Datacenter in Yaroslavl: the realization of the dream of the last five years
"Beeline" need a lot of computing power to work. The idea to build a large data center and solve the problems of growth for 10 years ahead has been around since 2005. I will briefly talk about the difficulties we faced when thinking about a new large facility.

New data center
The first problem was in the ratio of results and prices. It is clear that it would be desirable to build a data center in Moscow near an existing one, but not so much as to spend really large sums on construction and energy supply. At first, we saw about 30 objects in Moscow and the region, but then we came to the conclusion that it is economically more reasonable to build somewhere near the capital region, but not directly in it. There is another difficulty: between the data center in Moscow and the new data center should not be more than 200 kilometers of optical fiber, otherwise the speed of light will already significantly affect the lags with synchronous replication. In parallel, we bought new models of disk arrays and got the opportunity to test asynchronous replication. So it became clear that geographically distribute the centers can be.
')
The main indicator of any data center is the amount of electricity it consumes. We calculated the growth rates over the past 10 years, approximated this growth, corrected it after the 2008 crisis, and found out that we need 10 MW to solve the problem for the near future. Considering that it is not profitable to connect the power with pieces, it was necessary to immediately bring just such a line to the center.
The next factor of choice is the temperature of the region and its humidity. The colder the place is on average - the less energy is needed for forced cooling, and the more environmentally friendly and more economical the work of the data center. The situation with humidity is as follows: if the air is dry, static discharges begin to accumulate on the boards, and if it is too humid, dew falls out. The best place according to the evaluation results was Yaroslavl, which is close to Moscow, technically-provided, where you can take a lot of electricity, there is cheap land and where the temperature is suitable (90-95% of the time we do not use active cooling, that is, we work with outside air) .
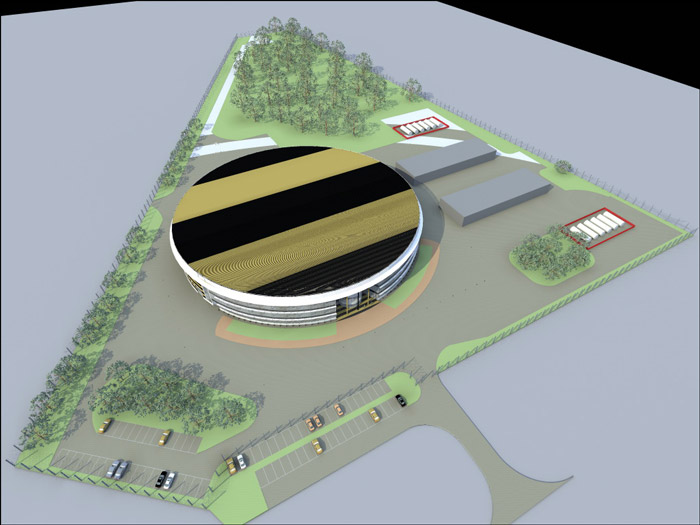
Data center building, top view
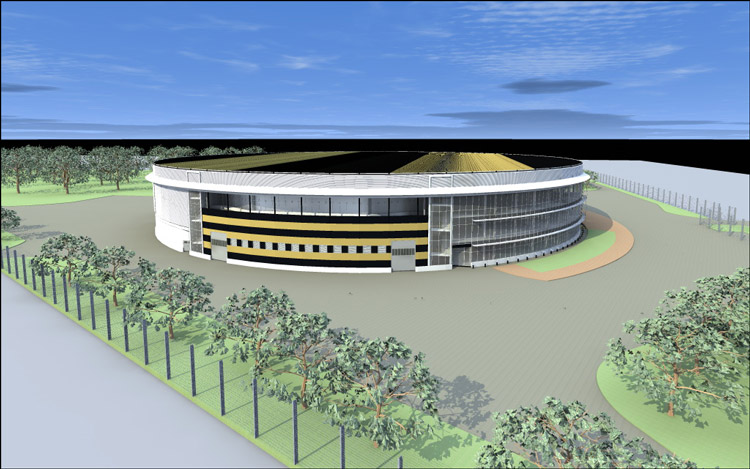
The data center immediately decided to make modular. After the competition, a solution based on AST (Smart Shelter) was chosen among 15 large companies. The main structural element is fire-resistant self-supporting panels, which are connected by a “dovetail” and are closed by profiles that protect against both temperature influences and unauthorized penetration attempts. The design of the modular data center consists of six autonomous modules, with a useful area of each 500 square meters.

