Writing GOST crypto-provider
The secrets of creating CSP for Windows are disclosed in the article of Yu.S.Zyryanov .
Russian GOST cryptographic algorithms are implemented in OpenSSL Gost .
Surprised that on the Internet, it was not possible to find confirmation that someone created the GOST crypto-provider interface for Windows using the above tools.
')
You would think that this task is only possible for large commercial companies with extensive experience in the field of information security, for example, such as:
- LLC Lissi
- OJSC InfoTeKS
- CJSC Signal-KOM
- OKB CAD
- and of course, CRYPTO-PRO LLC
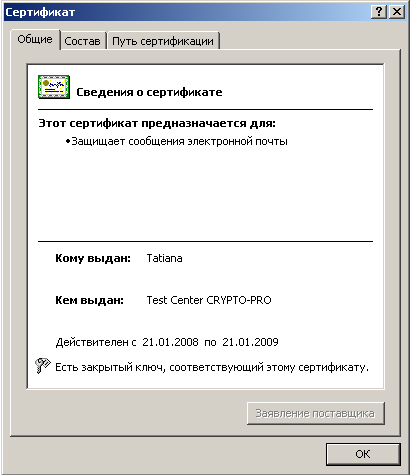
To begin with, we’ll restrict ourselves to small things; we’ll make it possible to check the integrity of GOST certificates using standard Windows tools, as in the figure. For simplicity, the creation of EDS will not be considered, we will not touch on the topic of key generation. In all places of the provider, except for digital signature verification and hashing functions, stubs already in the example from Microsoft will be used in the form of return TRUE, etc. The author plans to write a cycle of articles on the creation of a crypto-provider and in the future all these shortcomings will be gradually eliminated.
At the first stage, we need to do not so much, namely, first complete the points described in the article of Yu.S.Zyryanov, then get a list of OIDs from RFC-4357 , compile the OpenSSL library in terms of implementing GOST cryptoalgorithms, and finally, find Real root certificates CA , you can not only root, to test what we did.
So let's get started.
Downloading source
To get started, you need to download the Microsoft Cryptographic Service Provider Development Kit by clicking on the green Download Now button.
I apologize for the indirect link, but I could not find CSPDK on the site www.microsoft.com . It seems that it has been removed from the site, and the above link contains an outdated version from 2001, but even this one is quite suitable for us. After downloading and unpacking, we find the file csp.c in the sources and rename it to xyzcsp.c for subsequent modifications, csp.def and csp.rc - to xyzcsp.def and xyzcsp.rc respectively
Next, download the OpenSSL library. At the time of this writing, it has version 1.0.0e
Registration of crypto-provider xyzcsp.dll
We register the crypt provider in the registry. To do this, execute (with administrator rights) the file below with the command "regedit xyzcsp.reg"
File xyzcsp.reg:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Cryptography\Defaults\Provider\XYZ Provider] "Image Path"="xyzcsp.dll" "Type"=dword:0000007B [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Cryptography\Defaults\Provider Types\Type 123] "Name"="XYZ Provider" [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Cryptography\OID\EncodingType 0\CryptDllFindOIDInfo] [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Cryptography\OID\EncodingType 0\CryptDllFindOIDInfo\1.2.643.2.2.19!1] "Name"="GOST R 34.10-2001" "Algid"=dword:00002036 "ExtraInfo"=hex:00,00,00,00 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Cryptography\OID\EncodingType 0\CryptDllFindOIDInfo\1.2.643.2.2.3!2] "Name"="GOST R 34.11/34.10-2001" "Algid"=dword:00008037 "ExtraInfo"=hex:36,20,00,00,00,00,00,00 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Cryptography\OID\EncodingType 1\CryptDllConvertPublicKeyInfo] [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Cryptography\OID\EncodingType 1\CryptDllConvertPublicKeyInfo\1.2.643.2.2.19] "Dll"="xyzcsp.dll" "FuncName"="xyz_ConvertPublicKeyInfo" [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Cryptography\OID\EncodingType 1\CryptDllConvertPublicKeyInfo\1.2.643.2.2.98] "Dll"="xyzcsp.dll" "FuncName"="xyz_ConvertPublicKeyInfo" OpenSSL library
We'll leave the OpenSSL build from source, behind the scenes, just note that it’s easy, you need to have perl and MS Visual Studio installed, you need to follow the instructions in the Install.W32 file to compile, then you will get in the directory C: \ xyzcsp \ openssl-1.0.0e \ tmp32dll is a set of object files, which for simplicity I have collected into one file openssl.lib, which I used in my project.
