IPTV head station
Good day!
I want to tell you about the device IPTV headend on the example of our provider.
I hope that after reading the article you will have a good understanding of the work of the IPTV headend.

')
So, what we have:
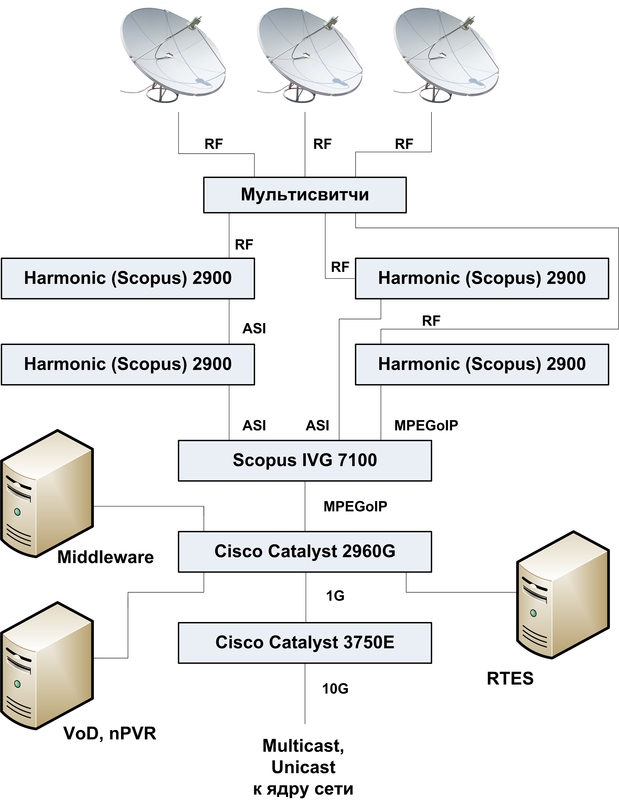

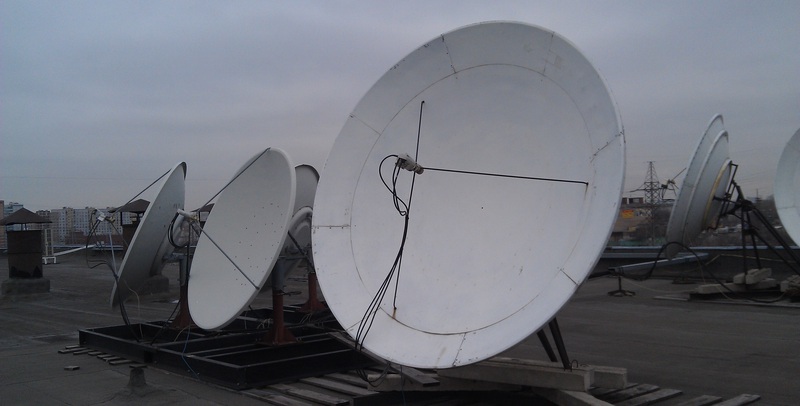
Well, everything is quite simple. Antennas are installed on the roof, tuned to the main satellites (Yamal, ABS, HotBird, Astra, W4 ... there are a total of 11). By all the rules, the system is grounded, securely bolted. From the roof go RF-cables to the hardware.

The cables from the roof are connected to the multiswitch inputs, the task of which is to switch (distribute) signals of different polarization from the antenna systems directly to the receivers.


