Talk about Docsis?

Good day to all habrazhiteli. Not so long ago I had the opportunity to work as a system administrator at a local provider. Nothing unusual, but the data transfer standard of this provider was not very common - it was Docsis. Rummaging through the search for Habr, I found only 1 more or less intelligible article about Docsis , in which it was a little bit about everything and it prompted me to write a post about this rare standard and its, perhaps, main part - CMTS. I ask all interested under cat.
First, a little theory. According to Wikipedia, this standard provides for the transfer of data to the subscriber over a cable television network with a maximum speed of up to 42 Mbps. (with a bandwidth of 6 MHz and the use of multipoint amplitude modulation 256 QAM) and receiving data from the subscriber at speeds up to 10.24 Mbit / s.
The most expensive and, accordingly, the most important part of building a network based on cable TV is the CMTS. In our case, it will be Casa C3200, about which I want to talk today.
')

What are its advantages?
Like the third generation CMTS, the Casa C3200 has a lot of advantages over the older CMTS.
- Today, the C3200 has high capacity when combining downstream (up to 24) and upstream (up to 8) channels. The bandwidth can easily reach 1 Gbit / s per subscriber.
- The C3200 has a higher channel density than its predecessors (support for up to 120 QAM channels downstream is possible).
- The C3200 supports the complete separation of downstream channel capacities from upstream channels in a single physical chassis, and thus provides flexible control of the downsream / upstream speed ratio.
- Full compliance with the specifications of DOCSIS / EuroDOCSIS 1.1 and DOCSIS / EuroDOCSIS 2.0.
- Extended frequency range - downstream frequency range increased to 1 GHz (48 ~ 1002 MHz).
Modularity and architecture flexibility
The CMTS C3200 has a compact 3RU form factor. It has a modular architecture that gives the cable operator maximum flexibility in the selection of equipment in accordance with the services provided. The C3200 consists of a base system with one slot for a switching and control module, six slots for DOCSIS modules (DQM modules for downstream or DCU modules for upstream). Any combination of downstream and upstream modules is supported by the platform. This allows you to flexibly adjust the downstream / upstream ratio. The DOCSIS QAM (DQM) module is a complete module under the DOCSIS downstream, which includes the processing of DOCSIS, QoS, DOCSIS downstream MAC, PHY, and up-conversion packets. There are 3 versions of downstream modules, 8-channel DQM 08, 16-channel DQM 16 and 24-channel DQM 24. All versions have 4 output ports.
The DOCSIS Control and Upstream Module (DCU) is a complete module under the DOCSIS upstream, which includes the processing of DOCSIS packets, upstream MACs and receivers. There are 2 versions of DCU modules, 8-channel DCU08 and 4-channel DCU04. In total, the C3200 platform supports various configurations from 8 DSx40US to 120DSx8US, and all this in 3 RU. A typical configuration using channel bonding can be 32DSx32US for a 1: 1 channel ratio, or 48DSx24US for a 2: 1 channel ratio. Each downstream QAM channel can support DOCSIS or MPEG / DVB-C video or a combination of these. In the minimum configuration, the C3200 has one DQM08 module and one DCU04 - 8DSx4US.
A little about the interface?
The C3200 has a user-friendly console interface and provides the user with extensive management capabilities such as
show cable modem summary total
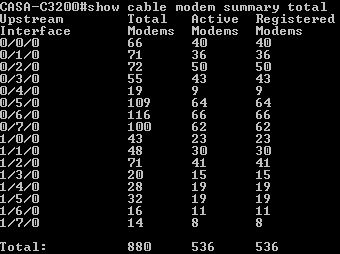
which allows you to see the number of modems on each of the interfaces, or
show docsis channel utilization
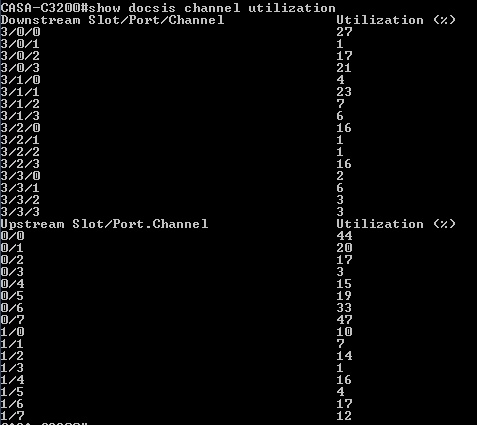
which allows you to view the workload of all direct and reverse channels.
When you click on "?" smart C3200 will give a list of possible continuation of commands, while maintaining all previously written text

A little bit more about setting up
I will not post a full working config, but I would like to highlight some interesting points.
- Mac domains:
to reduce the time the modem searches for its frequency, the forward and reverse channels are combined in Mac domains, which allows modems physically on a specific upstream to choose from the ones provided in the domain.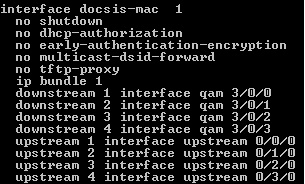
- Service groups and balancing within the domain:
C3200 allows you to do modem balancing within the domain either by the number of modems on the interface, or by channel utilization; to do this, you need to create service groups that define the forward or reverse channels on which such balancing is possible.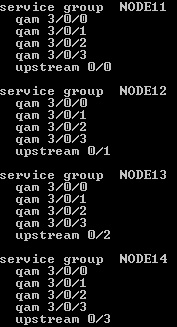
- Changing channel modulation depending on Signal Noise Ratio (SNR):
snr'y unstable and it often happens that because of the noise their level falls. In this case, the C3200 itself changes the modulation on the channel depending on its settings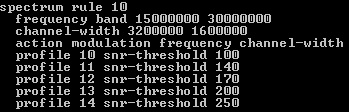
the profiles themselves look like this:
Well, at the end of the photo C3200 in greenhouse conditions:

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/134438/
All Articles