Building a data center, part 3: serve chilled
After the topics about the construction of a new data center in Yaroslavl and the choice of the data center power supply system, there were still questions about the hardware and its choice. In this series - about why we chose Natural Free Cooling and how it works.
Likbez
Technique is heated. It’s just impossible to give up on this fact: the increased temperature is dangerous for iron, first of all, processors and hard drives, plus it causes a number of negative effects. Many manufacturers strictly indicate the temperature conditions in which the equipment must operate. Plus - in our data center there is no unification of equipment, so there may well be a situation when devices from different manufacturers are standing next to each other.
')
The cooling system is, first of all, expensive equipment and a lot of energy consumed. Secondly, the density of use of the premises depends on the choice of such a system: it is possible to fit more servers, rather than auxiliary units, into the useful volume.
In addition to the servers themselves, other parameters must be taken into account: the number of personnel in the premises, manufacturers' requirements for the hardware, lighting systems (and the frequency of their inclusion), as well as other things, such as the thickness of the walls and their materials. On the basis of such data, a calculation is made of the heat that needs to be removed. This calculation makes it possible to choose the desired cooling system. Returning to the previous series, we specifically chose a place for the data center in conditions where the climate as a whole is cool and stable, since the system should be calculated by peaks, not average values.
We continue the educational program: at first glance it may seem that ordinary office air conditioners can solve the problem. Yes, they are acceptable to humans, but the data center needs precise temperature and humidity control. The maximum rate of temperature change can be no more than 5 degrees per hour in the range of 18-27 degrees Celsius, and humidity in the range of 40-60% This is due to many factors, but the main one is to protect the equipment from overheating and its failure due to dew (if it is too wet and cold) or static discharge, if it is dry and hot.
A little more detail
In the server it is necessary to create precision climatic conditions, the main of which is the temperature of the cooled air at the server entrance, the temperature of the hot air at the entrance to the air conditioner (the difference between these parameters is called ΔT), and the humidity measured by the hygrometer.
- The temperature at the entrance to the server can be very low (+10 or +12 degrees Celsius), but this will require a very productive air conditioning system and the enormous energy costs of creating such a cold that will be incommensurable in cost with the planned benefits.
- The temperature at the entrance to the air conditioner can not be too high (above 30-32 degrees) due to the peculiarities of the internal units of air conditioners, otherwise they simply will not cool or even blow out.
- ΔT - a parameter characterizing the performance of the air conditioning system, should vary within 10-12 degrees. Those. if at the outlet of the air conditioner 16 degrees, then at the entrance to the air conditioner, after passing the air through the hot server, should be 26-28 degrees. It is clear that the air inside the server heats up much higher and in order to lower its temperature, it is necessary to dilute the hot air with cold air at the outlet of the server: this is the so-called mixing. The task is not to overheat the indoor unit of the air conditioner. In this operation, the SCR loses its efficiency and energy is wasted.
- The relative humidity in the room should not be too low (below 30%), because server boards begin to accumulate static charge, which can disable them. There is also specific equipment such as magnetic tapes (and immediately - no, we do not use tape drives): it dries and deteriorates. High humidity (over 70%) can lead to condensation and contact closure.
- It is important to follow the standards of the Uptime Institute, with its classification TIER: the system should operate continuously, taking into account the possible failure of any of the nodes.
Decision making
In developing the Technical Specifications for SCR, we were guided by the recommendations of special standards in the field of design and construction of data centers (TIA 942, ASHRAE, BICSI) and adopted the following parameters:
- Reliability of all system components not lower than TIER 3 according to the Uptime Institute classification;
- Reservation of all components N + 2, where N is the number of components required for the project;
- Mode of operation around the clock, 365 days a year;
- The temperature at the entrance to the rack from +18 to +27 degrees Celsius;
- Humidity 40% -60%;
- The system should function in normal (non-emergency) mode at an external temperature of -40 to +40 degrees Celsius;
- The average annual PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness) is not higher than 1.3, and this is one of the most important selection criteria.
When choosing a solution for the organization of SLE, we considered a variety of options, ranging from classic air conditioners on freon, to Kyoto futuristic wheels. However, while meeting all the required parameters, we needed a solution, the implementation of which, and more importantly, long-term operation, should be cheaper than any classical schemes used in the data center.