Flist.txt file:
bf_buff.obj aes_core.obj aes_wrap.obj ameth_lib.obj asn1_gen.obj asn1_lib.obj asn1_par.obj asn_mime.obj asn_moid.obj asn_pack.obj a_bitstr.obj a_bool.obj a_bytes.obj a_d2i_fp.obj a_digest.obj a_dup.obj a_enum.obj a_gentm.obj a_i2d_fp.obj a_int.obj a_mbstr.obj a_object.obj a_octet.obj a_print.obj a_set.obj a_sign.obj a_strex.obj a_strnid.obj a_time.obj a_type.obj a_utctm.obj a_utf8.obj a_verify.obj bio_asn1.obj bio_b64.obj bio_cb.obj bio_enc.obj bio_err.obj bio_lib.obj bio_md.obj bio_ndef.obj bio_ok.obj bio_pk7.obj bio_ssl.obj bn_add.obj bn_asm.obj bn_blind.obj bn_const.obj bn_ctx.obj bn_depr.obj bn_div.obj bn_err.obj bn_exp.obj bn_exp2.obj bn_gcd.obj bn_gf2m.obj bn_kron.obj bn_lib.obj bn_mod.obj bn_mont.obj bn_mpi.obj bn_mul.obj bn_nist.obj bn_prime.obj bn_print.obj bn_rand.obj bn_recp.obj bn_shift.obj bn_sqr.obj bn_sqrt.obj bn_word.obj bss_dgram.obj bss_fd.obj bss_file.obj bss_log.obj bss_mem.obj bss_null.obj bss_sock.obj buffer.obj buf_err.obj by_dir.obj by_file.obj b_dump.obj b_print.obj b_sock.obj ca.obj camellia.obj cbc128.obj cbc_cksm.obj cbc_enc.obj cfb128.obj cfb64ede.obj cfb64enc.obj cfb_enc.obj ciphers.obj cmll_cbc.obj cmll_cfb.obj cmll_ctr.obj cmll_ecb.obj cmll_misc.obj cmll_ofb.obj cms.obj cms_asn1.obj cms_att.obj cms_cd.obj cms_dd.obj cms_enc.obj cms_env.obj cms_err.obj cms_ess.obj cms_io.obj cms_lib.obj cms_sd.obj cms_smime.obj comp_err.obj comp_lib.obj conf_api.obj conf_def.obj conf_err.obj conf_lib.obj conf_mall.obj conf_mod.obj conf_sap.obj cpt_err.obj crl.obj crl2p7.obj cryptlib.obj ctr128.obj cts128.obj cversion.obj c_all.obj c_allc.obj c_alld.obj c_cfb64.obj c_ecb.obj c_enc.obj c_ofb64.obj c_rle.obj c_skey.obj c_zlib.obj d1_both.obj d1_clnt.obj d1_enc.obj d1_lib.obj d1_meth.obj d1_pkt.obj d1_srvr.obj d2i_pr.obj d2i_pu.obj des_enc.obj des_old.obj des_old2.obj dgst.obj dh.obj dhparam.obj dh_ameth.obj dh_asn1.obj dh_check.obj dh_depr.obj dh_err.obj dh_gen.obj dh_key.obj dh_lib.obj dh_pmeth.obj dh_prn.obj digest.obj dsa.obj dsaparam.obj dsa_ameth.obj dsa_asn1.obj dsa_depr.obj dsa_err.obj dsa_gen.obj dsa_key.obj dsa_lib.obj dsa_ossl.obj dsa_pmeth.obj dsa_prn.obj dsa_sign.obj dsa_vrf.obj dso_beos.obj dso_dl.obj dso_dlfcn.obj dso_err.obj dso_lib.obj dso_null.obj dso_openssl.obj dso_vms.obj dso_win32.obj ebcdic.obj ec.obj ec2_mult.obj ec2_smpl.obj ecb3_enc.obj ecb_enc.obj ech_err.obj ech_key.obj ech_lib.obj ech_ossl.obj eck_prn.obj ecparam.obj ecp_mont.obj ecp_nist.obj ecp_smpl.obj ecs_asn1.obj ecs_err.obj ecs_lib.obj ecs_ossl.obj ecs_sign.obj ecs_vrf.obj ec_ameth.obj ec_asn1.obj ec_check.obj ec_curve.obj ec_cvt.obj ec_err.obj ec_key.obj ec_lib.obj ec_mult.obj ec_pmeth.obj ec_print.obj ede_cbcm_enc.obj enc.obj encode.obj enc_read.obj enc_writ.obj engine.obj eng_all.obj eng_cnf.obj eng_cryptodev.obj eng_ctrl.obj eng_dyn.obj eng_err.obj eng_fat.obj eng_init.obj eng_lib.obj eng_list.obj eng_openssl.obj eng_pkey.obj eng_table.obj err.obj errstr.obj err_all.obj err_prn.obj evp_acnf.obj evp_asn1.obj evp_enc.obj evp_err.obj evp_key.obj evp_lib.obj evp_pbe.obj evp_pkey.obj ex_data.obj e_aes.obj e_bf.obj e_camellia.obj e_cast.obj e_des.obj e_des3.obj e_gost_err.obj e_idea.obj e_null.obj e_old.obj e_rc2.obj e_rc4.obj e_rc5.obj e_seed.obj e_xcbc_d.obj fcrypt.obj fcrypt_b.obj f_enum.obj f_int.obj f_string.obj gendh.obj gendsa.obj genpkey.obj genrsa.obj gost2001.obj gost2001_keyx.obj gost89.obj gost94_keyx.obj gosthash.obj gost_ameth.obj gost_asn1.obj gost_crypt.obj gost_ctl.obj gost_eng.obj gost_keywrap.obj gost_md.obj gost_params.obj gost_pmeth.obj gost_sign.obj hmac.obj hm_ameth.obj hm_pmeth.obj i2d_pr.obj i2d_pu.obj i_cbc.obj i_cfb64.obj i_ecb.obj i_ofb64.obj i_skey.obj