HL7 - electronic medical records
 Within the framework of one study, the need arose to describe the HL7 electronic medical document standard. As a result, this article appeared. I share with the Habra community, I hope it will be interesting.
Within the framework of one study, the need arose to describe the HL7 electronic medical document standard. As a result, this article appeared. I share with the Habra community, I hope it will be interesting.Modern society is inevitably moving towards the informatization of more and more of its functions. Some structures quickly moved to a digital form, others, more conservative, lend themselves to change more slowly. Also, much depends on the willingness of society to accept these or other changes. And of course, the most important part is the initiative and support of the state to create and implement electronic services that allow it to more effectively implement its various functions.
')
One of these areas is the Health Information Exchange - HIE ( good presentation: Atif Zafar, MD, Health Information Exchange (HIE): Nuts and Bolts; AHRQ National Resource Center for Health IT ), for which there is a single standard throughout the country is one of the most important conditions for efficiency. It is clear that the effective exchange of medical data between various medical institutions (in particular, the introduction of an electronic medical history) will allow, in a simple way, to cure more people and also reduce the cost of treatment. The mutual understanding between medical institutions, individual specialists and the common man is increasing.
Of course, there are reasons for concern, and in the first place, this is unauthorized access to sensitive personal information about the state of human health.

This article describes the international standard of organization of the electronic health document management system Health Level 7 (HL7) www.hl7.org , Wikipedia: HL7 (medical standard ) , www.hl7.ru , www.hl7-russia.org developed since the beginning of the 70s in the United States and now adopted as national in some countries .
Over the past 40 years, the world has developed a large variety of standards for e-medicine SM Huff; Clinical data exchange standards and vocabularies for messages. . Although in general there is no universal standard and different standards often implement various aspects of such a huge area as medicine. The most common are Digital Imaging and Communication in Medicine (DICOM) , EDIFACT , Cisco Medical Data Exchange Solution , HL7 . It was the latter (HL7) that showed good results in comparative studies and is currently the most common.
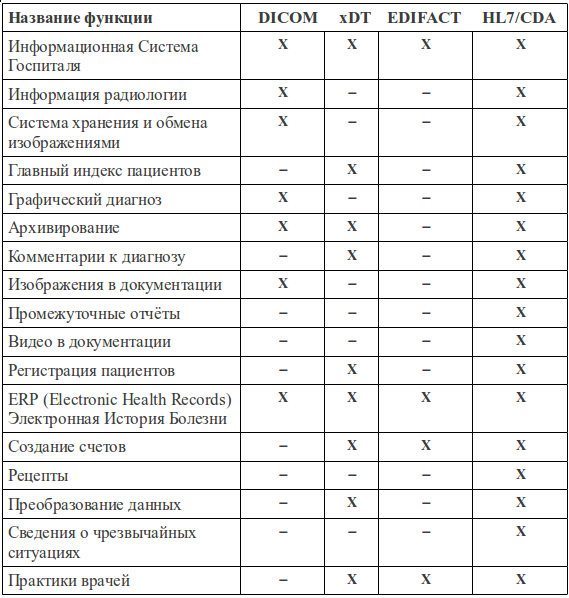
For example, here is published a comparative table of the functionality of the four standards:
Goals, concepts and general structure of HL7
The HL7 standard (Health Level 7 Seventh Level Medical Documentation) began its development in the 70s in the United States as part of a strategic medical initiative. This initiative consists of three areas:
UMLS
Unified Medical Language System The unified language of medical systems is an attempt to create a universal reference book of medical knowledge in the broadest possible sense using the most effective methods created in the field of computer processing of knowledge. Development started in 1986 at the US National Medical Library. Such powerful concepts as semantic representation and processing of medical knowledge are used, ontologies are created and are constantly being developed to describe all possible subject areas of the components of the universe of medical knowledge, lambda- numbered semantics are used to empower UMLS, and large and as detailed as possible ER-schemes are used constantly improving since the 70s of the 20th century.
The following table shows the structure of the UMLS and its position in the overall hierarchy of components of the US strategic medical initiative.
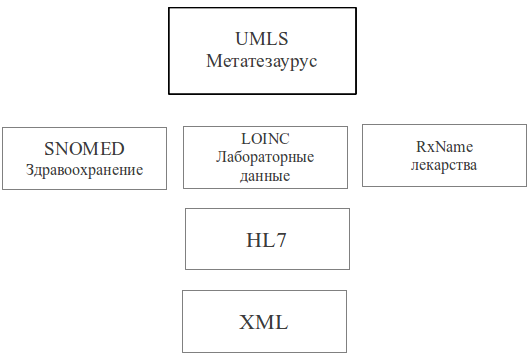
UMLS contains three knowledge bases: (knowledge source): Metatsaurus, Semantic Network, SPECIALIST-lexicon.