We use professional receivers of the company Harmonic
Receivers are configured on the necessary transponders, decode the signal, if it is encrypted.
Most professional receivers work with the front end of DVB-S and can decode only 2 TV channels at a time.
If we take more than two encrypted TV channels from one transponder, then we connect receivers in a chain using ASI outputs / inputs. Usually, no more than 1-2 receivers are connected through the chain. Also, receivers filter out unnecessary TV channels to reduce the load on the video gateway.
Next, using ASI or IP (unicast), we send the filtered and decrypted stream to the video gateway.
The video gateway receives streams from receivers via ASI or IP (it has a total of 16 ASI ports). It converts the received streams into multicast and broadcasts it to the network.
The gateway has:
To release a stream, it is necessary to “cross” the service from the input port with the virtual IP port.
These are the flows that the gateway sees, for example, on the first ASI input:

For example, to put the Kinopokaz HD channel into the network, you need to create a virtual port with the specified IP address and port, and then “cross-link” the channel to the created virtual port.
As a result, we will see that a channel has appeared on the virtual IP output:

Well, the stream is already delivered to subscribers using the IGMP router. But not everything is so easy because the channels are encrypted.
Yes, Verimatrix.
Like the vast number of IPTV providers, we use this system. Paid, closed.
By the way, this system is approved by all the largest film studios in the world. Therefore, we have no problems in concluding contracts with copyright holders of video content.
Using the ordered servers, we encrypt the stream by specifying the IP address of the input stream and the IP address of the output stream in the web admin. Servers encrypt TV channels in realtime.

In total, we have 2 servers, one is engaged in nPVR, the other is VOD. They have powerful network storage, allowing you to give content to hundreds of users simultaneously. We use the platform - Espial MediaBase.
The first server records the TV programs selected by subscribers on the allowed TV channels. Therefore, the subscriber can press the pause button on his remote at any time, move to the kitchen and make popcorn, return to the TV and continue watching from the same place. Or program the recording of the program in VCR mode. And then watch it at a convenient time.
The second server contains a movie library for “video on demand”. Custom STBs display a video stream with a frequency of 25 Hz and an aspect ratio for a 16x9 picture, so all movies are converted to H.264 1080i / 50 Hz before being added to the video server. Also formed Dolby Digital 5.1 soundtrack.

We have the most loaded servers.
To ensure fault tolerance, the entire software and hardware platform, the system is built according to a cluster scheme. Two powerful Middleware servers work, load balancing is configured. Under the database we use a separate server MSSQL.
Middleware is an intermediate software connecting the interface of the subscriber STB with the rest of the complex.
In the base of Middleware tariff plans are formed.
All consoles are activated through the Middleware server to gain access to the encrypted content.
Middleware controls the purchase of movies.
TV program gives subscribers the same Middleware.
Reading tweets from the TV also allows Middleware!
News feeds, Yandex.Probki, the status of applications on the website Gosuslugi - also handles Middleware.


Traffic flow monitoring is handled by Bridgetech's VB220 .
The levels of satellite signals are also monitored using Zabbix, which takes data via SNMP from receivers.

If the channel stops being decoded, the SNMP receiver reports this to the NOC service, which in turn informs the administrator on duty.
In addition to hardware monitoring, on-duty operators regularly visually watch all TV channels, checking the quality of the image and sound.
Build everything into a logical chain:
Satellite antenna -> receiver -> video gateway -> encryption server -> provider’s IP network -> Subscriber’s Set-Top-Box -> TV.
And vice versa:
Subscriber -> Set-Top-Box -> Middleware + IGMP Query.
This concludes a brief description of the main components of the head station.
The article just returned from draft - removed it to correct inaccuracies and add real photos.
I want to tell you about the device IPTV headend on the example of our provider.
I hope that after reading the article you will have a good understanding of the work of the IPTV headend.

')
So, what we have:
- 7 satellite dishes on 11 satellites
- Multiswitches in the right amount
- ~ 80 satellite receivers
- Video Gateways (Streamers)
- Middleware Servers
- Video server (VOD, NPVR)
- Streaming server encryption
- Monitoring system

Roof

Well, everything is quite simple. Antennas are installed on the roof, tuned to the main satellites (Yamal, ABS, HotBird, Astra, W4 ... there are a total of 11). By all the rules, the system is grounded, securely bolted. From the roof go RF-cables to the hardware.
Server
Multiswitch

The cables from the roof are connected to the multiswitch inputs, the task of which is to switch (distribute) signals of different polarization from the antenna systems directly to the receivers.
Receivers