krb5_asn.obj kssl.obj lhash.obj lh_stats.obj md4_dgst.obj md4_one.obj md5_dgst.obj md5_one.obj mdc2dgst.obj mdc2_one.obj md_rand.obj mem.obj mem_clr.obj mem_dbg.obj m_dss.obj m_dss1.obj m_ecdsa.obj m_md4.obj m_md5.obj m_mdc2.obj m_null.obj m_ripemd.obj m_sha.obj m_sha1.obj m_sigver.obj m_wp.obj names.obj nseq.obj nsseq.obj n_pkey.obj obj_dat.obj obj_err.obj obj_lib.obj obj_xref.obj ocsp.obj ocsp_asn.obj ocsp_cl.obj ocsp_err.obj ocsp_ext.obj ocsp_ht.obj ocsp_lib.obj ocsp_prn.obj ocsp_srv.obj ocsp_vfy.obj ofb128.obj ofb64ede.obj ofb64enc.obj ofb_enc.obj o_dir.obj o_names.obj o_str.obj o_time.obj p12_add.obj p12_asn.obj p12_attr.obj p12_crpt.obj p12_crt.obj p12_decr.obj p12_init.obj p12_key.obj p12_kiss.obj p12_mutl.obj p12_npas.obj p12_p8d.obj p12_p8e.obj p12_utl.obj p5_crpt.obj p5_crpt2.obj p5_pbe.obj p5_pbev2.obj p8_pkey.obj passwd.obj pcbc_enc.obj pcy_cache.obj pcy_data.obj pcy_lib.obj pcy_map.obj pcy_node.obj pcy_tree.obj pem_all.obj pem_err.obj pem_info.obj pem_lib.obj pem_oth.obj pem_pk8.obj pem_pkey.obj pem_seal.obj pem_sign.obj pem_x509.obj pem_xaux.obj pk12err.obj pk7_asn1.obj pk7_attr.obj pk7_doit.obj pk7_lib.obj pk7_mime.obj pk7_smime.obj pkcs12.obj pkcs7.obj pkcs7err.obj pkcs8.obj pkey.obj pkeyparam.obj pkeyutl.obj pmeth_fn.obj pmeth_gn.obj pmeth_lib.obj pqueue.obj prime.obj pvkfmt.obj p_dec.obj p_enc.obj p_lib.obj p_open.obj p_seal.obj p_sign.obj p_verify.obj qud_cksm.obj rand.obj randfile.obj rand_egd.obj rand_err.obj rand_key.obj rand_lib.obj rand_nw.obj rand_os2.obj rand_unix.obj rand_win.obj rc2cfb64.obj rc2ofb64.obj rc2_cbc.obj rc2_ecb.obj rc2_skey.obj rc4_enc.obj rc4_skey.obj read2pwd.obj req.obj rmd_dgst.obj rmd_one.obj rpc_enc.obj rsa.obj rsautl.obj rsa_ameth.obj rsa_asn1.obj rsa_chk.obj rsa_depr.obj rsa_eay.obj rsa_err.obj rsa_gen.obj rsa_lib.obj rsa_none.obj rsa_null.obj rsa_oaep.obj rsa_pk1.obj rsa_pmeth.obj rsa_prn.obj rsa_pss.obj rsa_saos.obj rsa_sign.obj rsa_ssl.obj rsa_x931.obj s23_clnt.obj s23_lib.obj s23_meth.obj s23_pkt.obj s23_srvr.obj s2_clnt.obj s2_enc.obj s2_lib.obj s2_meth.obj s2_pkt.obj s2_srvr.obj s3_both.obj s3_clnt.obj s3_enc.obj s3_lib.obj s3_meth.obj s3_pkt.obj s3_srvr.obj seed.obj seed_cbc.obj seed_cfb.obj seed_ecb.obj seed_ofb.obj sess_id.obj set_key.obj sha1dgst.obj sha1_one.obj sha256.obj sha512.obj sha_dgst.obj sha_one.obj smime.obj speed.obj spkac.obj ssl_algs.obj ssl_asn1.obj ssl_cert.obj ssl_ciph.obj ssl_err.obj ssl_err2.obj ssl_lib.obj ssl_rsa.obj ssl_sess.obj ssl_stat.obj ssl_txt.obj stack.obj str2key.obj s_cb.obj s_client.obj s_server.obj s_socket.obj s_time.obj t1_clnt.obj t1_enc.obj t1_lib.obj t1_meth.obj t1_reneg.obj t1_srvr.obj tasn_dec.obj tasn_enc.obj tasn_fre.obj tasn_new.obj tasn_prn.obj tasn_typ.obj tasn_utl.obj tb_asnmth.obj tb_cipher.obj tb_dh.obj tb_digest.obj tb_dsa.obj tb_ecdh.obj tb_ecdsa.obj tb_pkmeth.obj tb_rand.obj tb_rsa.obj tb_store.obj ts.obj ts_asn1.obj ts_conf.obj ts_err.obj ts_lib.obj ts_req_print.obj ts_req_utils.obj ts_rsp_print.obj ts_rsp_sign.obj ts_rsp_utils.obj ts_rsp_verify.obj ts_verify_ctx.obj txt_db.obj t_bitst.obj t_crl.obj t_pkey.obj t_req.obj t_spki.obj t_x509.obj t_x509a.obj uid.obj ui_compat.obj ui_err.obj ui_lib.obj ui_openssl.obj ui_util.obj uplink.obj v3err.obj v3_addr.obj v3_akey.obj v3_akeya.obj v3_alt.obj v3_asid.obj v3_bcons.obj v3_bitst.obj v3_conf.obj v3_cpols.obj v3_crld.obj v3_enum.obj v3_extku.obj v3_genn.obj v3_ia5.obj v3_info.obj v3_int.obj v3_lib.obj v3_ncons.obj v3_ocsp.obj v3_pci.obj v3_pcia.obj v3_pcons.obj v3_pku.obj v3_pmaps.obj v3_prn.obj v3_purp.obj v3_skey.obj v3_sxnet.obj v3_utl.obj verify.obj version.obj wp_block.obj wp_dgst.obj x509.obj x509cset.obj x509name.obj x509rset.obj