized in a system that serves Internet access. Accordingly, the other two systems (telephony and television billing) occupy a subordinate position and must be tailored to the requirements and features of the master system. These systems are implemented in the form of various modules of one system or it is generally systems of one manufacturer, does not matter, and historically, often (in Russian realities), these are different systems from different IT companies.
Let's take a schematic look at the pricing of Internet access on the example of an unlimited data plan, since in Russia, subscribers using limit tariff plans (by megabyte), there are no more than 5%. Two main algorithms are applied: the amount per month is written off either immediately on day X (and the subscriber's account decreases in steps), or in equal shares every day (and the subscriber's account decreases smoothly, but constantly). Below it is shown how the master billing stops the subscriber’s access to the Internet when a zero account balance is reached or if it goes to minus.
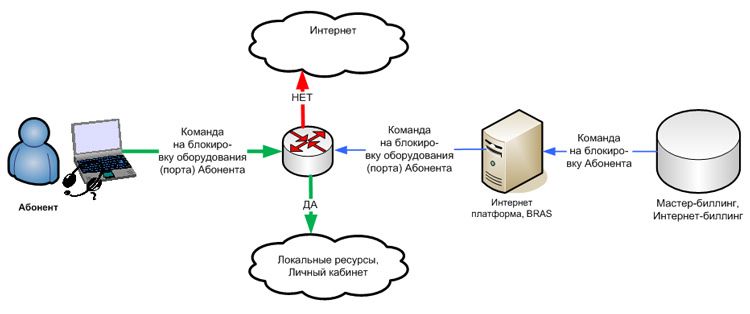
Internet subscriber account monitoring
The basis of telephone billing is the tariff tables in which all directions of possible sending of voice traffic and their cost are clogged. When a subscriber makes a call in any direction, the system analyzes the telephone prefix (country code, city code) and debits the funds, according to the tariff tables. At the same time, the call authorization algorithm, even in the prepaid 3P version, can be prepaid and postpaid (this is due to the implementation features of various billing systems and telephone platforms).
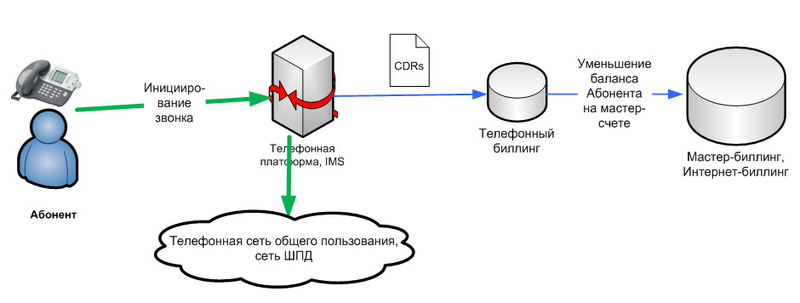
Postpaid phone call authorization
Below is a schematic diagram of the call authorization script in the case of a post-paging telephony setup option. In this case, the subscriber makes a call, the IMS platform checks that the subscriber is not blocked and passes the call to the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or to the VoIP network. During the call (and after it ends), the IMS platform generates CDR files (Call Detail Recording) containing all the information about the call of the subscriber. Telephone billing processes the data CDR files, displaying this information first on its internal accounts (minus the customer’s account on the results of incoming CDRs), and then on the subscriber’s account in master billing. You can reduce the subscriber's account in the master billing simultaneously with a decrease in telephone billing, but there are already performance issues in the interaction of systems, you need to find a balance between the number of subscribers served and the time intervals in the described chains.
