Details about the ReFS (Protogon) file system
The Windows 8 developer blog has published a large article describing the architecture of the new ReFS (Resilient File System) file system, previously known under the codename Protogon, which is being developed for Windows Server 8, and in the future it will be further developed and will be installed on Windows client machines. The past NTFS file system in version 1.2 was introduced back in 1993 as part of Windows NT 3.1, and the emergence of Windows XP in 2001 NTFS grew to version 3.1, and only then it began to be installed on client machines. Approximately the same development path expects ReFS.
For many reasons, NTFS does not meet the requirements for modern file systems, and it has never been considered elegant or performance efficient.
Surendra Verma, lead programmer and manager of the Windows Storage and File System division, explains that ReFS will be based on NTFS and preserve compatibility in key areas, but at the same time it will be a completely different architecture. Some features and NTFS semantics will be eliminated, including support for short names, object IDs, compression, file level encryption (EFS), disk limits (quotas), data streams, transactions, sparse files, extended attributes and hard links.
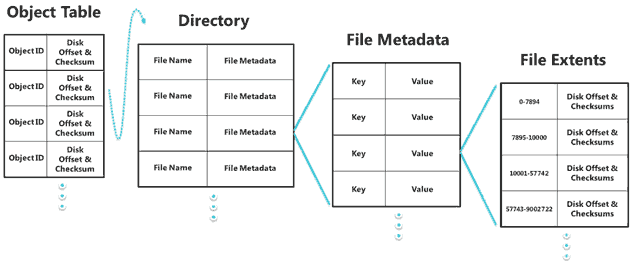
ReFS data structure is implemented as B + trees
')
In addition, ReFS inherits many of the features and semantics of NTFS, including BitLocker encryption, access control lists (ACLs), USN journal, change notifications, symbolic links, junction points, mount points, reparse points ( reparse points), volume snapshots, file IDs and oplock.
Of course, ReFS data will be available to clients through the same APIs that are used today in all operating systems to access NTFS partitions.
For many reasons, NTFS does not meet the requirements for modern file systems, and it has never been considered elegant or performance efficient.
Surendra Verma, lead programmer and manager of the Windows Storage and File System division, explains that ReFS will be based on NTFS and preserve compatibility in key areas, but at the same time it will be a completely different architecture. Some features and NTFS semantics will be eliminated, including support for short names, object IDs, compression, file level encryption (EFS), disk limits (quotas), data streams, transactions, sparse files, extended attributes and hard links.

ReFS data structure is implemented as B + trees
')
Key ReFS targets
- Maintain maximum compatibility with a set of widely used NTFS features, and at the same time get rid of unnecessary ones that only complicate the system
- Verification and autodetection of data.
- Maximum scalability.
- The inability to completely disable the file system due to the isolation of bad sections.
- Flexible architecture using the Storage Spaces feature, which is designed and implemented specifically for ReFS.
Key ReFS features
(some are only available with Storage Spaces)- Integrity of metadata with checksums.
- Integrity streams: a method of writing data to a disk for additional data protection in case of a damaged part of the disk
- Transactional model "allocate on write" (copy on write)
- Large limits on the size of partitions, files and directories. The partition size is limited to 2 78 bytes with a cluster size of 16 KB (2 64 * 16 * 2 10 ), the Windows stack supports 2 64 . Maximum number of files in a directory: 2 64 . Maximum number of directories in a section: 2 64 .
- Pooling and virtualization for easier partitioning and file system management.
- Segmentation of sequential data (data sriping) to improve performance, redundant write for fault tolerance.
- Support disk scrubbing in the background to detect hidden errors.
- Rescue data around the damaged area on the disk.
- Shared storage pools between machines for additional fault tolerance and load balancing.
In addition, ReFS inherits many of the features and semantics of NTFS, including BitLocker encryption, access control lists (ACLs), USN journal, change notifications, symbolic links, junction points, mount points, reparse points ( reparse points), volume snapshots, file IDs and oplock.
Of course, ReFS data will be available to clients through the same APIs that are used today in all operating systems to access NTFS partitions.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/136464/
All Articles