x509spki.obj x509type.obj x509_att.obj x509_cmp.obj x509_d2.obj x509_def.obj x509_err.obj x509_ext.obj x509_lu.obj x509_obj.obj x509_r2x.obj x509_req.obj x509_set.obj x509_trs.obj x509_txt.obj x509_v3.obj x509_vfy.obj x509_vpm.obj xcbc_enc.obj x_algor.obj x_all.obj x_attrib.obj x_bignum.obj x_crl.obj x_exten.obj x_info.obj x_long.obj x_name.obj x_nx509.obj x_pkey.obj x_pubkey.obj x_req.obj x_sig.obj x_spki.obj x_val.obj x_x509.obj x_x509a.obj I apologize for such a long list, but I don’t know a simple way how you can find out which obj files from this lib file are needed for building and which ones are not. Creating a map file does not help, so I had to use an almost complete list of obj files from the tmp32dll directory.
Create openssl.lib with the make_lib.bat command.
make_lib.bat:
call "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio 10.0\VC\vcvarsall.bat" lib /out:openssl.lib @flist.txt Let's start writing the necessary hashing functions and verifying the digital signature in accordance with GOST.
Let's call them my_hash_gost () and my_verify_gost (), respectively. To get them, ready-made chunks from the OpenSSL text were used, but a lot of time was spent on debugging, in particular, to understand that when we do a “flipping” of data, changing the order of bytes, we don’t need to turn the hash, and everything else , including public key and EDS - needed.
A bit of history. Initially, the my_verify_gost function was tested with a hash equal to a constant in all 32 bytes. And it saved me. Because the function earned fairly quickly, but when a real hash was inserted, consisting of a fairly random set of bytes, immediately after this the EDS was no longer checked. I could not understand for a long time that the constant hash is a mirror, therefore it is suitable for the function to work without turning it over. I was lucky if testing began with a real hash, then the OpenSSL library would be hard enough to configure to verify digital signature certificates, because this “tricky” behavior of the hash is not obvious enough.
Paste these lines into the xyzcsp.c file right after all #include there
#include "gosthash.h" #include "gost_lcl.h" static void perevorot_buf(unsigned char *obj, int k) { char buf[64]; int i; for( i = 0; i < k; i++ ) buf[i] = obj[k-1-i]; memcpy(obj, buf, k); } static int pkey_gost01_cp_verify(EC_KEY* pub_key, const unsigned char *sig, size_t siglen, unsigned char *tbs, size_t tbs_len) { int ok = 0; DSA_SIG *s=unpack_cp_signature(sig,siglen); if (!s) return 0; if (pub_key) ok = gost2001_do_verify(tbs,tbs_len,s,pub_key); DSA_SIG_free(s); return ok; } int my_verify_gost(char *in_hash, const BYTE *in_sign, char *in_pub1, char *in_pub2, int nid) { int res, errcode; EC_KEY *eckey = NULL; unsigned char sig[64], tbs[32]; int siglen=64, tbs_len=32; BIGNUM *X=NULL,*Y=NULL; char perevorot_pub[32]; EC_POINT *pub_key; // memcpy(tbs, in_pub1, 32); perevorot_buf(tbs, 32); X= getbnfrombuf((const unsigned char*)tbs,32); memcpy(tbs, in_pub2, 32); perevorot_buf(tbs, 32); Y= getbnfrombuf((const unsigned char*)tbs,32); memcpy(tbs, in_hash, 32); // ! perevorot_buf(tbs, 32); memcpy(sig, in_sign, 64); perevorot_buf(sig, 64); // if (!(eckey = EC_KEY_new())) { errcode = 1; goto err_exit; } if (!fill_GOST2001_params(eckey, nid)) { errcode = 2; goto err_exit; } if (!(pub_key = EC_POINT_new(EC_KEY_get0_group(eckey)))) { errcode = 3; goto err_exit; } if (!EC_POINT_set_affine_coordinates_GFp(EC_KEY_get0_group(eckey) ,pub_key,X,Y,NULL)) { errcode = 4; goto err_exit; } if (!EC_KEY_set_public_key(eckey,pub_key)) { errcode = 5; goto err_exit; } if (!pkey_gost01_cp_verify(eckey, sig, siglen, tbs, tbs_len)) { errcode = 6; goto err_exit; } else errcode = 0; //success err_exit: if (pub_key) EC_POINT_free(pub_key); if (X) BN_free(X); if (Y) BN_free(Y); if (eckey) EC_KEY_free(eckey); return errcode; } void my_hash_gost(const BYTE *buf, int buflen, char *hash_res) { gost_subst_block *b= &GostR3411_94_CryptoProParamSet; gost_hash_ctx ctx; init_gost_hash_ctx(&ctx,b); start_hash(&ctx); hash_block(&ctx,buf,buflen); finish_hash(&ctx,(byte *)hash_res); } // char hash_gost[32]; char hash_sha1[20]; char public_key[64]; Provider XYZ Provider
