The world's largest factory of Li-Ion batteries built in Russia

In the photo: LT-LYP 300 battery with a capacity of 300 Ah
In early December, the Russian-Chinese enterprise Liotech completed the construction and equipping of the world's largest lithium-ion battery plant. The plant with an area of more than 4 hectares (40,000 m 2 ) began work on the territory of the industrial and logistic park PNK-Tolmachevo, in the suburb of Novosibirsk. Construction took nine months, investment in the project exceeded 13.5 billion rubles.
According to experts, after reaching full capacity in the second half of 2013, this enterprise can take a share of 10-15% on the world market for lithium-ion batteries.
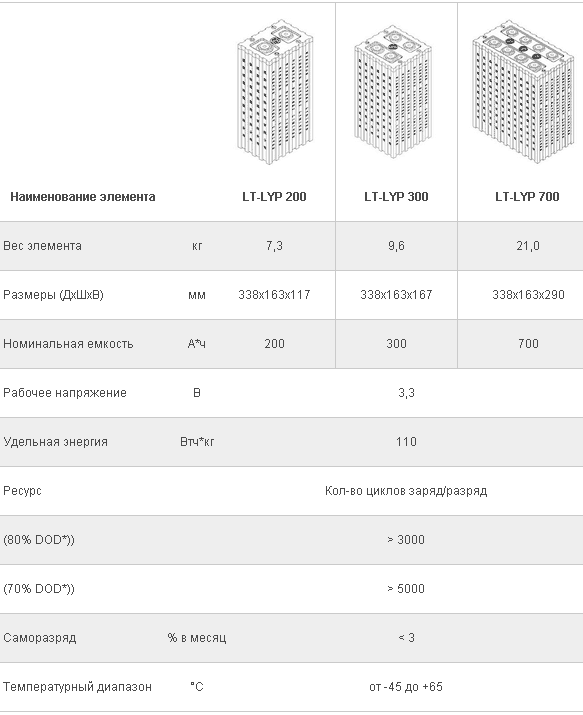
The Liotech plant will produce three types of batteries: 200 Ah (LT-LYP 200), 300 Ah (LT-LYP 300) and 700 Ah (LT-LYP 700) with cathodes on the lithium-iron-phosphate cathodes (LiFePO 4 ) , which provide an optimal price / quality ratio and gives good performance on energy density and resistance to ambient temperature. Liotech batteries operate at temperatures from -45 ° C to + 65 ° C and charge up to 70% capacity in 20 minutes with high amperage. For comparison, see specifications of lithium-ion batteries of foreign manufacturers.
')
Products "Liotech"
Now there is a certain shortage of lithium-ion batteries in the world market, so even before the plant was launched, we managed to conclude a number of long-term contracts for the sale of products. The largest buyer is still considered the Russian manufacturer of electric tractors and other vehicles, the company Mobel (contract for 3 billion rubles). But in the future, there will be a large demand for batteries from Chinese companies.
The total capacity of the plant allows producing about one million batteries per year, which are supposed to be equipped primarily with electric buses and minibuses. 1 million batteries per year will be enough for about 5,000 buses. In one bus, batteries are installed in approximately 200 laptops, so from the point of view of product sales, the automotive market is considered the main one, while computer electronics and household appliances can provide only auxiliary demand for batteries.
Electric cars are now considered one of the most promising areas in the automotive industry, so long-term demand for batteries is almost guaranteed.
The resource of Liotech car batteries is approximately 600 thousand km of travel on an electric motor. Then they lose a significant part of their capacity, but can be used for another 10-15 years in the energy industry. In the future, these batteries can also be used in alternative energy (for storing energy collected from photovoltaic cells and wind turbines), for leveling voltage in electrical networks, as backup power sources in hospitals, airports, data centers and other important facilities. Moscow Metro, Russian Railways, some energy companies, representatives of the military-industrial complex and telecommunications companies have already shown interest in the product. After a full test, the batteries can be safely buried in the vast Russian open spaces, since the materials are relatively safe for the environment.
The plant near Novosibirsk is a great example that in Russia it is possible to open new modern productions by importing high technologies from abroad (in this case, from the Chinese company Thunder Sky, which provided the scientific and technical base and sent its engineers for the production).
In the future, several more auxiliary plants are planned to be built near Novosibirsk: for the production of cathode material, for the production of anode material, and also plants for the production of other battery components.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/135519/
All Articles