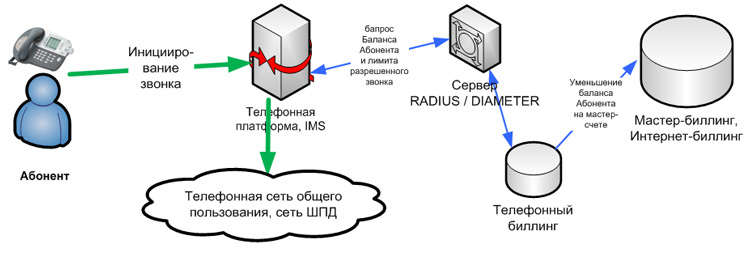
Pre-login phone call authorization
Here you can see the diagram of the call authorization script in the case of a prepaid telephony configuration option. In this case, the subscriber wants to make a call, the IMS platform contacts the authorization server (RADIUS or DIAMETER protocol), and the authorization server refers to phone billing. Telephone billing informs the authorization server that the subscriber is not blocked and reports the limit of possible minutes for the destination selected by the subscriber. That allows the IMS platform to skip a call to the public switched telephone network (PSTN) network or to the VoIP network.
At the same time, the telephone billing blocks a certain amount on the client’s account to pay for the call, which is adjusted (increased or decreased) as a result of the end of the call. Further, similar to postpaid billing, there is an adjustment on the subscriber’s account in the master billing. It is important to note here that in both scenarios the subscriber may go into a minus, only with the pre-scheme it will be less.
Ideologically, television billing is not different from billing other television services. In the case of cable TV, billing is quite simple - it is just writing off fixed amounts for certain packages of TV programs, and in the case of IP TV, the Video On Demand service (VoD) can be added when the subscriber pays an additional fee. then a separate movie or broadcast.
To implement these functions, a billing intermediary is used, which solves the following tasks:
Based on the above algorithms, one of the main problems immediately visible when launching Triple Play packages is correct management of subscriber balances. So, the operator needs to decide whether all the services will be blocked when the money is exhausted, or only those for which there is not enough money? Blocking all services at the same time requires an appropriate contract with the subscriber, since, according to Russian legislation, telephony, television and Internet access are considered as independent services with different rules for their provision (310th, 785th and 575th rules, respectively). Will the billing cycle be monthly or daily? If it is monthly, then the operator can correctly process all deductions within the subscriber account, but the risk of going into minus increases; and with daily write-off, all subscribers will eventually “disperse” by their numbers at the beginning of the billing month, which increases the requirements for the power and complexity of the operator billing system by an order of magnitude. You also need to provide for the conditions - in what order the funds from the subscriber’s balance are debited for services (or not charged at all until they are enough to pay all three services at once).
The 3P concept assumes that new services will be available to subscribers in a single environment. This is true, but many of them are either not needed or not familiar to users - for example, there is little point in taking a phone call on the TV screen while watching IP TV. The absolute majority of users do not tire at all to pick up the phone separately from the TV.
At the same time, there are services that are beginning to enter the user turnaround - video calls, instant messaging (sending messages) and chat. In a normal 3P environment, the operator is already highly desirable to support these services. And here a new problem arises - services are needed, and no one will pay for them, since There is a huge amount of free alternatives. Therefore, it is important for an operator when calculating a business case for 3P services to take into account such non-refundable costs.
Creating 3P proposals, even without taking into account technical problems (and there are also plenty of them) is a non-trivial task for the operator. And here statistics helps: the frequency of calls and their duration are analyzed, the amount of write-off for television and the frequency of VoD use are analyzed, typical user balances are analyzed when using the Internet access service and the rate of write-off on them. The ideal cannot be achieved here, but it is possible to choose the parameters of 3P-offers in such a way as to maximize user satisfaction and reduce the number of critical states that users can get into in the complex process of interaction of all 3P-systems.
Another significant problem is the implementation of a password protection system for services with 3P offers. The fact is that hacking an inernet account currently does not give a hacker anything - with an unlimited Internet, the subscriber loses nothing when an unauthorized person uses his account by an attacker - just more traffic is displayed on his account and that's it. Maximum - Froder will be able to order some additional services provided by the operator, for example, an antivirus license.
In the case of integration with the password of the IPTV password system, an attacker will be able to download films for the amount of the balance that relates to average risks. The fact is that he will not be able to capitalize the subscriber’s money himself - such IP TV films cannot be sold. But he will damage the operator, because if the hacking is proven, the operator returns the money to the client (although this is not the operator’s responsibility, but only his work to increase loyalty), but the operator himself will have to pay for these films to the right holder.
