How to cheat GLONASS. Part one - we spoil the trackers
Director driver: "And I know 27 ways to lower your salary."
A lot of good and bad things can be said about the universal introduction of GLONASS. In general, the idea is excellent: the world has been using satellite technologies for a long time for logistic purposes and to reduce the fixed costs of transport. In Russia, everything is turned upside down: the connection of the vehicle fleet to GPS / GLONASS monitoring systems is initiated from above and sometimes implanted where there is no special sense from it.
In those cases when the introduction of GLONASS monitoring is absolutely justified, the process is hampered by company employees, especially drivers. Everything is used: from open sabotage and vandalism to the law on privacy. At specialized forums (for example, here ), operators and integrators of monitoring systems share with each other new ways of bullying innocent GLONASS terminals. I thought about it and decided to combine everything I read and heard in one interview in one article: it will be useful for pests to know what their tricks have long been known to employers, and employers, on the contrary, will find out what they will have to face.
The most common type of sabotage is manipulation of the antenna and the body of the GLONASS tracker. Someone, without thinking twice, simply breaks off the antenna, someone cautiously pierces it with a needle, someone wraps the entire unit or its individual parts with foil, someone, like in the picture below, places a hefty piece of iron or magnet on the controller. The most hardworking and inventive drivers make a special box of lead or other metal, which completely closes the terminal. All these actions have a common goal - to make it impossible to receive a signal from satellites.
')
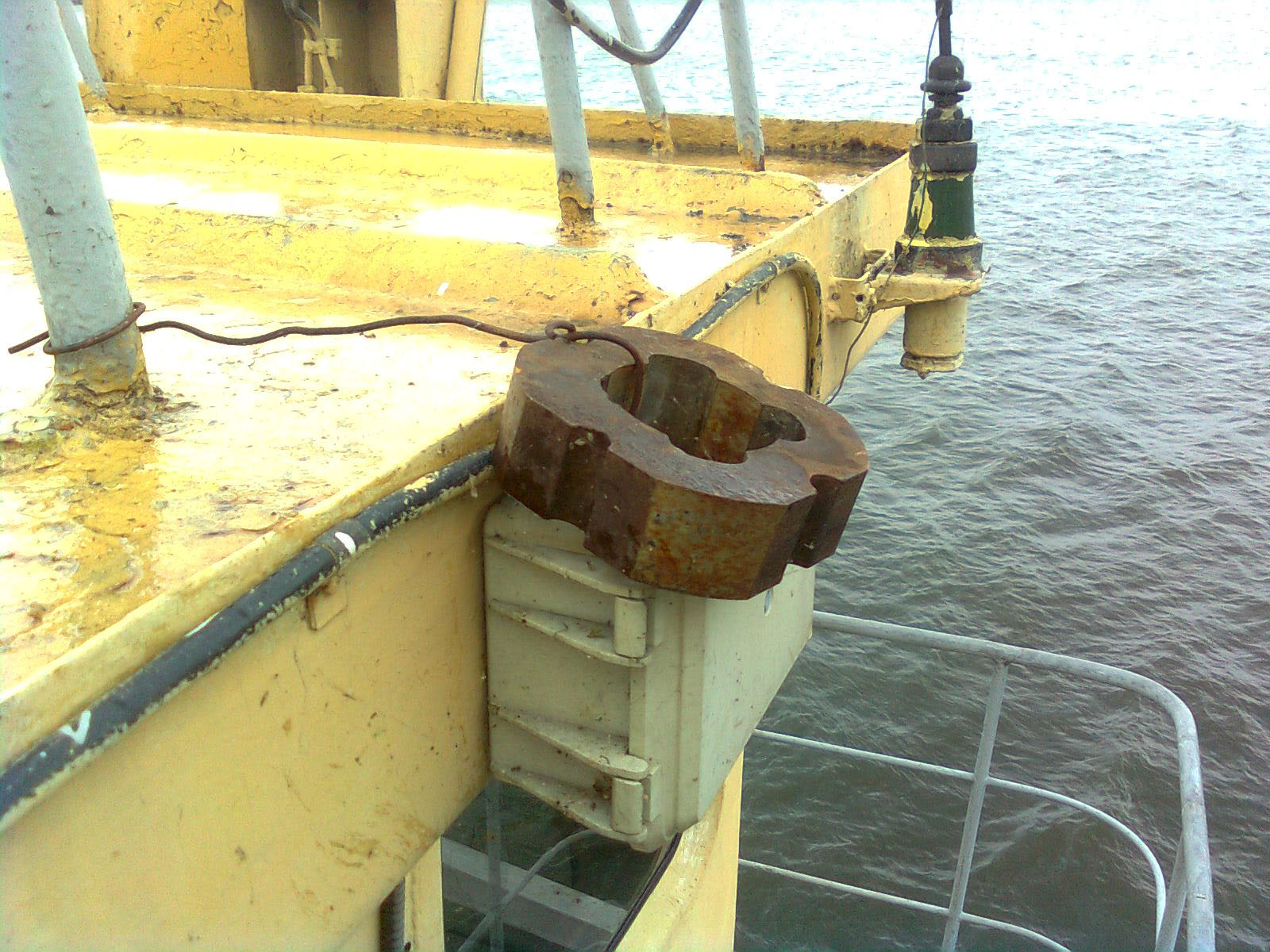