Choices
The classic system of precision air conditioning built on freon air conditioners DX
These systems operate on an approved type of freon that does not destroy the ozone layer. Freons are the substances formed on the basis of two gases - ethane and methane with the substitution of hydrogen atoms for chlorine and fluorine atoms (therefore they are also called chlorofluorocarbons). All refrigerants used in air conditioners are non-combustible and safe for humans and animals. However, it is believed that most of the chlorofluorocarbons destroy the ozone layer (there is no exact evidence, but effective refrigerants are banned just in case). One way or another, but European manufacturers, as well as manufacturers targeting the European market, were forced to look for a replacement for the “classic” R-22 freon, which is used in 90% of air conditioners. R-410A and R-407C refrigerants were chosen as replacements. The unit of danger for the ozone layer is the potential of frenon R-12, which still has a lot of refrigerators. The ozone-depleting potential of R-22 freon is 0.05, and the new R-410A and R-407C freons are zero.

Precision freon split air conditioner with outdoor unit DX
This is a kind of fridge. Server is the place where servers (products) are stored. The use of this technology implies a high cost of electricity. The minimum PUE that can be achieved, ceteris paribus, will not be more effective than the value 2.0. Those. in order to provide power for the 500 Kilowatt server, we need to bring 1000 Kilowatts to the server, so we spend 500 Kilowatts just to the wind.
Electricity is spent on the work of a large number of mechanical systems: a compressor, fans of the indoor unit, a humidifier pump, outdoor fans. Heat is removed due to the circulation of freon in a closed circuit. Hot freon is pumped by the compressor through the tubes to the radiator of the external unit, the fan cools the tubes and the cooled freon flows back to the internal unit, which is installed in the server room. The operation of this type of air conditioning does not depend on the season and works all the time in uneconomical mode.
This solution is applicable in rooms where there is no access to the chilled water system or where you cannot place the chiller. The oldest and least efficient technology.
Precision air conditioning system built on CW chillers (free cooling)
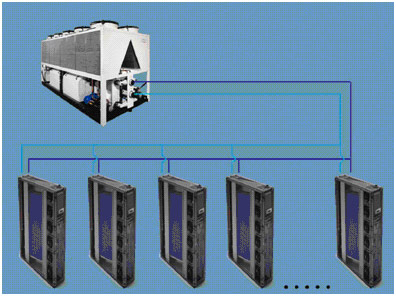
Precision air conditioner with water coolant (water, glycol), with external chiller and dry cooling tower
The system combines a dry cooling tower and chiller using the technology of Free-cooling (free cooling) running on chilled water. The solution is similar to the previous option - there is a coolant (water) that runs between the internal and external unit. Energy is spent on the rotation of the external and internal fans, as well as the pump group, which drives this same water. However, the water supply is foreseen by a large volume (the so-called cold accumulator); therefore, during the cold and relatively cold season (up to +10 degrees), the system spends the minimum amount of energy only on the distillation of water, which is cooled due to contact with the surrounding air.
This solution allows you to optimize the energy consumption of the data center engineering infrastructure , as well as to ensure the modularity and flexibility of the entire SCR system. The use of this system allows to reduce the PUE value to 1.7, however, the initial investment is much higher than in the case of the use of DX-systems.
Direct air cooling. Direct Free Cooling (DFC)
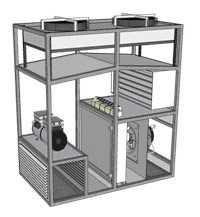
Direct Air Cooled (DFC) System Block Diagram
The cooling system using external atmospheric air, which directly enters the server from the street. The system is organized as follows: the fans take air from the street, drive it through the air ducts through the filters, and the filtration system must be consistent: first, coarse cleaning (filtering according to EU1-3 class), then removing harmful suspensions and particles (filtering according to EU4-7 ), then the final preparation and air supply to the server (filtering EU8-13). Hot air from the server is emitted to the street by fans, rising by convection to the ceiling of the room.
The effectiveness of such a system is much higher - PUE to 1.3 - but a large number of minuses appear. It is necessary to constantly change the filters. Due to the large number of filters, the air flow rate drops, therefore it is necessary to install more powerful fans, and this creates increased vibration and noise. In fact, atmospheric air with the same humidity parameters as in the street gets into the server room: if it rains in the fall, the humidity in the north will rise to 100%, then it will be necessary to use an air dehumidification system. In conditions of low humidity or forest fires, it will be necessary to restrict access to the outside air or close the damper altogether and switch to cooling the server with traditional DX or CW air conditioners, which will reduce energy efficiency and increase operating costs, including electricity.
Moreover, the system of natural direct cooling, as well as any system using the freecooling technology, cannot work all year round, since in summer, the air heats up and will not allow the server to cool. To do this, you need to use an additional air conditioning system of the first two options (CW or DX system). Of course, the time of their work will be much less than in the first two cases (no more than 50%). But in the aggregate, the DFC solution is more efficient and cheaper than the pure DX or CW system .
