Designing web applications using Data Management System (based on scaffolding technology)

In the previous article I talked about why I consider development using the Content Management System to be ineffective. In this article, I will talk about what approach I use in building web applications.
CMS Alternatives
In the comments to the previous article there were suggestions to use the Content Management Framework instead of the Content Management System. This does allow much more flexible design of the web application architecture, but is more costly in terms of resources.
I offer an alternative in the form of a Data Management System.
Before continuing, you should separate the concepts of Content Management System, Content Management Framework, and Data Management System.
In the article under the Content Management System, I understand a system that has its own specified database structure and a set of domain objects.
By Content Management Framework, I understand a certain set of classes and methods that helps automate work with data at the level of program code.
By Data Management System, I mean a stand-alone web application that provides data management capabilities. Wherein
The peculiarity of the approach when developing with the use of a data management system
When developing with the use of a data management system, the project is divided into several independent parts: a database, a frontend and a backend.
- Frontend - part of a web application that in most cases includes a large number of screens with a variety of design and user interface)
- Backend is a part of the project which in this case does not require a separate development and is just a data management system.
- The database is allocated separately, because, unlike the approach using the CMS, it contains a clean structure that reflects the subject area. Thus, there is no need to store foreign tables in the database, as is usually the case when using WordPress, Joomla and other CMS.
')
It should also be noted that we do not need to create a user interface for each project, as well as to implement CRUD logic (create retrieve update delete, because this functionality is provided by the data management system itself).
The key functionality on which the Data Management System works is scaffolding. Scaffolding is a technology supported by some MVC frameworks, which allows using an additional description (for example, class attributes) of a data scheme to build an application that supports CRUD functionality for interacting with the database. One project that actively applies this technology is Ruby on Rails. Also, systems that use scaffolding should include ASP.NET Dynamic Data (.NET) and Django (Python).
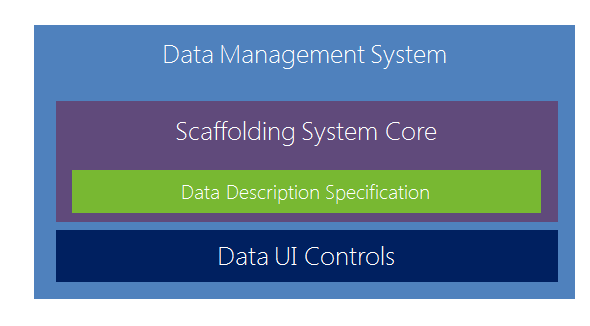
So, in general, the data management system is based on:
- Scaffolding System Core is a scaffolding system that allows you to dynamically build a user interface based on domain classes.
- Data UI Controls - a set of user interface controls that are used by the scaffolding system;
- Data Description Specification - a set of rules by which domain classes are supplemented with attributes that help the scaffolding system more accurately build the user interface.
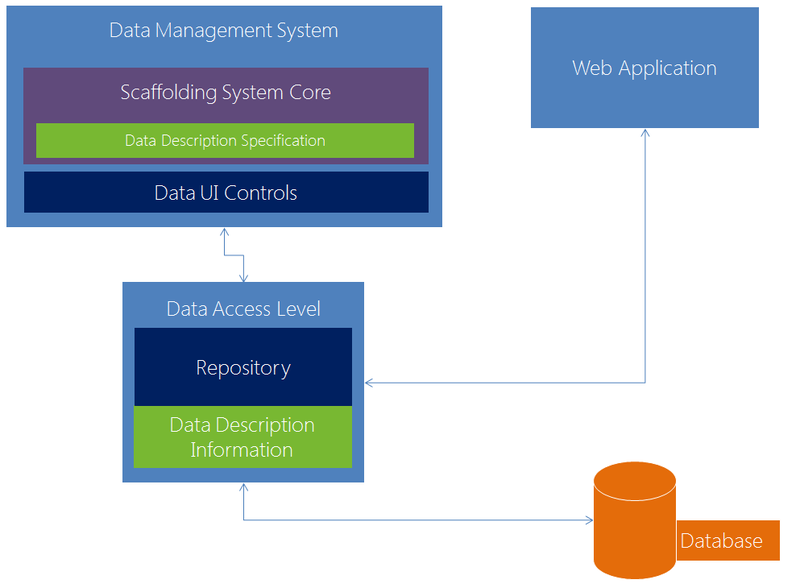
Building a web application using DMS
The design process using the DMS can be described as follows:
- Database Design
- Creating domain classes using ORM (Hibernate, EntityFramework, another object-relational mapping system).
- Supplementing domain classes with attributes (For example, a text field in a database can be displayed in the user interface as: a regular text field, a multi-line text field, a WYSIWYG editor).
- Development of the Frontend part (the actual web application)
- Development of Backend, which is reduced to the configuration and, if necessary, customization of the Data Management System (in most cases, the implementation of the CRUD model does not require modification).
Below is a diagram of the interaction of various components of the project.
Limitations with Data Management System
In the case of a data management system, there are also limitations.
- There is no possibility of separation of access rights to specific records of the table. However, if necessary, this problem can be circumvented in two ways:
- The first is adding the necessary logic to the data selection mechanism;
- The second is the creation of a customized form for working with data that requires difficult rights verification.
- The first is adding the necessary logic to the data selection mechanism;
- The need to add attributes to the classes of the subject area for a more correct construction of the user interface.
Benefits of using DMS
When using a data management system, we get the following benefits:
- complete separation of the frontend and backend parts of the project;
- creating and maintaining a “clean” database structure;
- Fast CRUD data management functionality
Practical use
In my practice, I use a data management system built on the basis of such components as:
- ASP.NET Dynamic Data;
- Extended set of user interface controls;
- Specification of attributes used in the description of the domain classes;
- A set of attributes, base classes and interfaces for extending domain classes.
In most cases, when creating a web application, I do not need to customize the data management system. For example, it is enough for me to change the path to the library containing the set of domain classes - and I can manage it completely by another application.
findings
Thus, the technology of scaffolding in conjunction with advanced libraries of controls and flexible specification of the description of attributes and classes of the domain allows you to build much more flexible and powerful web applications, without restrictions imposed by common Content Management System.
Links
These links will be more useful to novice developers than to those who already have experience in building web applications:
What is scaffolding?
Django
ASP.NET Dynamic Data
Asp. NET Dynamic Data - example of use
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/141207/
All Articles