But unification with the general password of the telephony service will lead to a real capitalization of the account hacking - the attacker can sell this traffic, i.e. due to the subscriber’s balance, the connections of VoIP operators working in accordance with this scheme will be paid.
To prevent such situations, operators can firstly enter different passwords for all three services (which, however, reduces the usability of the 3P service package), and secondly, increase the overall quality of password protection for all three services, especially Internet access services.
Triple Play also creates another difficulty when organizing a customer support service (from the point of view of services for the mass market). The implementation of the concept involves the allocation of a single number to receive all incoming calls from subscribers, but the presence of three different technical and billing subsystems requires the creation of various groups of qualified engineers to resolve issues separately on the Internet, separately on television and telephony.
A possible solution to this problem is to create different groups of the 2nd support line, which is located behind the common 1st support line, as in the picture:
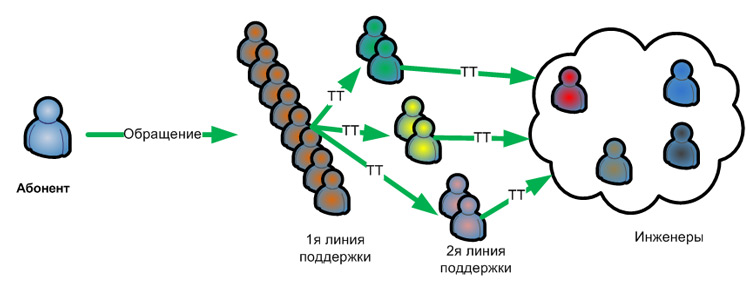
Multi-level customer support service for triple play subscribers
In this case, the 1st line of support solves the most popular questions of subscribers: financial blocking when reaching a zero balance, informs subscribers about the write-offs, advises on general issues of connection-disconnection of services. In the case of a specialized question on, for example, IP TV inoperability, the 1st line operator sends a call to the 2nd support line (opens Trouble Ticket), where the IP TV group technician will be able to answer the call competently. If he cannot solve the problem, the technician discovers the incident, where engineers are already attracted from the general pool of the operator’s technical block, where the engineers have specific systems and technologies for services.
- Telephone service;
- Internet access;
- Television
Technologically, all three basic services “live” on different platforms, but in the same environment, so there are many difficulties with billing, working with SORM, blocking services with zero balance (while maintaining the possibility of an emergency call), technical support and anti-fraud.

Triple Play services and their IT systems
Platforms:
- Telephony - on telephone switches (Private branch exchange - abbreviated to PBX) or VoIP-platforms (sometimes called IP Multimedia Subsystem - IMS);
- Internet access — for example, on Broadband Remote Access Servers (BRAS or BBRAS);
- Television Includes the head station and TV content distribution system. In the case of cable TV, content is distributed on the physical layer (transmitters), and in the case of IP television, the IP TV control platform is used.
')
The essential feature of the implementation of the 3P concept is a certain unified environment of the operator, on the basis of which all three services are built. The picture above shows the most widely used to date implementation of such services: the operator creates a broadband access network on the basis of the fiber-optic network and subnets are created on its base to provide telephony and television services.
Actual implementation
Historically, the cable television networks and the ADSL network were the first to create 3P environments. And there, and there used analog frequency division for voice, Internet connections and television. Now these technologies make up the bulk of all 3P connections on the planet.
But such solutions are actively being supplanted by optics-based connections. The fiber-optic network used for 3P services in the Russian realities can have both a ring and a star-shaped structure. Almost all operators use one of the FTTx technologies (Fiber to the X - optics to point X):
- FTTH - Fiber To The Home (bringing fiber to the apartment);
- FTTB - Fiber To The Building (bringing the fiber to the building);
- FTTC - Fiber To The Curb (bringing the fiber to the cable cabinet);
- FTTCab - Fiber To The Cabinet (analog FTTC);
- FTTR - Fiber To The Remote (bringing the fiber to a remote module, hub);
- FTTP - Fiber To The Premises (bringing the fiber to the point of presence of the client);
- FTTO - Fiber To The Office (bringing fiber to the office);
- FTTOpt - Fiber To The Optimum (bring the fiber to the optimal point).