Module. From the outside, in reality, it looks like a big gray box.
The data center itself uses many different systems that will survive any disaster: protection from water and fire damage, temperature protection, physical protection, protection from the most severe weather, internal fires, penetration, fool, EM-fields, and so on. Each module has its own decentralized engineering infrastructure. If necessary, individual modules can be dismantled and quickly transported to a new location. If a meteorite hits a module, it does not affect the operation of other modules.

The module is inside, taken not in the new data center.
Considering that it was possible to use any solutions for the center itself, since there were no limitations, we focused on what would ensure the minimum consumption of resources, that is, it would be profitable and environmentally friendly. In general, it is beneficial to be environmentally friendly to a modern data center: this coincides with the main paradigm of reducing power consumption and optimal use of resources. According to the reports of consulting companies, there were about 40 different solutions for building cooling systems and maintaining uninterrupted power. We immediately dismounted technology not related to the engineering systems of the data center associated with water cooling servers, power management and server cooling at the level of software or BIOS, because this can be done in parallel with making decisions on the choice of technologies. Exotic cooling systems - such as chilled beams, deep-sea cooling and others, as well as exotic systems of primary or secondary power systems - ultracapacitors, geothermal sources, solar panels, tidal power systems, windmills, too, quickly "fell off." The rest of the systems did not cause rejection during the direct analysis and were subjected to additional research.
At first they thought about the Kyoto wheel. However, taking into account the requirements of Tier-3, it was necessary to make two more of the same backup nodes, which would require a lot of space. They looked at the UPSs integrated into the servers with interest - this technology looked promising, since it did not require a centralized UPS. On the other hand, there is a lot of different hardware (disk arrays, tape libraries, high-end servers), and it will not be able to unify it quickly, so I had to refuse. This technology can be used only in a homogeneous environment from the point of view of servers and imposes large restrictions on the architecture of the data center as a whole. Our task was to build a universal data center, where the motley equipment, which was produced 10 years ago, will be used, will be made now and will be in the next 10 years. Then we began to look at the thermal storage - but there was a need for a large amount, for 10 MW just astronomical. Trigeneration on turbines or fuel cells using adsorption or absorption systems looked good until we found a case comparing the cost of ownership of the trigeneration and DDIBP systems with the data center and freecoling modules. It turned out that the business case becomes positive after 30 years of use. Highly efficient static UPS - we already use such systems, we are well aware of how much it costs to implement such a solution, which means we can compare it with new solutions.
The most interesting technology in terms of economic feasibility turned out to be DDIBP - diesel-dynamic uninterruptible power supply. Its basic principle is that it accumulates kinetic, rather than chemical energy, like ordinary UPS systems on batteries.

Power scheme
It works on the same principle as the classic uninterruptible power systems - with short-term failures or poor-quality power (wrong AC voltage sine wave, frequency fluctuations, amplitudes, etc.), the accumulated kinetic energy is used, with long-term power outages the diesel generator is activated . Thanks to the "top" power switching occurs very quickly and imperceptibly for consumers, that is, without voltage jumps, for example.

