What is the difference between femtocell and GSM repeater, Wi-Fi router and macro cell? Who uses which uplink?
The post about femtocells showed that you can easily get confused about what equipment is used: what is a base station, what is a Femto AP, how does all this relate to Wi-Fi and so on. In the topic is a simple explanation about the various types of equipment and the classification of base stations for multistandard cellular networks.
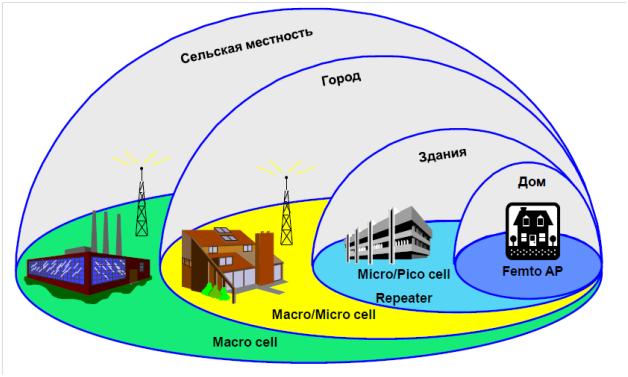
Network hierarchy
If you want to know what the thing is hanging on the next house and how it creates you a cellular coverage, welcome under the cat.
')
The first thing to understand is that consoles such as macro, pico, etc., do not characterize the change in the quantitative parameters of the base station, they only indicate the place of the class in the hierarchy.

Base station

Sector antennas
These are standard base stations on which the operator’s mobile network is built. The principles of operation, the transport solutions used, are given in any article about the architecture of cellular networks. The main transport at the moment is standard SDH-TDM networks, but the moment of mass transition to IP / Ethernet is getting closer. They are characterized by high power - up to 60W, large coverage radius - 10 ... 100 km, large mass-dimensional indicators (rack up to 200kg). There are varieties of macro base stations - such as distributed bases (Distributed BTS), but this classification is not significant. There are any standards allowed for use in Russia: GSM / UMTS / CDMA in the future - LTE .

Micro Base Station
A very common solution in the networks of a large operator. In fact, it is a compact version of the first type, with reduced characteristics in terms of base capacity, radiated power - up to 5 ... 10W, coverage radius - 1 ... 5 km and mass-dimensional characteristics (compact body weighing up to 50 kg). Used by the operator where it is difficult to install a macro base station, or where high power and capacity are not required. For example: large shopping centers, office complexes, remote villages, etc. Often used in conjunction with the Distributed Antenna System (DAS), which consists of cables and antennas spread across the building. Antennas can look different, for example, as in the subway:

Panel antennas
Also, there are GSM / UMTS / CDMA standards in the future - LTE.

Picosot

"Nanosote"
This is a more exotic option. Base station of low power office / home execution. As a backbone transport network, it uses only IP / Ethernet networks, in which the necessary bandwidth is reserved for passing traffic generated by the base station. Typical power up to 0.2W, dimensions - about a laptop. Despite its small size, it is still a base station that belongs to the operator and cannot be transferred to the subscriber for independent launch and use. Usually installed in the offices of corporate clients, or in places of possible concentration of users - in restaurants, hotels, etc.
Technically, GSM / UMTS / CDMA may also be in the future - LTE. However, now there is a practice - that the pico / nano base stations call only low-power GSM bases.

Home Femto
A femtocell is no longer a base station; it is an Access Point. The difference in terminology arises from the fact that this equipment is initially designed for use as a home or office, and it is assumed that the owner is the user. Transport - only IP / Ethernet, and both the channel allocated by the provider and the public Internet. The principal difference from all other types of base stations is the autoconfiguration when switched on in the transport network and connected to the operator’s network. Femto AP independently evaluates the radio parameters at the launch point, selects the best settings for itself, and is activated if the operator permits. For data protection, all interaction with the operator’s equipment begins only after the creation of the IPSec tunnel. Typical radiated power - up to 0.1W, dimensions - roughly correspond to a home Wi-Fi router.
Same GSM / UMTS / CDMA standards, in the future - LTE. However, now Femto AP is firmly associated only with the UMTS (3G) standard, in the future mass appearance of such LTE devices is expected.

GSM Repeater
This equipment is included in the review solely for the reason that many also consider it as equipment for creating a cellular network. It's a delusion! A repeater is just an external signal amplifier from a macro station, and its purpose is to transmit a signal from the street inside the building. The repeater does not create additional network capacity, that is, if the donor base station is overloaded - inside the building you also will not be able to use the phone due to overload. Despite the seeming simplicity of the device and its installation, the correct setup of the repeater requires specific skills and instruments to control the coating being created. Moreover, according to Russian law, only a licensed company can own such equipment, as well as install and run it. It is often impossible to use the repeater, since its work requires the installation of an external antenna on the facade of a building that receives a signal from a macro base station.
There are options for a variety of repeaters. Different power, performance and standards. The most common in the networks of operators received repeaters with a high gain, standards GSM / UMTS. They are used for communication in hard-to-reach areas (for example, with a height difference), as a temporary solution until the launch of a full-fledged base station of one of the types described above.
What is better than such a Femto AP than my native Wi-Fi router? The answer is very simple - they are completely different types of equipment! All the base stations described above are designed to create a mobile GSM / UMTS network, voice and packet services are available on these networks, which you can receive by using a phone that supports GSM / UMTS standards. The familiar Wi-Fi router is simply a wireless copper cable extender from your provider, and you can be provided with packet services only, including: Voice / Video over IP (for example, Skype).
Anyone (or certain people you entered in the lists) can enter the femto cell coverage area with a 3G phone without Wi-Fi and get access directly to the operator’s network.
There are femtocell models equipped with a Wi-Fi transmitter, and so you can use both UMTS and Wi-Fi networks using one CPE, but do not forget - these are not competing technologies, but complementary technologies.
Hopefully, the confusion is now fixed. If something else remains, ask in the comments, I will try to answer in detail.

