Automatic server cloning to virtual machines by cron
Formulation of the problem
Description of the problem
The work uses a large number of physical servers based on Debian GNU / Linux. Developers often need to be provided at the mercy of clones of these servers, each time it is inefficient to clone with their hands. Note: the specific distribution is not important for the described method, the method is very easily adapted to any distribution.
picture for beauty
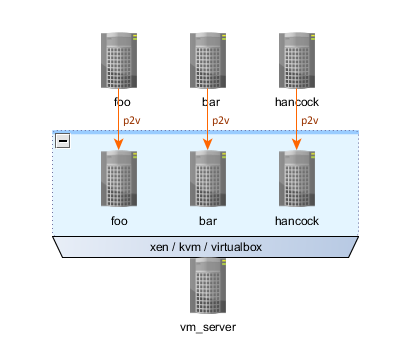
Task
Make an automatic cloning system of combat servers into virtual machines by crown.
')
What happened
virt_server> p2v.py foo full WORKING WITH SERVER: 'foo' READING CONFIG FOR 'foo' CHECKING LOCAL CONFIG CHECKING LOCAL CONFIG FOR 'foo' COMPLETED SUCCESSFULLY CHECKING REMOTE CONFIG CHECKING NODUMP FLAG: "lsattr -d /home/backupman/dumps | egrep '[\\w-]+d[\\w-]+[ ]/data/dumps'" CHECKING REMOTE DUMP: 'sudo /sbin/dump a0f /dev/null /dev/null' CHECKING IF WE ARE ABLE TO SSH TO: "ssh -T backupman@foo 'if [ -d /data/dumps ] ; then exit 0 ; else exit 1 ; fi'" CHECKING REMOTE CONFIG FOR 'foo' COMPLETED SUCCESSFULLY DUMPING FILESYSTEMS GETTING THE DUMPS STOPPING VM: foo2 MAKING FS TYPE: ext3 ON PARTITION: /dev/mapper/foo RESTORING DUMPS FOR: foo INSTALLING BOOTLOADER FOR: foo RESTORING CONFIG FOR: foo STARTING VM: /etc/xen/foo.xm How come
Battle Server Cloning Process
I consider the following to be the simplest and fastest way to clone a combat server without stopping it:
- Creation of its dump on the server itself using the
dumputility. Considerations are as follows:- Possible problems when dumping a live file system for a virtual machine are not terrible, this is not a backup. By experience, in practice, I have not yet encountered problems with beaten files.
- Server dump is done quickly, which is important
- Copy dump to server with virtual machines. I use
scp, because at our speeds, the network is still the bottleneck, and therefore the cost of encrypting files during transmission is not terrible - Expanding a dump to a pre-allocated LVM partition using the
restoreutility - Install the bootloader
- Copying configs relevant to a virtual machine (
/etc/network/interfaces, /etc/hostname, /etc/mailname, /etc/aliases, etc.) - Running a freshly prepared virtual machine.
The virtualization system used is completely unimportant, the only requirement for it is to be able to provide the virtual machine with an LVM partition as a virtual disk. I personally use XEN.
For clarity, I will give an example. Suppose that we have a virtual machine server
virt_server , as well as a physical server that needs to be cloned, server1 .- The XEN configuration for
server1clone lies onvirt_serverin/etc/xen/server1.xm - The LVM partition of the
server1virtual machine is:/dev/mapper/server1 - We will do
server1:/dumps/server1/inserver1:/dumps/server1/, and copy tovirt_server:/dumps/server1 server1'll keep thevirt_server:/dumps/server1/cfg/invirt_server:/dumps/server1/cfg/
In order for everything to work, on
server1 you need to add the user backupman , and allow him to sudo dump without a password. On virt_server you need to configure key authentication to backupman@server1 . On virt_server we will do everything from under root.With this configuration from the console, the cloning procedure looks like this:
root@virt_server> xm destroy server1 root@virt_server> ssh backupman@server1 backupman@server1$ sudo dump -a0f /dumps/server1.root / backupman@server1$ for i in var usr home ; do sudo dump a0f /dumps/server1.$i /$i ; done backupman@server1$ exit root@virt_server> scp backupman@server1:/dumps/server1.* /dumps/server1/ root@virt_server> mkfs.ext4 /dev/mapper/server1 root@virt_server> mount /dev/mapper/server1 /mnt/server1 root@virt_server> cd /mnt/server1 root@virt_server> restore -rf /dumps/server1.root root@virt_server> for i in var usr home ; do cd /mnt/$i && restore /dumps/server1.$i ; done root@virt_server> dd if=/usr/share/syslinux/mbr.bin of=/dev/mapper/server1 root@virt_server> extlinux --install /dev/mapper/server1 root@virt_server> scp -R /dumps/server1/cfg/* /mnt/server root@virt_server> xm start server1.xm Process automation
Now that the server’s cloning algorithm is clear, you can start writing a script. Work with the script will be as follows:
- The script config describes the cloning of each server.