Now let's do, finally, the provider. Choose his name: "XYZ Provider". Accordingly, the main file will be called xyzcsp.c, also need the files xyzcsp.def and xyzcsp.rc
In the original sample, which can be found in the CSPDK, in the csp.c file, we are only interested in the functions CPAcquireContext, CPHashData, CPGetHashParam, CPVerifySignature. It is easy to see that these are functions for creating a provider handle, hashing function and verifying digital signature. Replace these functions with the ones below.
In addition to them, we will write one remarkable function, xyz_ConvertPublicKeyInfo, which will be engaged in converting the public key of the digital signature. Do not forget to add xyz_ConvertPublicKeyInfo to the xyzcsp.def file so that the linker exports this name. The conversion will consist in ignoring the first two bytes in the ASN1 record of the public key notation, thereby obtaining the key in its pure form, the two halves of 32 bytes each.
Remove the DllMain function and the old CPAcquireContext, CPHashData, CPGetHashParam, CPVerifySignature from xyzcsp.c, remove the outdated DESCRIPTION command and the names DllRegisterServer and DllUnregisterServer from xyzcsp.def
Add to the end of the xyzcsp.c file:
BOOL WINAPI CPAcquireContext( OUT HCRYPTPROV *phProv, IN LPCSTR szContainer, IN DWORD dwFlags, IN PVTableProvStruc pVTable) { *phProv = 123; return TRUE; } BOOL WINAPI CPHashData( IN HCRYPTPROV hProv, IN HCRYPTHASH hHash, IN CONST BYTE *pbData, IN DWORD cbDataLen, IN DWORD dwFlags) { my_hash_gost(pbData, cbDataLen, hash_gost); SHA1(pbData, cbDataLen, hash_sha1); return TRUE; } BOOL WINAPI CPGetHashParam( IN HCRYPTPROV hProv, IN HCRYPTHASH hHash, IN DWORD dwParam, OUT LPBYTE pbData, IN OUT LPDWORD pcbDataLen, IN DWORD dwFlags) { switch(dwParam) { case HP_HASHVAL: if(*pcbDataLen == 20) // sha1 { memcpy(pbData, hash_sha1, 20); break; } default: *pcbDataLen = 0; SetLastError(E_INVALIDARG); return FALSE; } return TRUE; } BOOL WINAPI CPVerifySignature( IN HCRYPTPROV hProv, IN HCRYPTHASH hHash, IN CONST BYTE *pbSignature, IN DWORD cbSigLen, IN HCRYPTKEY hPubKey, IN LPCWSTR szDescription, IN DWORD dwFlags) { #define NTE_IC_ERROR_PREDEF 0x89900000L INT err; err = my_verify_gost(hash_gost, pbSignature, public_key, public_key+32, NID_id_GostR3410_2001_CryptoPro_A_ParamSet); if ( err ) { SetLastError( NTE_IC_ERROR_PREDEF | err ); return FALSE; } return TRUE; } BOOL WINAPI xyz_ConvertPublicKeyInfo( DWORD dwCertEncodingType, VOID *EncodedKeyInfo, DWORD dwAlg, DWORD dwFlags, BYTE** ppStructInfo, DWORD* StructLen ) { memcpy(public_key, ((CERT_PUBLIC_KEY_INFO*)EncodedKeyInfo)->PublicKey.pbData + 2, 64); return TRUE; } I think it’s unnecessary to comment on the sources of the crypto-provider in detail. Everything is clear in the text.
Writing a test program
Why do you need a separate test program? In addition to running tests, it will patch the system to change the functions of SystemFunction035 in ADVAPI32.dll and I_CryptGetDefaultCryptProv in CRYPT32.dll to their “correct” version. This program will work successfully in both Windows XP and Windows 7.
