3D printing: nylon, ice, chocolate and others

Chocolate Bunny printed by RichRap universal extruder.
Currently, PLA and ABS plastics remain the most popular materials for amateur 3D printing. However, other materials are not ignored.
Nylon
A user with instructables.com taulman working on a universal machine that can be easily converted between CNC and a 3D printer, experimented with Nylon 6.6. Since nylon is resistant to high temperatures and has a low coefficient of friction, he has unpacked some of the parts for his apparatus from nylon.
The difference between printing ABS and nylon is small, but still there are some features:
- requires a higher temperature hot end - about 320ºC
- ventilation with air exhaust outside is required, since molten nylon emit toxic components in small quantities
- nylon is very slippery, so it is desirable that the extruder that feeds the material has spikes
- nylon easily absorbs water and other liquids, so keep it in a dry place.
- nylon does not stick to anything when it is cold, and easily sticks to everything at the right temperature.
- cools slower than ABS
- more fluid, pulling back material does not work well with nylon
- to the cold nylon only molten nylon sticks, therefore, if the part consists of several parts, then it is necessary to consider a mechanical connection
Despite all these features, you can successfully print nylon parts. Details are not so rigid and you can make the hinges slip.
')
Reference: instructions for creating a universal CNC machine - a 3D printer including hot end fabrication for nylon printing.
Clear acrylic

The same guy tried to print transparent acrylic. For this, I developed a special, more complex head than for printing with nylon. Acryl requires a higher temperature than ABS. The source material contains air bubbles, which is unacceptable for printing, as there will be not only visual distortions, but also tiny spots with sharp edges can form.
Due to the optical properties of acrylic, any inaccuracies when printing are visually enhanced. And these inaccuracies will be many, as the material cools very quickly, in comparison with other plastics. As he writes, any play in the bearings, belt slack, and even the crying of a neighbor's child modulate the shape of the stiffened material and change the reflections in the material. As you can see the result in the picture is not very impressive.
Link: part of the instructions, which says about acrylic.
Ice
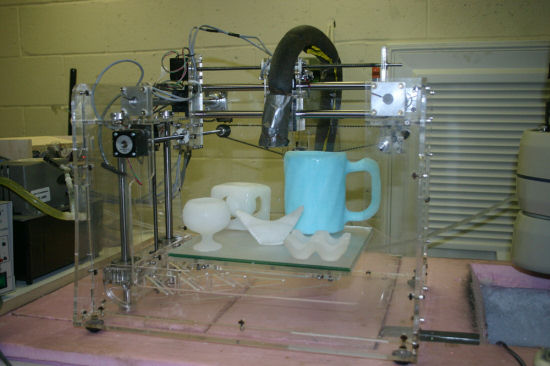
In 2006, a pair of Canadian professors received a research grant ($ 173k) for creating structures made of ice using a computer. For 3 years they have learned how to print small ice objects. The process takes place at -22ºC. The seal is water and methyl ether is heated to 20ºC. Methyl ether serves as a support and form. And since it thaws at a lower temperature than ice, it is easy to remove at the end of the process.


Figure in the process of printing. Yellow is methyl ester. Its use is due to the fact that water freezes more slowly, so you have to print a support structure of quick-freezing material. It took 132 hours to print this figure 30 cm high.
Chocolate and others

In February, Tom Salo published his chocolate extruder scheme . In it around the pump there is a shirt through which warm air is passed (about 30ºC) to maintain the temperature of the chocolate. In his experiments, Tom used the air from a hairdryer to dry his shoes. PLA is recommended for the extruder, as it is safer in terms of compatibility with food, plastic.
RichRap extruder
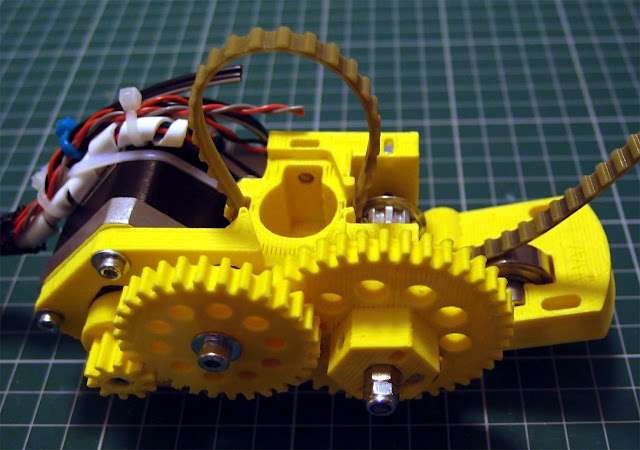
There is also a universal extruder created by RichRap - an engineer from the UK. The extruder allows you to print any paste, not just chocolate, which can be charged into a standard syringe. Only there is no heating, so the time for printing with melted chocolate is very limited.
Printing porcelain clay.
link: about the universal extruder in the author's blog .
Claystruder
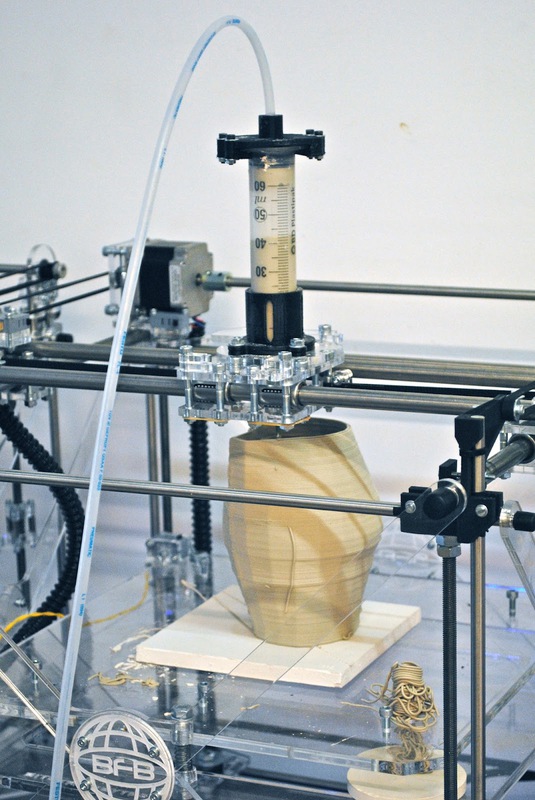

Another extruder for printing ceramics. Uses a compressor for his work.
link: unfoldfab blog
Filabot Reclaimer - recycling waste into consumables for a 3D printer
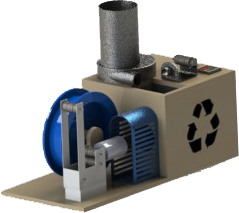
This machine allows you to recycle plastic waste and makes a consumable bar for a 3D printer.
This crusher inside the machine will not choke with an iron jar, let alone plastic trash.
Filabot Reclaimer will be able to recycle different types of plastic: HDPE (milk plastic bottles, caps, pipes), LDPE (plastic wrap, pallets), PET (bottles), ABS, NYLON, PLA. The project has successfully collected the necessary amount on the kickstarter . In addition, the competition successfully turned up with a prize fund of $ 40k, in which the device with minor modifications fit. Follow the news on the site and you can provide yourself with consumables yourself.
Reference: Filabot Reclaimer
My previous posts on the topic:
Low-cost 3D printers for printing photopolymers
A brief excursion into the methods of 3D printing
New budget 3D printer
The first 3D printing event in the Netherlands
Event on 3D printing (end)
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/145139/
All Articles