The main objectives of the UMLS are:
- Creation of comprehensive intellectual components of medical information systems;
- Promotion of free distribution of developed procedures and intellectual components among professional developers for standardization of terminology, specialized dictionaries and classification schemes for creating false systems related to electronic support of medical processes at the state level;
- Knowledge Base unification of the language environment.
Medical Information System VistA
Medical Information Scheme (MIS) VistA (Veterans Health Information Systems and Technology Architecture - Medical System Department of Veterans). The largest medical information system in the USA. Provides medical care to 4 million veterans, 180 thousand employees work in it in 163 hospitals, 800 clinics and 135 nursing homes. It is an extensive system covering almost all aspects of medical care.
The system is built on the language / platform MUMPS, has a core and about a hundred application software packages. The ideas embodied in MUMPS are implemented in VistA to the maximum extent: starting from the consideration of the finest nuances of equipment management to expert systems for making medical decisions.
The system is centralized and its main Austin Automation Center is located in Austin.
The following figure shows the general structure of the interaction of the components of the VistA system:
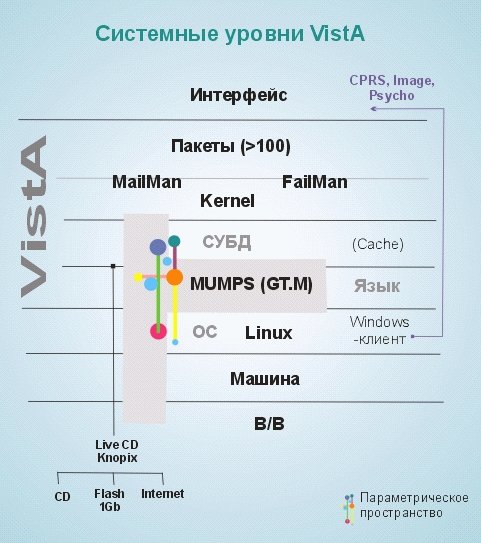
The standard for its presentation is splitting into levels:
1. Interface - a graphic / software interface for working with the system;
2. About 100 packages that implement the basic functional features;
3. MailMan / FailMan - system integrators / managers;
4. Kernel - the core of the system, high-performance software in the MUMPS language;
5. DBMS - the database, the most frequently used base is Caché [4], which is also created using MUMPS, which is the key to its effective interaction with VistA;
6. MUMPS - ( Massachusetts General Hospital Utility Multi-Programming System - Massachusetts basic multi-program system for hospitals; sometimes M or M-system). A programming language created in 1966-1967 for use in the medical industry. It is a very powerful tool, but in view of some of the shortcomings laid down at the system level, it is not widely used outside the specific framework of medical systems;
7. OS - most of the most common operating systems of the * nix and Windows families are supported;
8. Machine - hardware requirements are not high;
9. I / O - the I / O subsystem does not impose any specific requirements.
Messaging in VistA is performed in accordance with the HL7 standard, work with medical images is provided in the DICOM standard. VistA can be used both in a separate hospital and in a regional hospital system.
HL7
Health Level 7 (Seventh Level of Medical Document Management) is a standard for the exchange, management and integration of electronic medical information.
The seventh level is called the system by analogy with the seven levels of open systems interaction, Open Systems Interconnection or OSI. Those. these are processes of the highest level.
The seventh level supports the execution of such tasks as:
- Structuring the transmitted data;
- System design capabilities;
- Achieving consistency of gear;
- Security;
- Identification of participants;
- Availability.
The overall structure of the components of HL7 technology is shown in the following figure:

Let us consider in more detail the most interesting components of the HL7 application stack, their goals and features
Rim
Reference Information Model, Reference Information Model. The basic concept for the whole HL7 - the information model of medicine - the main source of data content of all HL7 messages and documents.
The elements of the information model — classes, class state transitions, data types, and imposed constraints — use system concepts and graphical expression of the UML language.
In turn, RIM consists of several technologies:
USAM - Unified Service Action Model - a general model of service actions. Object model for any possible action in the system;
MIM - Message Information Model - message models;
R-MIM Refined Message Information Model - context-bound model.
A thumbnail image (a full-size table occupies a sheet of A3 paper) The UML scheme describing the full RIM specification is shown in the following figure.