The main way to connect in the Russian Federation is now FTTB. A typical network usually has a ring structure in the city (to provide reservation for highways) and take-out into quarters, which are reserved by a ring only in the case of a very large number of houses / apartments.
Traffic balancing, of course, is applied across the city - at the level of aggregation nodes, appropriate solutions are used to balance the traffic between the main links. Traffic balancing between quarters or even houses is also used, but usually the scheme is simpler - i.e. balancing between semirings is used and, of course, depends on the volume of subscribers on a specific object.
Further, almost all Russian operators have the same technical design: in the attics or in the basements there are metal cabinets containing Ethernet equipment for connecting end users. At the same time, the design by telephony may differ: it is possible to install VoIP gateways in common metal cabinets (and then the subscriber receives an analog RJ-11 telephone jack), or put the VoIP adapter / VoIP phone immediately in the subscriber’s apartment. The design of IP television is also the same - the set-top box (STB, Set Top Box) is always placed in the subscriber’s apartment, after the Internet router.
Among the most significant organizational and technological problems in this part it is necessary to note the need to configure individual subnets:
- For telephony. It is necessary to play answering machines about various telephony events, it is necessary for emergency calls to work;
- For IP TV, a dedicated subnet is needed to display the required federal Russian 8 channels, even in the case of financial blocking of the subscriber (often associated with the cut-off of Internet services).
Telephony: emergency calls and communication with SORM
Let us describe separately the implementation of calls to emergency services (01, 02, 03, 04, 112 in certain regions). The scheme of implementation of IP-telephony with the requirements of the legislation assumes the presence of a certain switching node in each city providing the service. It is this node that is entrusted with the task of routing emergency calls to specific emergency numbers of each city. The picture 2 shows for comparison the passage of a green normal call (telephone signaling goes through the core of the system, the call is set by an border device) and a red emergency call (control is not used, the call is immediately forwarded to the public telephone network, PSTN).
Boundary devices in telephony are commonly called Session Border Controllers (SBC). Their functions are similar to firewalls in the Internet environment, plus a number of specific functions to ensure the normal operation of VoIP connections.

Differences between regular and emergency VoIP calls
Here we also note an interesting Russian peculiarity of the implementation of telephone connections within 3P: the duty of every Russian law-abiding operator to send all calls to SORM. And here a technological problem arises, because All multimedia platforms are configured to provide direct connectivity of all registered users among themselves. And we have two problems:
- First, there are two types of calls (calls with dialing, which are RF calls telephone calls, because with numbering, and calls over the broadband network, which under RF legislation cannot have PSTN numbering);
- And, secondly, different cities with different units of the FSB, which control only their regional numbering.
To solve these problems, again, SBC are used, to which the FSB consoles are connected (well, or SBC are connected to local telephone switches). All calls with SBC numbers are output to such consoles. This solves the problem of telephone SORM. And all calls with logins, nicknames, etc. (i.e., calls over the broadband access network, including video calls) are output to the telematic SORM, which is used to monitor Internet connections.
Bandwidth requirements
The bandwidth requirements for traffic for services are different. Telephony is a low bandwidth service. The following voice coding algorithms are mainly used: G.711 A-law / G.711 u-law with a bandwidth (bit rate) of 64 kbit / s, G.729 variants with a band of 8 kbit / s, and a GSM codec with a bitrate of 13 kbit / s with. Taking into account the total volume of IP packet headers, we get the necessary bandwidth from 30 to 90 kbps.
IP television requires significantly more bandwidth (for example, MPEG2 / MPEG4 codecs are often used): so, ordinary SD TV channels require from 2 to 4 Mbps, and high-quality HD channels from 8 to 12 Mbps. It is clear that for such containers smart control of multicast television traffic is required: each channel is fed to the site and / or residential quarter only once, regardless of the number of subscribers watching. It helps statistics - if subscribers in one quarter include all non-overlapping channels, then the operator, providing 100-120 normal channels and 5-20 channels of HD network in this area will fail. But this is not how it happens in life - the distribution of “viewing” usually allows placing requirements on IP TV in the 1-2 Gbit / s band by district / quarter.
