(Not) safe surfing?
 Today, many popular browsers support auto-update, but a significant part of the plug-ins to them need to be updated independently. An impressive number of users do this extremely rarely, without thinking or knowing that in most cases not only browsers, but also plugins are attacked!
Today, many popular browsers support auto-update, but a significant part of the plug-ins to them need to be updated independently. An impressive number of users do this extremely rarely, without thinking or knowing that in most cases not only browsers, but also plugins are attacked!Under the cut, there is an interesting statistic of browsers and plugins security checks for potential vulnerabilities based on the results of the online service SurfPatrol in 2011. Data is provided on Runet.
Go
Check platforms: Windows, MacOS, Android, iOS.
')
Checked browsers: IE 6+, Safari 3+, Firefox 1+, Chrome (all versions), Opera 9.5+, Opera Mini, Android Browser, Mobile Safari, Opera Mobile.
SurfPatrol defines both the browser itself and a whole list of plugins, including: .Net Framework, Adobe Flash Player, Adobe Reader Plugin, Foxit Reader Plugin, Java Deployment Toolkit, Microsoft DirectX, Microsoft Office 2003, Microsoft Office 2007, Microsoft Office 2010, Microsoft Office Visio 2003 Viewer, Microsoft Silverlight, Microsoft XML Core Services 3.0, Microsoft XML Core Services 4.0, Microsoft XML Core Services 6.0, QuickTime Plugin, Real Player, SAP Component, Shockwave for Director, Sun Java, VideoLan VLC Media Player, Windows Media Player .
The scan component is considered vulnerable if an “unclosed” vulnerability is detected (a patch has not been installed or the update has not yet been released).
So, 89% of web surfers have at least one vulnerability in a browser-plugin bundle, while almost half of all checks revealed more than 3 vulnerabilities.
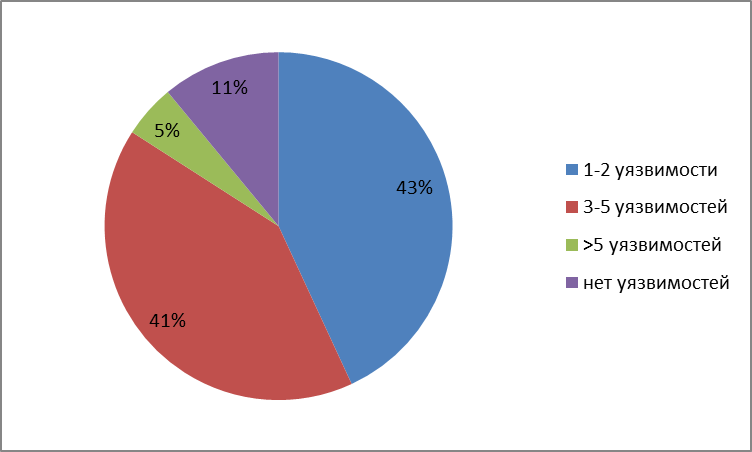
Most of the checks of devices running Android were performed for version 2.3 (62%), while vulnerabilities were found in 73% of checks in the most popular browser of this platform - Android Browser.
On the iOS platform, vulnerabilities were found in 39% of cases, the most popular version at that time, the fourth, was most often checked. MacOS was vulnerable in the overwhelming majority of inspections (about 91%). Check out Safari and Chrome browsers on MacOS v.10.7.2 from the general statistics - vulnerabilities were found in 70% of cases.
The largest number of checks occur on Windows - the most widespread platform. A certain optimism suggests that the percentage of checks with the found vulnerabilities for the latest at the time version of Windows 7 is insignificant, but less than in earlier versions of Windows.
At the same time, the combination of “browser + plugins” on the Windows platform turned out to be most vulnerable to Chrome and IE in 75% and 79% of checks, respectively.
But how “guilty” are the browsers themselves? In general, for all platforms vulnerabilities in browsers (excluding plug-ins) were found in the following percentage of checks: IE - 62%, Chrome - 30%, Firefox - 22%, Safari - 21%, Opera - 17%.
And the percentage of checks that resulted in the detection of vulnerabilities in a plugin (of the most common plug-ins) of the number of all plugin checks is shown in the graph:
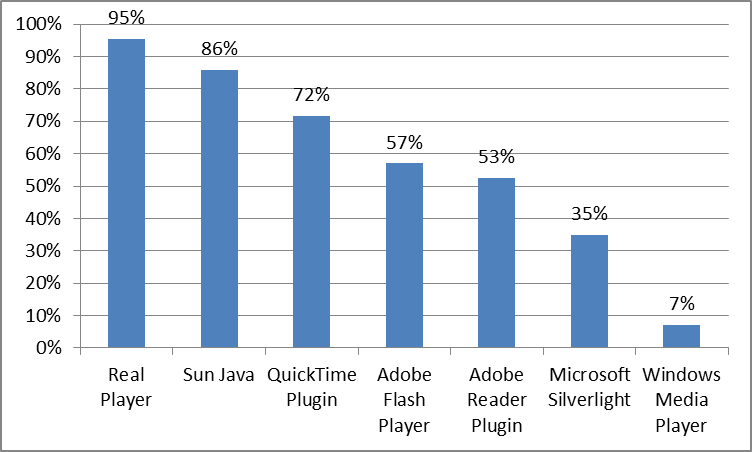
Draw conclusions
9 out of 10 Runet users are at risk of cyber attacks. Even with the latest version of the browser, the presence of a flaw in one of the plug-ins can negate all security efforts.
The reliability of web surfing can be enhanced not only by introducing a forced automatic update of browsers and plug-ins, but also through more active user education about threats, attacks and methods of protection, and all-in-one joint promotion of Internet hygiene.
By the way, you can check how safe your web surfing is today =)
If you have any questions, write! Be sure to answer.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/141520/
All Articles