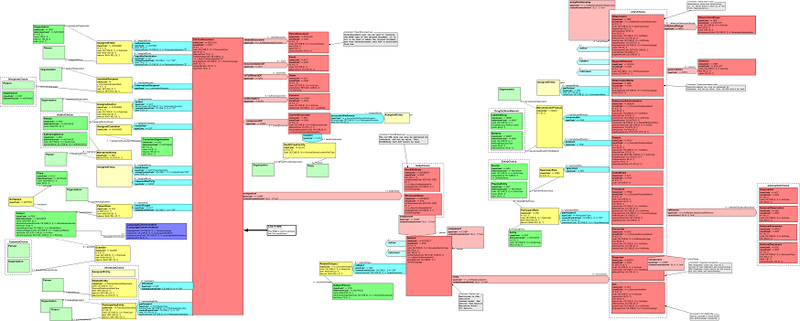
Storyboard
Storyboard
The functional model is in terms of system design, UML. The concept of a storyboard (storyboard) is taken from the film industry and makes it possible to use HL7 to convey meaningful message passing moments as frames. Each frame describes the key participants and their interaction. A set of frames represents both the transmission of a message and the operation of a large system.
The description of the work of triggers (trigger) of triggering events (for example, the form after filling switches to the “filled” and / or “signed” state).
Each interaction is described by a storyboard (in UML sequence diagram).
By means of RIM and a storyboard it is possible to express a highly personalized patient history.
Vocalbulary
Dictionaries.
Presented in the form of thesauri or even ontologies descriptions of the specificity of subject areas.
The attribute in the RIM description may be a dictionary element.
Dictionaries can be:
- multi-column, based on the principles of the metathesaurus UMLS table described by means of HL7
- LOINC, SNOMED, HIPAA, local, national dictionaries.
HMD
Hierarchial Message Descriptor - the determinant of the hierarchical structure of the message.
Principles of HMD:
- transmission system must understand the genesis of classes.
- the message during transmission is arranged in a linear structured sequence.
EHR System
Electronic Health Record Systems - Electronic Health Record System.
Description of the full functionality of the sectioned EHR:
- Care Management
- Clinical Support (Clinical Support),
- Information Infrastructure (Information Infrastructure) - a total of 125 functions.
Arden Syntax
Arden syntax
Specification adopted by HL7 for the definition and dissemination of medical knowledge. Arden syntax is the language of Medical Logic Modules (MLM - Medical Logic Modules) for coding medical knowledge. Each MLM contains sufficient information for making a medical decision. MLM is used to generate alarms, understanding medical data, diagnosing, filtering medical data and administrative tasks. Under certain conditions, a computer program (event monitor) generating expert support can be developed. MLM can be connected with other MLM and form a network.
CDA
Clinical Document Architecture - Clinical Document Architecture.
The scope standard is HL7, ISO approved (ISO / HL7 27932: 2009 Data Exchange Standards - HL7 Clinical Document Architecture, Release 2).
This standard fully defines the syntax and set of data structures allowing to fully describe the semantics of any clinical document. CDA is based on XML.
When creating a clinical document (CD), its markup, structure and semantics is taken from the description of CDA. The specification itself is derived from the RIM data reference. The clinical CDA document is a complete information object, with fully defined components. In addition, it may contain text, images, sound and other multimedia content.
Initially, HL7 began to develop as a standard message. The transmitted clinical document itself is independent of the format of the message in which it is transmitted. The transferred CD has authorship, history of changes, it is stable and intended for human perception. In turn, the message is intended for reading by a computer, it exists only during the transmission of the document.
CD itself is described in XML, but it may also contain other types of data, such as audio / video information, binary image data, digital signatures.
Clinical expressions can be expressed in the CD sections, such as the procedures performed, the current situation of the patient, administrative orders, undesirable events and factors. The CD consists of a header and body. The title can express a complex system of authors, performers, responsibility, the current situation of the document, access to it, classifying information about the patient, etc. The high-level representation of all the expressive possibilities of the header is defined by the UML scheme.
The CD body contains a clinical record / report (clinical report) collected from sections.
One of the goals of the CDA is the comparability of CD, which allows you to organize work with them.
The data types enclosed in the section can be simple, such as for example whole numbers or data of a complex time system (for example, general timing specification). In the section, you can use previously defined concepts (structural data types) that are filled over time and events.
As far as I know, it is on the basis of HL7 that an electronic medical record has been developed and successfully implemented in Estonia.
Russia is also working in this area. I was more interested in academic research, so I can recommend the following master's thesis abstract: Fam Van Tap; ALGORITHMIC AND SOFTWARE MEANS OF INTEGRATING DATA WHEN CREATING ELECTRONIC MEDICAL CARDS
The topic, in my opinion, is very interesting, the prospects for such systems are excellent, the benefits are great.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/139904/
All Articles