Separation by type of traffic to ensure the quality of work of all three services is usually used in the segment of corporate customers and is not used in services for individuals. This is due to the following factors, since residential buildings are quite predictable in terms of consumption.
Problems with Triple Play Billing Services
Depending on which service is more important for the operator, a billing master system is chosen, let's say. For example, account management is organized in a system that serves Internet access. Accordingly, the other two systems (telephony and television billing) occupy a subordinate position and must be tailored to the requirements and features of the master system. These systems are implemented in the form of various modules of one system or it is generally systems of one manufacturer, does not matter, and historically, often (in Russian realities), these are different systems from different IT companies.
The work of the master billing for tariffing Internet access
Let's take a schematic look at the pricing of Internet access on the example of an unlimited data plan, since in Russia, subscribers using limit tariff plans (by megabyte), there are no more than 5%. Two main algorithms are applied: the amount per month is written off either immediately on day X (and the subscriber's account decreases in steps), or in equal shares every day (and the subscriber's account decreases smoothly, but constantly). Below it is shown how the master billing stops the subscriber’s access to the Internet when a zero account balance is reached or if it goes to minus.

Internet subscriber account monitoring
Job phone billing
The basis of telephone billing is the tariff tables in which all directions of possible sending of voice traffic and their cost are clogged. When a subscriber makes a call in any direction, the system analyzes the telephone prefix (country code, city code) and debits the funds, according to the tariff tables. At the same time, the call authorization algorithm, even in the prepaid 3P version, can be prepaid and postpaid (this is due to the implementation features of various billing systems and telephone platforms).

Postpaid phone call authorization
Below is a schematic diagram of the call authorization script in the case of a post-paging telephony setup option. In this case, the subscriber makes a call, the IMS platform checks that the subscriber is not blocked and passes the call to the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or to the VoIP network. During the call (and after it ends), the IMS platform generates CDR files (Call Detail Recording) containing all the information about the call of the subscriber. Telephone billing processes the data CDR files, displaying this information first on its internal accounts (minus the customer’s account on the results of incoming CDRs), and then on the subscriber’s account in master billing. You can reduce the subscriber's account in the master billing simultaneously with a decrease in telephone billing, but there are already performance issues in the interaction of systems, you need to find a balance between the number of subscribers served and the time intervals in the described chains.

Pre-login phone call authorization
Here you can see the diagram of the call authorization script in the case of a prepaid telephony configuration option. In this case, the subscriber wants to make a call, the IMS platform contacts the authorization server (RADIUS or DIAMETER protocol), and the authorization server refers to phone billing. Telephone billing informs the authorization server that the subscriber is not blocked and reports the limit of possible minutes for the destination selected by the subscriber. That allows the IMS platform to skip a call to the public switched telephone network (PSTN) network or to the VoIP network.
At the same time, the telephone billing blocks a certain amount on the client’s account to pay for the call, which is adjusted (increased or decreased) as a result of the end of the call. Further, similar to postpaid billing, there is an adjustment on the subscriber’s account in the master billing. It is important to note here that in both scenarios the subscriber may go into a minus, only with the pre-scheme it will be less.
Television billing job
Ideologically, television billing is not different from billing other television services. In the case of cable TV, billing is quite simple - it is just writing off fixed amounts for certain packages of TV programs, and in the case of IP TV, the Video On Demand service (VoD) can be added when the subscriber pays an additional fee. then a separate movie or broadcast.
To implement these functions, a billing intermediary is used, which solves the following tasks:
- Blocks subscribers on the TV platform when they are blocked in master billing;
- Directs tasks to master billing for debiting funds when using VoD service.
