Unity3D 3.x Introduction to Surface Shaders
Sooner or later, the capabilities of standard shaders will be missed, and then Surface Shaders will come to your aid. In fact, this is an add-on for ordinary shaders, which allows you to write more understandable and compact code.
In the Surface Shader, you can control the lighting, shadows, rendering paths using the same Cg / HLSL code.
Here is the full version of the shader, where I will take the pieces for consideration
The first line is the shader path.
In this way it will be available in the inspector.
Next come the Properties , these are the parameters that you can set in the inspector. Each parameter has a variable name, description, type and default value.
')
Data types:
name ("display name", Range (min, max)) = number
The range of values of type float from min to max, in the inspector will be displayed as a slider
name ("display name", Color) = (number, number, number, number)
The value of the color type, the default value should be an RGBA float from 0 to 1. In the inspector it will be displayed as a color picker
name ("display name", 2D) = "def_col" {options}
Describes the texture. In the inspector will be as a texture
name ("display name", Rect) = "def_col" {options}
Describes a texture with a size not 2 n . In the inspector will be as a texture
name ("display name", Cube) = "def_col" {options}
Describes the cubemap texture. In the inspector will be as a texture
name ("display name", Float) = number
Just float, in the inspector will be as an input field with a number
name ("display name", Vector) = (number, number, number, number)
Describes a vector
The default value (def_col) for the Rect, 2D and Cubemap types can be empty, or: “white”, “black”, “gray”, “bump”. It indicates what color the pixels will be by default inside the texture.
Here is what we will see as a result in the inspector:
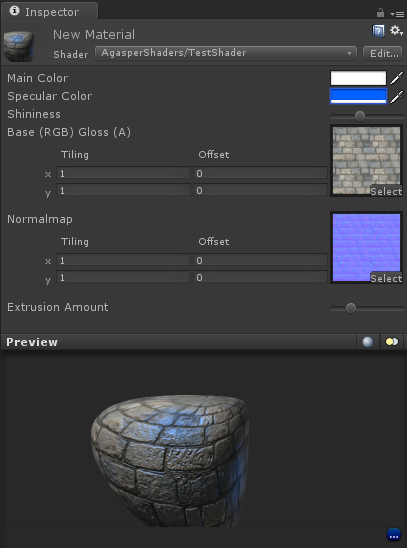
Next is SubShader. When a unit tries to draw an object, it searches for the first suitable SubShader in the list, this is a shader. If no SubShader is found, an error will occur. For example, this may be necessary in a situation when you want to realize the capabilities of Shader Model 3.0, but leave the opportunity to play to people with the old video card.
Inside the Surface SubShader are the SubShader tags and the code itself.
The RenderType = "Opaque" tag means that we are going to render an opaque object. Read more about tags here and here.
In the SurfaceShader code, you can describe three functions (in principle, more is possible, but rarely needed):
For example, let's write a Diffuse Bumped Specular shader with morphing. I will not describe the lighting calculation function in this article; we will assemble the standard BlinnPhong.
CGPROGRAM is a directive that declares what we write in the Cg language (terminated by the ENDCG directive).
The second line we declare that:
Now we declare the variables that will be used in the code:
Unity will take care that the data from the shader parameters declared above are in these variables. It is important to name them as well as in the shader parameters.
And here is the procedure for the vertex part of our shader. For example, take the coordinates of the current vertex and add to them the normal multiplied by the current coordinates and the coefficient of the shader parameters. Of course, some kind of crap will turn out, but for example it is quite enough. Slider Amount you can adjust the degree of distortion of the object.
Example:

The official documentation has an example of a swollen soldier . They just picked up all the vertices along the normal:

What else is inside:
Here you can read the full article on vertex shaders.
In the Input structure, you can ask the shader for additional variables that you will need for calculations in the surface procedure. We asked for the UV coordinates of both textures. The variable should be called uv_ Texture Name for the first UV coordinates and uv2_ Texture Name for the second, respectively.
A complete list of what you can specify there is here .
Here is the procedure for drawing the surface:
The Input structure is passed to it, and inside it is necessary to fill the SurfaceOutput structure, which has the following form:
We finish the shader with a string
This means that if for some reason the shader does not work on the client machine, then you need to roll back to the Specular shader.
The full version of the shader from the example
Materials used to write the article:
http://unity3d.com/support/documentation/Components/SL-SurfaceShaders
http://unity3d.com/support/documentation/Components/SL-SurfaceShaderExamples.html
http://unity3d.com/support/documentation/Components/SL-SubShader
http://unity3d.com/support/documentation/Components/SL-SubshaderTags
http://unity3d.com/support/documentation/Components/SL-ShaderReplacement.html
In the Surface Shader, you can control the lighting, shadows, rendering paths using the same Cg / HLSL code.
Creating a shader from scratch
Here is the full version of the shader, where I will take the pieces for consideration
The first line is the shader path.
Shader "AgasperShaders/TestShader" { In this way it will be available in the inspector.
Properties
Next come the Properties , these are the parameters that you can set in the inspector. Each parameter has a variable name, description, type and default value.
')
Properties { _Color ("Main Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1) _SpecColor ("Specular Color", Color) = (0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 1) _Shininess ("Shininess", Range (0.03, 1)) = 0.078125 _MainTex ("Base (RGB) Gloss (A)", 2D) = "white" {} _BumpMap ("Normalmap", 2D) = "bump" {} _Amount ("Extrusion Amount", Range(-1,1)) = 0.5 } Data types:
name ("display name", Range (min, max)) = number
The range of values of type float from min to max, in the inspector will be displayed as a slider
name ("display name", Color) = (number, number, number, number)
The value of the color type, the default value should be an RGBA float from 0 to 1. In the inspector it will be displayed as a color picker
name ("display name", 2D) = "def_col" {options}
Describes the texture. In the inspector will be as a texture
name ("display name", Rect) = "def_col" {options}
Describes a texture with a size not 2 n . In the inspector will be as a texture
name ("display name", Cube) = "def_col" {options}
Describes the cubemap texture. In the inspector will be as a texture
name ("display name", Float) = number
Just float, in the inspector will be as an input field with a number
name ("display name", Vector) = (number, number, number, number)
Describes a vector
The default value (def_col) for the Rect, 2D and Cubemap types can be empty, or: “white”, “black”, “gray”, “bump”. It indicates what color the pixels will be by default inside the texture.
Here is what we will see as a result in the inspector:

Subshaders
Next is SubShader. When a unit tries to draw an object, it searches for the first suitable SubShader in the list, this is a shader. If no SubShader is found, an error will occur. For example, this may be necessary in a situation when you want to realize the capabilities of Shader Model 3.0, but leave the opportunity to play to people with the old video card.
Inside the Surface SubShader are the SubShader tags and the code itself.
The RenderType = "Opaque" tag means that we are going to render an opaque object. Read more about tags here and here.
SubShader { Tags { "RenderType" = "Opaque" } //code } Actually the code itself
In the SurfaceShader code, you can describe three functions (in principle, more is possible, but rarely needed):
- The function of calculating the vertices
- Surface drawing function
- Lighting calculation function
For example, let's write a Diffuse Bumped Specular shader with morphing. I will not describe the lighting calculation function in this article; we will assemble the standard BlinnPhong.
CGPROGRAM #pragma surface surf BlinnPhong vertex:vert CGPROGRAM is a directive that declares what we write in the Cg language (terminated by the ENDCG directive).
The second line we declare that:
- the surface drawing procedure is called surf
- BlinnPhong light will be used in the shader (it is also Lambert, Unlit, or its own procedure)
- the procedure for changing vertices is called vert
Now we declare the variables that will be used in the code:
sampler2D _MainTex; sampler2D _BumpMap; fixed4 _Color; half _Shininess; float _Amount; Unity will take care that the data from the shader parameters declared above are in these variables. It is important to name them as well as in the shader parameters.
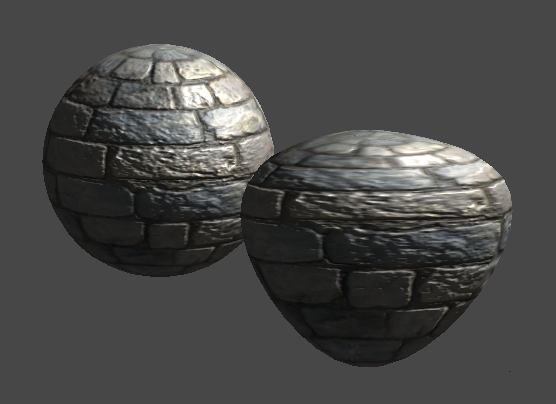
void vert (inout appdata_full v) { v.vertex.xyz += v.normal * v.vertex.xyz * _Amount ; } And here is the procedure for the vertex part of our shader. For example, take the coordinates of the current vertex and add to them the normal multiplied by the current coordinates and the coefficient of the shader parameters. Of course, some kind of crap will turn out, but for example it is quite enough. Slider Amount you can adjust the degree of distortion of the object.
Example:

The official documentation has an example of a swollen soldier . They just picked up all the vertices along the normal:
v.vertex.xyz += v.normal * _Amount ; 
What else is inside:
- float4 vertex - coordinates of the current vertex
- float3 normal - normal to the surface at the current point
- float4 texcoord - UV coordinates of the first texture
- float4 texcoord1 - UV coordinates of the second texture
- float4 tangent - tangent vector
- float4 color - vertex color
Here you can read the full article on vertex shaders.
struct Input { float2 uv_MainTex; float2 uv_BumpMap; }; In the Input structure, you can ask the shader for additional variables that you will need for calculations in the surface procedure. We asked for the UV coordinates of both textures. The variable should be called uv_ Texture Name for the first UV coordinates and uv2_ Texture Name for the second, respectively.
A complete list of what you can specify there is here .
Here is the procedure for drawing the surface:
void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceOutput o) { // UV . fixed4 tex = tex2D(_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex); // o.Albedo = tex.rgb * _Color.rgb; // o.Gloss = tex.rgb; // o.Specular = _Shininess; // o.Normal = UnpackNormal(tex2D(_BumpMap, IN.uv_BumpMap)); } The Input structure is passed to it, and inside it is necessary to fill the SurfaceOutput structure, which has the following form:
struct SurfaceOutput { half3 Albedo; // () half3 Normal; // half3 Emission; // ( ) half Specular; //"" ( (dot(viewDir, Normal)) half Gloss; // half Alpha; // ( "RenderType" = "Opaque") }; We finish the shader with a string
FallBack "Specular" This means that if for some reason the shader does not work on the client machine, then you need to roll back to the Specular shader.
The full version of the shader from the example
Materials used to write the article:
http://unity3d.com/support/documentation/Components/SL-SurfaceShaders
http://unity3d.com/support/documentation/Components/SL-SurfaceShaderExamples.html
http://unity3d.com/support/documentation/Components/SL-SubShader
http://unity3d.com/support/documentation/Components/SL-SubshaderTags
http://unity3d.com/support/documentation/Components/SL-ShaderReplacement.html
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/144622/
All Articles