- The script arguments specify the server name and the required action.
- Skrpit reads the config section named for the server, then does automatic cloning of the server and starting the virtual machine
- The script runs on the crown at night.
- ????
- Benefit!
Configure the virtual machine server and the cloned server
On the virtual machine server, do the following:
- Create a disk partition for the virtual machine
- Create a virtual machine configuration file
- Create a script configuration file
On the cloned server, do the following:
- Install
dumputility - Create
backupmanuser - Allow this user to run a dump by adding the following to / etc / sudoers:
backupman ALL=NOPASSWD: /sbin/dump - Create a dump directory
- Make
chattr +ddirectory on this directory so that the dumps are not dumped - Allow ssh from the north of virtual machines to the cloned server by keys
Script config
The config in the standard .ini format is placed in the directory with the script. It looks like this:
[server1] vm_config = /etc/xen/server1.xm vm_name = server1 ssh = backupman@server1.site scp = backupman@server1.site dumps_list = /,/var,/usr,/home remote_dumps_dir = /home/bakupman/dumps local_dumps_dir = /dumps/server1 mount_dir = /mnt/server1 partition = /dev/mapper/server1 fs = ext3 You should give a small explanation of the parameters
ssh and scp . These parameters define the format of the ssh and scp call, respectively, and both are needed because the ssh port will get the -p key, and the scp key will have the -P key.Script itself
I don’t see the point of bringing the script in full, because I posted it on github, so I will only describe the work of the script as a whole.
The script takes as input two parameters, namely the name of the server, which is the name of a section in the configuration file, and the required action.
Here is the main function that allows you to specify which actions we want to take. You can check the configuration, make a full clone, make server dumps, or deploy existing dumps.
def main(): """Main function, calls all other ones""" if len(sys.argv) < 3: sys.exit('Usage: %s <servername> <action> (check|full|dump|get|restore)' % sys.argv[0]) server = sys.argv[1] action = sys.argv[2] print "\nWORKING WITH SERVER: %r\n" % server if action == "check": try: conf=read_config(server) check_config_local(conf) check_config_remote(conf except Exception, e: sys.exit("\nERROR: %r\n" % e) elif action == "full": try: conf=read_config(server) check_config_local(conf) check_config_remote(conf) stop_vm(conf) dump_physical(conf) get_dumps(conf) restore_vm(conf) install_bootloader(conf) restore_config(conf) start_vm(conf) except Exception, e: cleanup(conf) sys.exit("\nERROR: %r\n" % e) <...> All script work is structured in such a way that if some action cannot be performed, an exception is thrown and the script ends with an error message.
The configuration specified in the configuration file is checked, and if something is wrong, the script ends. If everything is in order, then skrpit simply executes all those commands that can be entered from the console, checking the status of their completion.
The most "difficult" part of the script are checks. I would like to draw attention to this fragment:
def check_config_local(conf): """Checks config by trying to ssh, checking existence of local and remote folders, destination partition, mount point, and remote dump utility""" print "\nCHECKING LOCAL CONFIG\n" # check for ensuring we won't delete accidentaly specified host os parittion if conf['partition'] == "/dev/sda" or conf['partition'] == "/dev/sda1" or \ conf['partition'] == "/dev/sda2" or conf['partition'] == "/dev/sda3" or \ conf['partition'] == "/dev/sda4" or conf['partition'] == "/dev/sda5": raise Exception, "DON'T KILL THE SERVER! %S IS A SYSTEM PARTITION!!" % conf['partition'] I have an operating system on the virtual machine server installed on these partitions, LVM was made for the virtual machines themselves. Because When a virtual machine is deployed on a partition destined for it, a new file system is created, then in order to protect against the accidental destruction of the virtual machine server, enter your system partitions here.
github
That's it, you can get the script here: github.com/sistemshik/p2v
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/144655/
All Articles