Based on the above algorithms, one of the main problems immediately visible when launching Triple Play packages is correct management of subscriber balances. So, the operator needs to decide whether all the services will be blocked when the money is exhausted, or only those for which there is not enough money? Blocking all services at the same time requires an appropriate contract with the subscriber, since, according to Russian legislation, telephony, television and Internet access are considered as independent services with different rules for their provision (310th, 785th and 575th rules, respectively). Will the billing cycle be monthly or daily? If it is monthly, then the operator can correctly process all deductions within the subscriber account, but the risk of going into minus increases; and with daily write-off, all subscribers will eventually “disperse” by their numbers at the beginning of the billing month, which increases the requirements for the power and complexity of the operator billing system by an order of magnitude. You also need to provide for the conditions - in what order the funds from the subscriber’s balance are debited for services (or not charged at all until they are enough to pay all three services at once).
New services
The 3P concept assumes that new services will be available to subscribers in a single environment. This is true, but many of them are either not needed or not familiar to users - for example, there is little point in taking a phone call on the TV screen while watching IP TV. The absolute majority of users do not tire at all to pick up the phone separately from the TV.
At the same time, there are services that are beginning to enter the user turnaround - video calls, instant messaging (sending messages) and chat. In a normal 3P environment, the operator is already highly desirable to support these services. And here a new problem arises - services are needed, and no one will pay for them, since There is a huge amount of free alternatives. Therefore, it is important for an operator when calculating a business case for 3P services to take into account such non-refundable costs.
Creating 3P proposals, even without taking into account technical problems (and there are also plenty of them) is a non-trivial task for the operator. And here statistics helps: the frequency of calls and their duration are analyzed, the amount of write-off for television and the frequency of VoD use are analyzed, typical user balances are analyzed when using the Internet access service and the rate of write-off on them. The ideal cannot be achieved here, but it is possible to choose the parameters of 3P-offers in such a way as to maximize user satisfaction and reduce the number of critical states that users can get into in the complex process of interaction of all 3P-systems.
Frode
Another significant problem is the implementation of a password protection system for services with 3P offers. The fact is that hacking an inernet account currently does not give a hacker anything - with an unlimited Internet, the subscriber loses nothing when an unauthorized person uses his account by an attacker - just more traffic is displayed on his account and that's it. Maximum - Froder will be able to order some additional services provided by the operator, for example, an antivirus license.
In the case of integration with the password of the IPTV password system, an attacker will be able to download films for the amount of the balance that relates to average risks. The fact is that he will not be able to capitalize the subscriber’s money himself - such IP TV films cannot be sold. But he will damage the operator, because if the hacking is proven, the operator returns the money to the client (although this is not the operator’s responsibility, but only his work to increase loyalty), but the operator himself will have to pay for these films to the right holder.
But unification with the general password of the telephony service will lead to a real capitalization of the account hacking - the attacker can sell this traffic, i.e. due to the subscriber’s balance, the connections of VoIP operators working in accordance with this scheme will be paid.
To prevent such situations, operators can firstly enter different passwords for all three services (which, however, reduces the usability of the 3P service package), and secondly, increase the overall quality of password protection for all three services, especially Internet access services.
Users support
Triple Play also creates another difficulty when organizing a customer support service (from the point of view of services for the mass market). The implementation of the concept involves the allocation of a single number to receive all incoming calls from subscribers, but the presence of three different technical and billing subsystems requires the creation of various groups of qualified engineers to resolve issues separately on the Internet, separately on television and telephony.
A possible solution to this problem is to create different groups of the 2nd support line, which is located behind the common 1st support line, as in the picture:

Multi-level customer support service for triple play subscribers
In this case, the 1st line of support solves the most popular questions of subscribers: financial blocking when reaching a zero balance, informs subscribers about the write-offs, advises on general issues of connection-disconnection of services. In the case of a specialized question on, for example, IP TV inoperability, the 1st line operator sends a call to the 2nd support line (opens Trouble Ticket), where the IP TV group technician will be able to answer the call competently. If he cannot solve the problem, the technician discovers the incident, where engineers are already attracted from the general pool of the operator’s technical block, where the engineers have specific systems and technologies for services.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/145424/
All Articles