UPS device
For cooling, the natural free cooling system “Natural Free Cooling” was chosen - this is air conditioning of the internal space of the MTSOD based on the principle of heat exchange between the outside air and air circulating in the MTSOD, while ensuring cleanliness of the air and humidity control. The system consists of two open loop. The data center air circulates in the internal circuit, external air is supplied to the external circuit. The main element of the system is a recuperative heat exchanger, in which heat is exchanged between the ambient outside air and the air in the MCF room. The heated air is removed from the hot zones by exhaust ducts, and the cooled air is fed into the cold corridors. The use of adiabatic cooling (injecting water into the air flow of the external circuit) allows you to increase the temperature range of the cooling system without connecting the compressor circuit of the cold supply from +19 to +24 degrees Celsius.

Territory. Trees are planted so as not to interfere with the wind and protection.
Interestingly, when calculating the technologies used, it turned out that the total cost of ownership of bleeding edge technological solutions turned out to be lower with shorter implementation terms.
The main parameter for evaluating the efficiency of a data center in this regard is Power Usage Effectiveness, its physical meaning is the ratio of the total energy consumed by the data center to the amount of energy consumed by the payload. According to our calculations, the average annual PUE will not exceed 1.3.
If the topics are interesting, you can make a separate topic about the cooling systems and uninterrupted power of the data center, plus a separate talk about how we synchronize data and protect against various failures. In the comments, you can ask questions in general on any topic: either I will answer immediately, or I will promise another topic.

New data center
Stronger, higher, faster, cheaper
The first problem was in the ratio of results and prices. It is clear that it would be desirable to build a data center in Moscow near an existing one, but not so much as to spend really large sums on construction and energy supply. At first, we saw about 30 objects in Moscow and the region, but then we came to the conclusion that it is economically more reasonable to build somewhere near the capital region, but not directly in it. There is another difficulty: between the data center in Moscow and the new data center should not be more than 200 kilometers of optical fiber, otherwise the speed of light will already significantly affect the lags with synchronous replication. In parallel, we bought new models of disk arrays and got the opportunity to test asynchronous replication. So it became clear that geographically distribute the centers can be.
')
Choosing a place
The main indicator of any data center is the amount of electricity it consumes. We calculated the growth rates over the past 10 years, approximated this growth, corrected it after the 2008 crisis, and found out that we need 10 MW to solve the problem for the near future. Considering that it is not profitable to connect the power with pieces, it was necessary to immediately bring just such a line to the center.
The next factor of choice is the temperature of the region and its humidity. The colder the place is on average - the less energy is needed for forced cooling, and the more environmentally friendly and more economical the work of the data center. The situation with humidity is as follows: if the air is dry, static discharges begin to accumulate on the boards, and if it is too humid, dew falls out. The best place according to the evaluation results was Yaroslavl, which is close to Moscow, technically-provided, where you can take a lot of electricity, there is cheap land and where the temperature is suitable (90-95% of the time we do not use active cooling, that is, we work with outside air) .

Data center building, top view
Estimate the cost of construction
The data center immediately decided to make modular. After the competition, a solution based on AST (Smart Shelter) was chosen among 15 large companies. The main structural element is fire-resistant self-supporting panels, which are connected by a “dovetail” and are closed by profiles that protect against both temperature influences and unauthorized penetration attempts. The design of the modular data center consists of six autonomous modules, with a useful area of each 500 square meters.

Module. From the outside, in reality, it looks like a big gray box.
The data center itself uses many different systems that will survive any disaster: protection from water and fire damage, temperature protection, physical protection, protection from the most severe weather, internal fires, penetration, fool, EM-fields, and so on. Each module has its own decentralized engineering infrastructure. If necessary, individual modules can be dismantled and quickly transported to a new location. If a meteorite hits a module, it does not affect the operation of other modules.