And, of course, it would have been achieved if it were not for one “but”: equipment installers have long learned to protect devices from such antics. Some operators of GLONASS monitoring systems initially recommend equipment with built-in antennas - i.e. those for which damage it is necessary to disassemble the terminal. Well, and then - the matter of technology: devices are installed in places difficult to reach for drivers, parts that need to be removed for access to the antenna are sealed, and special stickers are attached to the unit itself. In addition, the satellite monitoring software is configured in such a way that when the controller detects an open or short circuit in the antenna, it automatically sends a corresponding alarm message to the system. It certainly will not save from vandalism, but it will warn you that the tracker “dropped out of the zone” is not accidental. And delicately hints at a name, who should be fined at the cost of damaged iron.
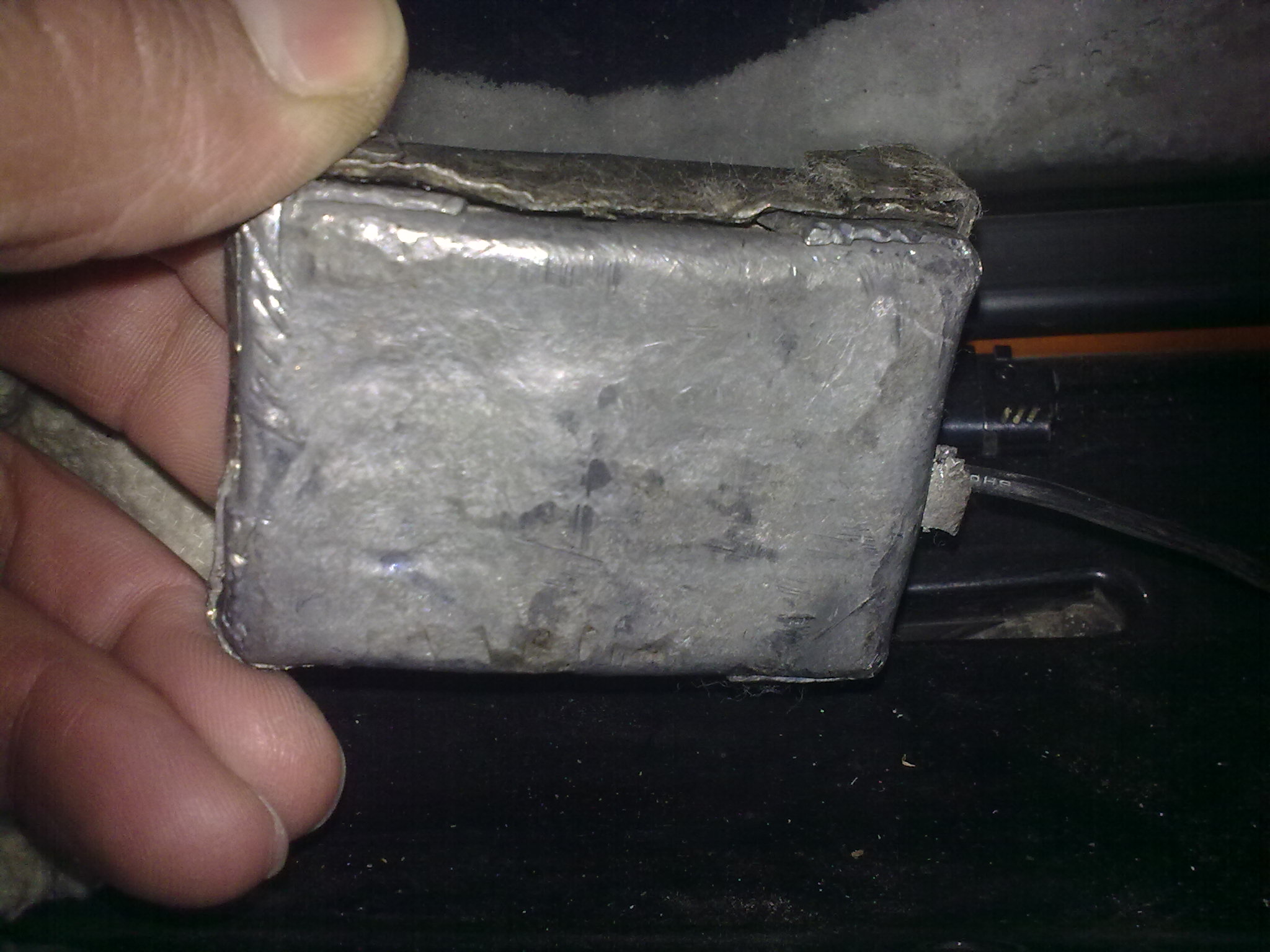

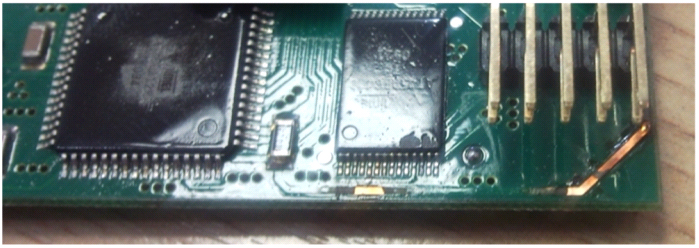
With the same purpose - to cut off the GLONASS receiver from the navigation network - drivers try to damage the power system: they pull out fuses, cut the wires, change the polarity of the power supply and even torment the unfortunate device with a stun gun. Let's start with the fact that almost all models of controllers are equipped with a backup power system: i.e. some time after sabotage the terminal will work. This time will be enough for him to send an alarming message to the system that some bad person poshamanil and disabled the controller - and the message recipients will again know who to cut the salary. Well, and, of course, if possible, the device is sealed from all sides, so that it is disreputable.
Example of damaged equipment: the track is charred due to the impact on the power supply:
But all that I described above is about technically savvy drivers who are familiar with the mechanism of operation of the GLONASS equipment . There are those who prefer not to delve into the subtleties - but simply to disable the hated box that hinders with impunity to drive official vehicles for non-official matters. Such break the terminal entirely (for sure), flood it with water, causing a short circuit, - in general, they pervert as they can. There is a control to them and her name is an anti-vandal case, a strong box like this that is not so easy to damage.
Protecting a specific device from a specific person is, in principle, a simple task. It is worse when employees of different departments enter into a tacit agreement between themselves - and sabotage the work of a friendly company. For example, drivers may collectively complain about the malfunction of the equipment and the inaccuracy of its readings, the dispatchers to keep silent about the “left” flights, and the mechanics to delay and impede the installation of instruments on vehicles. There is one antidote here - a manager who has to do with the results of the system’s work. As practice shows, government organizations, where there is no owner and a flexible bonus system, will not be helped by any paid or free satellite monitoring system - even GLONASS, even GPS.
Of course, this text is unlikely to draw on the practical manual “How to deceive GLONASS without losing a job”, to combine all the achievements of creative drivers in one material is difficult. So if I forgot about something - write in the comments, I think it will be interesting and informative.
In the meantime, I will prepare the next series - about how fuel sensors are being tricked. There the problem is actually more difficult than with satellite terminals. But that's another story.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/136843/
All Articles