We use professional receivers of the company Harmonic
Receivers are configured on the necessary transponders, decode the signal, if it is encrypted.
Most professional receivers work with the front end of DVB-S and can decode only 2 TV channels at a time.
If we take more than two encrypted TV channels from one transponder, then we connect receivers in a chain using ASI outputs / inputs. Usually, no more than 1-2 receivers are connected through the chain. Also, receivers filter out unnecessary TV channels to reduce the load on the video gateway.
Video gateway
Next, using ASI or IP (unicast), we send the filtered and decrypted stream to the video gateway.
The video gateway receives streams from receivers via ASI or IP (it has a total of 16 ASI ports). It converts the received streams into multicast and broadcasts it to the network.
How the video gate works
The gateway has:
- physical ASI ports; it takes streams from them.
- physical Ethernet ports (for management, input streams, output streams).
- virtual IP ports (for streaming, for streaming)
To release a stream, it is necessary to “cross” the service from the input port with the virtual IP port.
These are the flows that the gateway sees, for example, on the first ASI input:

For example, to put the Kinopokaz HD channel into the network, you need to create a virtual port with the specified IP address and port, and then “cross-link” the channel to the created virtual port.
As a result, we will see that a channel has appeared on the virtual IP output:

Well, the stream is already delivered to subscribers using the IGMP router. But not everything is so easy because the channels are encrypted.
Encryption server
Yes, Verimatrix.
Like the vast number of IPTV providers, we use this system. Paid, closed.
By the way, this system is approved by all the largest film studios in the world. Therefore, we have no problems in concluding contracts with copyright holders of video content.
Using the ordered servers, we encrypt the stream by specifying the IP address of the input stream and the IP address of the output stream in the web admin. Servers encrypt TV channels in realtime.

Server video
In total, we have 2 servers, one is engaged in nPVR, the other is VOD. They have powerful network storage, allowing you to give content to hundreds of users simultaneously. We use the platform - Espial MediaBase.
The first server records the TV programs selected by subscribers on the allowed TV channels. Therefore, the subscriber can press the pause button on his remote at any time, move to the kitchen and make popcorn, return to the TV and continue watching from the same place. Or program the recording of the program in VCR mode. And then watch it at a convenient time.
The second server contains a movie library for “video on demand”. Custom STBs display a video stream with a frequency of 25 Hz and an aspect ratio for a 16x9 picture, so all movies are converted to H.264 1080i / 50 Hz before being added to the video server. Also formed Dolby Digital 5.1 soundtrack.
Middleware

We have the most loaded servers.
To ensure fault tolerance, the entire software and hardware platform, the system is built according to a cluster scheme. Two powerful Middleware servers work, load balancing is configured. Under the database we use a separate server MSSQL.
Middleware is an intermediate software connecting the interface of the subscriber STB with the rest of the complex.
In the base of Middleware tariff plans are formed.
All consoles are activated through the Middleware server to gain access to the encrypted content.
Middleware controls the purchase of movies.
TV program gives subscribers the same Middleware.
Reading tweets from the TV also allows Middleware!
News feeds, Yandex.Probki, the status of applications on the website Gosuslugi - also handles Middleware.

Monitoring

Traffic flow monitoring is handled by Bridgetech's VB220 .
The levels of satellite signals are also monitored using Zabbix, which takes data via SNMP from receivers.

If the channel stops being decoded, the SNMP receiver reports this to the NOC service, which in turn informs the administrator on duty.
In addition to hardware monitoring, on-duty operators regularly visually watch all TV channels, checking the quality of the image and sound.
Total
Build everything into a logical chain:
Satellite antenna -> receiver -> video gateway -> encryption server -> provider’s IP network -> Subscriber’s Set-Top-Box -> TV.
And vice versa:
Subscriber -> Set-Top-Box -> Middleware + IGMP Query.
This concludes a brief description of the main components of the head station.
The article just returned from draft - removed it to correct inaccuracies and add real photos.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/141694/
All Articles