At the end of the article shows how to patch the system files in Windows XP SP3, in this case, a special test program will not be needed.
File testcsp.cpp:
#include "stdafx.h" #include <windows.h> #include <wincrypt.h> typedef HCRYPTPROV (WINAPI *pI_CryptGetDefaultCryptProv)(ALG_ID algid); HCRYPTPROV hProv = NULL; typedef int (__stdcall *def_CryptExtOpenCER)( HWND hwnd, HINSTANCE hinst, LPSTR lpszCmdLine, int nCmdShow); def_CryptExtOpenCER CryptExtOpenCER; typedef int (__stdcall *def_MyProc)(void); def_MyProc MyProc; #define PATCH_NUM 2 char *patch_list[2*PATCH_NUM]={ "ADVAPI32.dll","SystemFunction035", "CRYPT32.dll","I_CryptGetDefaultCryptProv" }; void WriteMem(int pos, char *patch, int len) { DWORD my_id = GetCurrentProcessId(); HANDLE p_hand = OpenProcess(PROCESS_VM_WRITE | PROCESS_VM_OPERATION, NULL, my_id); if (WriteProcessMemory(p_hand, (LPDWORD)pos, patch, len, NULL)==0) { printf("Error write to memory\nHint: run from Administrator rigths"); } CloseHandle(p_hand); } HCRYPTPROV PASCAL old_I_CryptGetDefaultCryptProv(int AlgID) //call MS Provider { __asm mov eax,0; //, 10 __asm mov eax,0; return NULL; } HCRYPTPROV PASCAL my_I_CryptGetDefaultCryptProv(int AlgID) { if (AlgID!=0 && AlgID!=0x2036) return old_I_CryptGetDefaultCryptProv(AlgID); //old MS return hProv; } int StartPatch(void) { BYTE *p; HMODULE h_dll; char buf[10]; DWORD new_addr; for(int i=0;i<PATCH_NUM;i++) { h_dll = LoadLibrary(patch_list[i*2]); if (h_dll==NULL) { printf("Error! Can not LoadLibrary(%s)\n", patch_list[i*2]); return 1; } MyProc = (def_MyProc)GetProcAddress(h_dll, patch_list[i*2+1]); if (MyProc==NULL) { printf("Error! Can not GetProcAddress(%s)\n", patch_list[i*2+1]); return 1; } p = (BYTE*)MyProc; if (i==1) { memcpy(buf, p, 5); buf[5]=0xe9; new_addr = (DWORD)p; new_addr -= (DWORD)old_I_CryptGetDefaultCryptProv; new_addr -= 5; memcpy(buf+6, &new_addr, 4); WriteMem((DWORD)old_I_CryptGetDefaultCryptProv, buf, 10); buf[0]=0xe9; new_addr = (DWORD)my_I_CryptGetDefaultCryptProv; new_addr -= (DWORD)MyProc; new_addr -= 5; memcpy(buf+1, &new_addr, 4); WriteMem((DWORD)MyProc, buf, 5); } else { WriteMem((int)p, "\xb8\x01\x00\x00\x00\xC2\x04\x00", 8); //mov ax,1 - ret 4 } } return 0; } int RunCert(char *certName) { HMODULE h_dll; h_dll = LoadLibrary("C:\\windows\\system32\\CRYPTEXT.dll"); if (h_dll==NULL) return 1; CryptExtOpenCER = (def_CryptExtOpenCER)GetProcAddress(h_dll, "CryptExtOpenCER"); if (CryptExtOpenCER==NULL) return 2; CryptExtOpenCER(NULL, NULL, certName, SW_SHOW); FreeLibrary(h_dll); return 0; } int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { if (StartPatch()) { printf("Error Patch\n"); return 1; } if (RCRYPT_FAILED(CryptAcquireContext(&hProv, "test", NULL, 123, 0))) { printf("CryptAcquireConext returned error %x\n", GetLastError()); printf("FAILED\n"); return 1; } printf("SUCCEED\n"); RunCert("gnivc_2006.cer"); RunCert("rootsber.cer"); return 0; } File compilation
Provider compilation file comp_xyzcsp.bat:
call "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio 10.0\VC\vcvarsall.bat" cl /I"..\include" /nologo /MT /O2 /c xyzcsp.c rc /I"..\include" xyzcsp.rc link /SUBSYSTEM:WINDOWS",5.0" /NODEFAULTLIB /DLL /DEF:xyzcsp.def /MACHINE:x86 /OUT:xyzcsp.dll xyzcsp.obj openssl.lib advapi32.lib kernel32.lib msvcrt.lib gdi32.lib user32.lib xyzcsp.res copy xyzcsp.dll ..\testcsp\ rem copy xyzcsp.dll c:\windows\system32 Compile test comp_test.bat file:
call "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio 10.0\VC\vcvarsall.bat" cl /I"..\include" testcsp.cpp advapi32.lib Certificates for testing
File gnivc_2006.cer, in which lies the root certificate of the FTS:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIDGjCCAsegAwIBAgIQPx2a1ZtKRIBLiHKukksltTAKBgYqhQMCAgMFADCBwDEe MBwGCSqGSIb3DQEJARYPdWNpbmZvQGduaXZjLnJ1MQswCQYDVQQGEwJSVTEVMBMG A1UEBwwM0JzQvtGB0LrQstCwMTAwLgYDVQQKDCfQpNCT0KPQnyDQk9Cd0JjQktCm INCk0J3QoSDQoNC+0YHRgdC40LgxMDAuBgNVBAsMJ9Cj0LTQvtGB0YLQvtCy0LXR gNGP0Y7RidC40Lkg0YbQtdC90YLRgDEWMBQGA1UEAxMNR05JVkMgRk5TIFJVUzAe Fw0wNjA5MjcwOTI5NTdaFw0xMjA5MjcwOTM4MjdaMIHAMR4wHAYJKoZIhvcNAQkB Fg91Y2luZm9AZ25pdmMucnUxCzAJBgNVBAYTAlJVMRUwEwYDVQQHDAzQnNC+0YHQ utCy0LAxMDAuBgNVBAoMJ9Ck0JPQo9CfINCT0J3QmNCS0KYg0KTQndChINCg0L7R gdGB0LjQuDEwMC4GA1UECwwn0KPQtNC+0YHRgtC+0LLQtdGA0Y/RjtGJ0LjQuSDR htC10L3RgtGAMRYwFAYDVQQDEw1HTklWQyBGTlMgUlVTMGMwHAYGKoUDAgITMBIG ByqFAwICIwEGByqFAwICHgEDQwAEQCzY8VGw9ged02ijaj2KWOMXJVvzY1FEcg7G xedUtKx0wqyTVti0kmodEmm2cVfAbDkp0xAdBS9/mdDfeIrKXLajgZYwgZMwCwYD VR0PBAQDAgGGMA8GA1UdEwEB/wQFMAMBAf8wHQYDVR0OBBYEFBMQt5JPv+eiD7j1 nYkVJssQ6/RfMBAGCSsGAQQBgjcVAQQDAgEAMEIGCCsGAQUFBwEBBDYwNDAyBggr BgEFBQcwAoYmaHR0cDovL3d3dy5nbml2Yy5ydS91Yy9HTklWQ0ZOU1JVUy5jcnQw CgYGKoUDAgIDBQADQQDgEyWPI+fdXXiTYMLHdV76v8kVFIxCHCYtastcvZiM3cG1 wTFhio8fDx6sLgHHriOwQFg0zRUYHIs9nZEptLvM -----END CERTIFICATE----- The rootsber.cer file, which contains the Sberbank root certificate:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIDKjCCAtmgAwIBAgIGMDBDQT0HMAgGBiqFAwICAzCBwTELMAkGA1UEBhMCUlUx LTArBgNVBAoMJNCh0LHQtdGA0LHQsNC90Log0KDQvtGB0YHQuNC4INCe0JDQnjE4 MDYGA1UECwwv0JTQtdC/0LDRgNGC0LDQvNC10L3RgiDQsdC10LfQvtC/0LDRgdC9 0L7RgdGC0LgxJjAkBgNVBAMMHdCh0LHQtdGA0LHQsNC90Log0KDQvtGB0YHQuNC4 MSEwHwYJKoZIhvcNAQkBFhJjYXNicmZAc2JlcmJhbmsucnUwHhcNMDkwODA1MDAw MDAwWhcNMTcwODA1MDAwMDAwWjCBwTELMAkGA1UEBhMCUlUxLTArBgNVBAoMJNCh 0LHQtdGA0LHQsNC90Log0KDQvtGB0YHQuNC4INCe0JDQnjE4MDYGA1UECwwv0JTQ tdC/0LDRgNGC0LDQvNC10L3RgiDQsdC10LfQvtC/0LDRgdC90L7RgdGC0LgxJjAk BgNVBAMMHdCh0LHQtdGA0LHQsNC90Log0KDQvtGB0YHQuNC4MSEwHwYJKoZIhvcN AQkBFhJjYXNicmZAc2JlcmJhbmsucnUwYzAcBgYqhQMCAhMwEgYHKoUDAgIjAgYH KoUDAgIeAQNDAARAaYzyi29YQ9NC5cb/kq//J1kKhOgcvGWqsQu50mldjADTGfrl JUVXwu4fMUTHoF9TjY0O1kgrLYWT/kI4jABAWKOBsjCBrzAdBgNVHQ4EFgQUZmHo Zo41vw/U74ZlC8k/bcQODuowDAYDVR0TBAUwAwEB/zAzBgNVHR8ELDAqMCigJqAk hiJodHRwOi8vd3d3LnNicmYucnUvY2EvMDAwMHg1MDkuY3JsMAsGA1UdDwQEAwIC hDA+BgcqhQMDewMBBDMMMTAwQ0ExODUzetCa0L7RgNC90LXQstC+0Lkg0LrQu9GO 0Ycg0KPQpiDQodCRINCg0KQwCAYGKoUDAgIDA0EAD9Umnh/EZgjgQvpypdVwe0wa GnTi+dHhVwoNAX1tquxQNbAptbBs2OKzkRU7/mrBfDD4EdVV5xC1f2DTcH8NAg== -----END CERTIFICATE----- Work results
Run the test program, we get the result:

To remove the last obstacle, include the certificate in the list of trusted ones, as recommended. To do this, click the Install certificate button and click Next several times. At the end of testing, you need to remove the test certificate from the trusted root repository so as not to expose your system to possible danger.