Natural cooling. Natural Free Cooling (NFC)
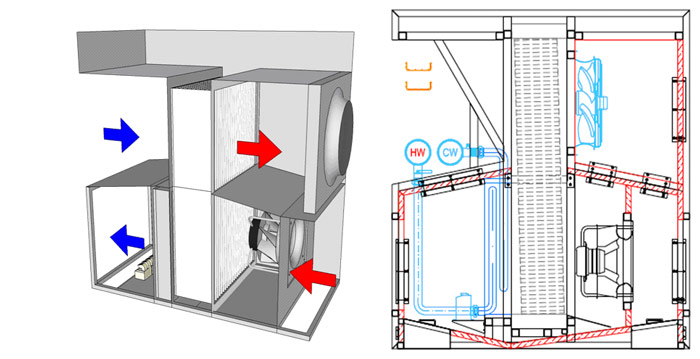
Block diagram of the natural cooling system (NFC)
The cooling system using external atmospheric air, however, the air does not go directly into the server, but cools the heat exchanger. In this case, we are freed from the need to use a filtering chain, it is enough just to clean the air at the entrance to the heat exchanger, and also get rid of the problem of constantly maintaining the desired humidity inside the server room, because server cooling circuit closed. The PUE of such a system reaches values of 1.09 in our climatic latitudes.
Like the DFC, the NFC system cannot work all year round, however, the efficiency of the solution allows increasing the total annual cycle of operation up to 80% without using CW or DX. Another important factor is the possibility of quite simple (in comparison with exotic systems) duplication of nodes. We chose it - Natural Free Cooling (NFC).
How it works
The system consists of two open separate circuits, external and internal. The data center air circulates in the inner loop, and outside air is supplied to the outer loop. The main element of the system is a recuperative heat exchanger, in which heat is exchanged between the ambient outside air and the air in the MCF room. The heated air is removed from the hot zones by exhaust ducts, and the cooled air is fed into the cold corridors. If you add fans to the heat exchanger and put it all in a box, you get an NFC module.
In normal operation, up to +18 outside air, the NFC system works as follows:
- Fans take air from the hot server corridor (with a temperature range from 35ºC to 40ºC) created by equipment in telecommunication racks and transport it to the lower area of the heat exchanger. Outside air is drawn in from the outside and fed to the upper zone of the heat exchanger. Passing through the heat exchanger, the external air cools the internal circuit, after cold air flows back into the server room, into the raised floor area.
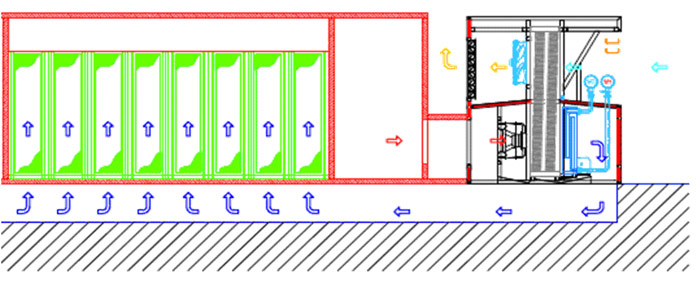
The principle of NFC.
When the outdoor temperature rises in the range from +18 to +24, an additional adiabatic cooling system is activated:

The scheme of adiabatic cooling.
This system is used to create water mist, passing through which the outside air will be cooled. Reduced temperature is achieved by evaporation of water.
When the temperature rises above +24 or in case of accidents or signs of burning in the outside air, an additional cooling circuit built on the CW system is included in the work (chiller-type, dual-circuit installation, the redundancy of which is itself carried out according to the N + 2 principle)

Remote condensing unit.

Chiller
Conclusion
We were faced with the task of creating a technical center that is optimal in terms of the cost of launch time from scratch. The selection of technologies was not easy: of course, first of all, everyone was looking in the direction of classic, proven solutions, mistaken that everything new and innovative is necessarily expensive. However, as it turned out, all the technologies and no more expensive than the classical ones from the TCO point of view are not so new, they are successfully used in Europe, which we personally saw when driving through the main data center of European telecommunications operators.
The risk of being the first in a number of decisions and stepping on a rake is great, but we have insurance in the form of conventional chiller systems that are time-tested and will work in case of any accidents or abnormal situations.
The materials are used by Ivan Prokofiev, an expert on engineering systems in the team of the project for the construction of a data center in the city of Yaroslavl.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/141363/
All Articles