Network hierarchy
If you want to know what the thing is hanging on the next house and how it creates you a cellular coverage, welcome under the cat.
')
The first thing to understand is that consoles such as macro, pico, etc., do not characterize the change in the quantitative parameters of the base station, they only indicate the place of the class in the hierarchy.
Macro (large)

Base station

Sector antennas
These are standard base stations on which the operator’s mobile network is built. The principles of operation, the transport solutions used, are given in any article about the architecture of cellular networks. The main transport at the moment is standard SDH-TDM networks, but the moment of mass transition to IP / Ethernet is getting closer. They are characterized by high power - up to 60W, large coverage radius - 10 ... 100 km, large mass-dimensional indicators (rack up to 200kg). There are varieties of macro base stations - such as distributed bases (Distributed BTS), but this classification is not significant. There are any standards allowed for use in Russia: GSM / UMTS / CDMA in the future - LTE .
Microcell (10 -6 )

Micro Base Station
A very common solution in the networks of a large operator. In fact, it is a compact version of the first type, with reduced characteristics in terms of base capacity, radiated power - up to 5 ... 10W, coverage radius - 1 ... 5 km and mass-dimensional characteristics (compact body weighing up to 50 kg). Used by the operator where it is difficult to install a macro base station, or where high power and capacity are not required. For example: large shopping centers, office complexes, remote villages, etc. Often used in conjunction with the Distributed Antenna System (DAS), which consists of cables and antennas spread across the building. Antennas can look different, for example, as in the subway:

Panel antennas
Also, there are GSM / UMTS / CDMA standards in the future - LTE.
Pico or nano base station (10 -12 and 10 -9 )

Picosot

"Nanosote"
This is a more exotic option. Base station of low power office / home execution. As a backbone transport network, it uses only IP / Ethernet networks, in which the necessary bandwidth is reserved for passing traffic generated by the base station. Typical power up to 0.2W, dimensions - about a laptop. Despite its small size, it is still a base station that belongs to the operator and cannot be transferred to the subscriber for independent launch and use. Usually installed in the offices of corporate clients, or in places of possible concentration of users - in restaurants, hotels, etc.
Technically, GSM / UMTS / CDMA may also be in the future - LTE. However, now there is a practice - that the pico / nano base stations call only low-power GSM bases.
Femtocell or femto access point (10 -15 )

Home Femto
A femtocell is no longer a base station; it is an Access Point. The difference in terminology arises from the fact that this equipment is initially designed for use as a home or office, and it is assumed that the owner is the user. Transport - only IP / Ethernet, and both the channel allocated by the provider and the public Internet. The principal difference from all other types of base stations is the autoconfiguration when switched on in the transport network and connected to the operator’s network. Femto AP independently evaluates the radio parameters at the launch point, selects the best settings for itself, and is activated if the operator permits. For data protection, all interaction with the operator’s equipment begins only after the creation of the IPSec tunnel. Typical radiated power - up to 0.1W, dimensions - roughly correspond to a home Wi-Fi router.
Same GSM / UMTS / CDMA standards, in the future - LTE. However, now Femto AP is firmly associated only with the UMTS (3G) standard, in the future mass appearance of such LTE devices is expected.
Repeater

GSM Repeater
This equipment is included in the review solely for the reason that many also consider it as equipment for creating a cellular network. It's a delusion! A repeater is just an external signal amplifier from a macro station, and its purpose is to transmit a signal from the street inside the building. The repeater does not create additional network capacity, that is, if the donor base station is overloaded - inside the building you also will not be able to use the phone due to overload. Despite the seeming simplicity of the device and its installation, the correct setup of the repeater requires specific skills and instruments to control the coating being created. Moreover, according to Russian law, only a licensed company can own such equipment, as well as install and run it. It is often impossible to use the repeater, since its work requires the installation of an external antenna on the facade of a building that receives a signal from a macro base station.
There are options for a variety of repeaters. Different power, performance and standards. The most common in the networks of operators received repeaters with a high gain, standards GSM / UMTS. They are used for communication in hard-to-reach areas (for example, with a height difference), as a temporary solution until the launch of a full-fledged base station of one of the types described above.
Who will beat anyone: Wi-Fi router or femtocell?
What is better than such a Femto AP than my native Wi-Fi router? The answer is very simple - they are completely different types of equipment! All the base stations described above are designed to create a mobile GSM / UMTS network, voice and packet services are available on these networks, which you can receive by using a phone that supports GSM / UMTS standards. The familiar Wi-Fi router is simply a wireless copper cable extender from your provider, and you can be provided with packet services only, including: Voice / Video over IP (for example, Skype).
Anyone (or certain people you entered in the lists) can enter the femto cell coverage area with a 3G phone without Wi-Fi and get access directly to the operator’s network.
There are femtocell models equipped with a Wi-Fi transmitter, and so you can use both UMTS and Wi-Fi networks using one CPE, but do not forget - these are not competing technologies, but complementary technologies.
Hopefully, the confusion is now fixed. If something else remains, ask in the comments, I will try to answer in detail.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/130649/
All Articles