After restarting the test, we see a different picture:

What was required to get.
Sberbank Root Certificate
With the certificate of Sberbank, this can not be done:

This is due to the fact that Sberbank uses the B constant from RFC 4357, namely GostR3410_2001_CryptoPro_B_ParamSet.
We then change the constant A to B in our xyzcsp.c file in the CPVerifySignature function, that is, when calling my_verify_gost we will use the following parameter: NID_id_GostR3410_2001_CryptoPro_B_ParamSet.
After compiling the provider and running the test, we observe the opposite picture, the FTS certificate is not checked, and Sberbank is working fine. It would seem a significant drawback, but for the simplest crypto-provider this is forgivable.
Of course, such an option is possible: check two EDS at once and, if at least one of them converges, declare that the EDS is correct, but this is fundamentally wrong. You need to look at the public key OID and look for the required parameters of the elliptic curve.
In the next article, which is now being prepared for publication, we will look at how to avoid such a situation in detail, and also write a function for creating EDS keys with various parameters.
Creating a universal patch
In conclusion, a few words about creating a universal patch.
For Windows XP SP3, simply substitute the following files:
c: \ windows \ system32 \ advapi32.dll
c: \ windows \ system32 \ dllcache \ advapi32.dll
c: \ windows \ system32 \ crypt32.dll
c: \ windows \ system32 \ dllcache \ crypt32.dll
You need to patch by booting from another disk in order for the system to be free (possible from the Windows boot disk in recovery mode), then we replace these two files both in the system32 directory and in system32 \ dllcache, where their copies are stored. Patching on a running system will fail, because the files are “locked” and cannot be changed.
After that, do not forget to copy the file with the xyzcsp.dll cryptographic provider to the c: \ windows \ system32 directory for the system to find it.
Now you can click on the certificate and it will be checked directly in the operating system, without launching special programs.
You need to replace the files with their patched version:
advapi32.dll C:\xyzcsp\PATCH\ADVAPI32.DLL 00017585: 8B B8 00017586: FF 01 00017587: 55 00 00017588: 8B 00 00017589: EC 00 0001758A: 81 C2 0001758B: EC 04 0001758C: 50 00 crypt32.dll C:\xyzcsp\PATCH\CRYPT32.DLL 00008F66: 8B E9 00008F67: FF 47 00008F68: 55 09 00008F69: 8B 00 00008F6A: EC 00 000098B2: 90 55 000098B3: 90 8B 000098B4: 90 EC 000098B5: 90 8B 000098B6: 90 45 000098B7: 90 08 000098B8: 53 83 000098B9: 00 F8 000098BA: 6F 00 000098BB: 00 74 000098BC: 66 21 000098BD: 00 3D 000098BE: 74 36 000098BF: 00 20 000098C0: 77 00 000098C2: 61 74 000098C3: 00 1A 000098C4: 72 3D 000098C5: 00 35 000098C6: 65 66 000098C8: 5C 00 000098C9: 00 74 000098CA: 50 13 000098CB: 00 3D 000098CC: 6F 37 000098CD: 00 80 000098CE: 6C 00 000098D0: 69 74 000098D1: 00 0C 000098D2: 63 3D 000098D3: 00 38 000098D4: 69 AA 000098D6: 65 00 000098D7: 00 74 000098D8: 73 05 000098D9: 00 E9 000098DA: 5C 8D 000098DB: 00 F6 000098DC: 4D FF 000098DD: 00 FF 000098DE: 69 6A 000098E0: 63 68 000098E1: 00 7B 000098E2: 72 00 000098E4: 6F 00 000098E5: 00 6A 000098E6: 73 00 000098E7: 00 8D 000098E8: 6F 05 000098E9: 00 40 000098EA: 66 A5 000098EB: 00 A7 000098EC: 74 77 000098ED: 00 50 000098EE: 5C 8D 000098EF: 00 45 000098F0: 53 08 000098F1: 00 50 000098F2: 79 FF 000098F3: 00 15 000098F4: 73 00 000098F5: 00 10 000098F6: 74 A7 000098F7: 00 77 000098F8: 65 83 000098F9: 00 F8 000098FA: 6D 00 000098FB: 00 74 000098FC: 43 DC 000098FD: 00 8B 000098FE: 65 45 000098FF: 00 08 00009900: 72 C9 00009901: 00 C2 00009902: 74 04 For Windows 7, you can also create a universal patch, anyone can try to do it yourself.
In a real system, in which a GOST cryptographic provider is installed, problems with a patch are usually solved by installing a special PatchEngine driver, which monitors the loading of system DLLs and patches them on the fly.
All files in one archive
In conclusion, I will provide a link by which all the files from this article can be downloaded in one archive:
files.mail.ru/1OVVDB
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/134037/
All Articles