The module is inside, taken not in the new data center.
We select the filling
Considering that it was possible to use any solutions for the center itself, since there were no limitations, we focused on what would ensure the minimum consumption of resources, that is, it would be profitable and environmentally friendly. In general, it is beneficial to be environmentally friendly to a modern data center: this coincides with the main paradigm of reducing power consumption and optimal use of resources. According to the reports of consulting companies, there were about 40 different solutions for building cooling systems and maintaining uninterrupted power. We immediately dismounted technology not related to the engineering systems of the data center associated with water cooling servers, power management and server cooling at the level of software or BIOS, because this can be done in parallel with making decisions on the choice of technologies. Exotic cooling systems - such as chilled beams, deep-sea cooling and others, as well as exotic systems of primary or secondary power systems - ultracapacitors, geothermal sources, solar panels, tidal power systems, windmills, too, quickly "fell off." The rest of the systems did not cause rejection during the direct analysis and were subjected to additional research.
Primary selection
At first they thought about the Kyoto wheel. However, taking into account the requirements of Tier-3, it was necessary to make two more of the same backup nodes, which would require a lot of space. They looked at the UPSs integrated into the servers with interest - this technology looked promising, since it did not require a centralized UPS. On the other hand, there is a lot of different hardware (disk arrays, tape libraries, high-end servers), and it will not be able to unify it quickly, so I had to refuse. This technology can be used only in a homogeneous environment from the point of view of servers and imposes large restrictions on the architecture of the data center as a whole. Our task was to build a universal data center, where the motley equipment, which was produced 10 years ago, will be used, will be made now and will be in the next 10 years. Then we began to look at the thermal storage - but there was a need for a large amount, for 10 MW just astronomical. Trigeneration on turbines or fuel cells using adsorption or absorption systems looked good until we found a case comparing the cost of ownership of the trigeneration and DDIBP systems with the data center and freecoling modules. It turned out that the business case becomes positive after 30 years of use. Highly efficient static UPS - we already use such systems, we are well aware of how much it costs to implement such a solution, which means we can compare it with new solutions.
Nutrition
The most interesting technology in terms of economic feasibility turned out to be DDIBP - diesel-dynamic uninterruptible power supply. Its basic principle is that it accumulates kinetic, rather than chemical energy, like ordinary UPS systems on batteries.

Power scheme
It works on the same principle as the classic uninterruptible power systems - with short-term failures or poor-quality power (wrong AC voltage sine wave, frequency fluctuations, amplitudes, etc.), the accumulated kinetic energy is used, with long-term power outages the diesel generator is activated . Thanks to the "top" power switching occurs very quickly and imperceptibly for consumers, that is, without voltage jumps, for example.

UPS device
Cooling
For cooling, the natural free cooling system “Natural Free Cooling” was chosen - this is air conditioning of the internal space of the MTSOD based on the principle of heat exchange between the outside air and air circulating in the MTSOD, while ensuring cleanliness of the air and humidity control. The system consists of two open loop. The data center air circulates in the internal circuit, external air is supplied to the external circuit. The main element of the system is a recuperative heat exchanger, in which heat is exchanged between the ambient outside air and the air in the MCF room. The heated air is removed from the hot zones by exhaust ducts, and the cooled air is fed into the cold corridors. The use of adiabatic cooling (injecting water into the air flow of the external circuit) allows you to increase the temperature range of the cooling system without connecting the compressor circuit of the cold supply from +19 to +24 degrees Celsius.

Territory. Trees are planted so as not to interfere with the wind and protection.
Interestingly, when calculating the technologies used, it turned out that the total cost of ownership of bleeding edge technological solutions turned out to be lower with shorter implementation terms.
The main parameter for evaluating the efficiency of a data center in this regard is Power Usage Effectiveness, its physical meaning is the ratio of the total energy consumed by the data center to the amount of energy consumed by the payload. According to our calculations, the average annual PUE will not exceed 1.3.
If the topics are interesting, you can make a separate topic about the cooling systems and uninterrupted power of the data center, plus a separate talk about how we synchronize data and protect against various failures. In the comments, you can ask questions in general on any topic: either I will answer immediately, or I will promise another topic.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/134961/
All Articles