PNG - not gif!
Good day!
Have you ever wanted to know how PNG files are organized? Not? And I still tell.
The PNG (Portable Network Graphics) format was invented in 1995 to become a replacement for GIF , and as early as 1996, with the release of version 1.0, it was recommended by the W3C as a full-fledged network format. Today PNG is one of the main formats of web graphics.
Under the cat you will find a general description of the structure of the PNG-file, a number of picture schemes, preparation in the hex editor, and, of course, the link to the specification.
in the hex editor, and, of course, the link to the specification.
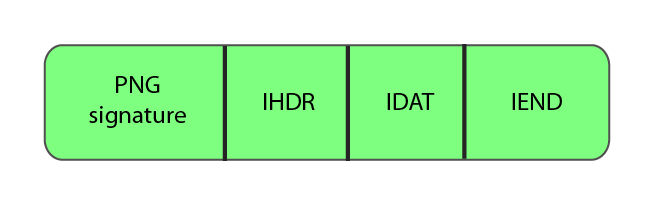
The PNG structure in its most general form is presented in the following figure.
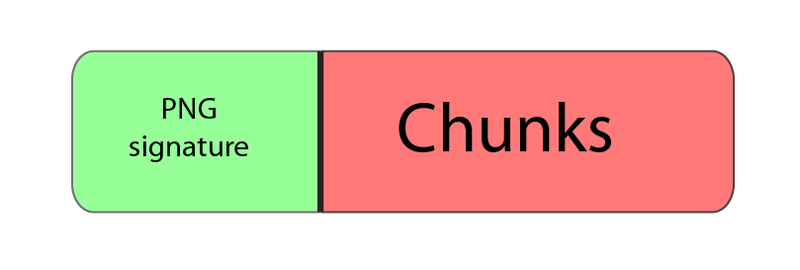
That is, the file consists of a signature and a certain number of blocks (chunks, chunks), each of which carries some information (thanks to KO!). But why the signature can not be considered one of the chunks? Let's see more in detail.
The signature of the PNG file is always the same, consists of 8 bytes, and is (in hex)
What does this mean?
')
Chunks are the data blocks that make up a file. Each chunk consists of 4 sections.
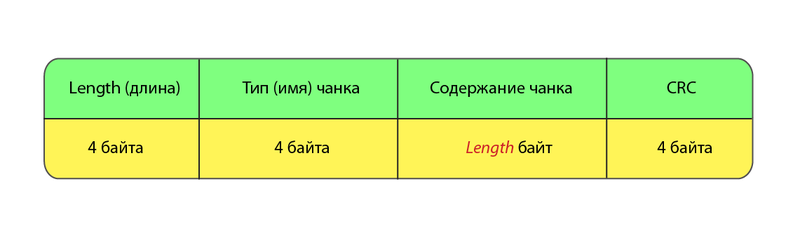
Let's sort these sections in order.
Well, everything seems to be clear with length. Just the numeric value of the length of the data block.
With type a bit more interesting. The type is 4 case sensitive ASCII characters. The character registers (the fifth bit in the numeric character entry) in the name of the chunk are not for nothing, these are flags that tell the decoder some additional information.
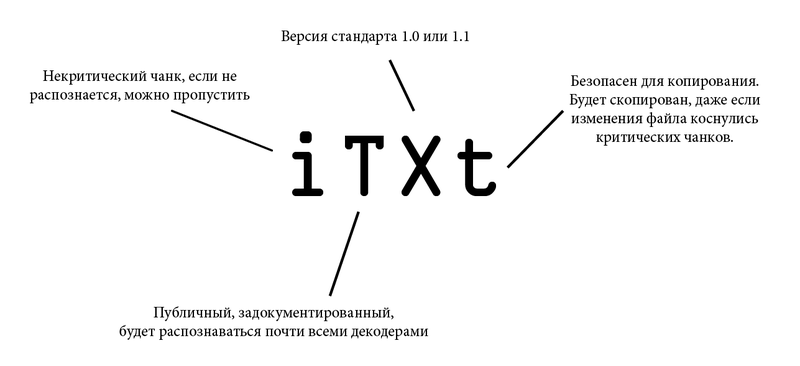
For a better understanding, let's look at the flags using the example of a chunk containing text.
Below is a list of chunk types with brief explanations.
Critical chunks
Auxiliary chunks
More information can be found in the specification.
CRC-32 checksum. By the way the other day was a topic about counting it in Windows.
With the overall structure sorted out. Now analyze the content of the mandatory chunks. But which of them are mandatory (not critical, critical are required to be recognized by the decoder, and not present in each file), and what does the minimal PNG file look like? That's how:
The data block in the IHDR contains the following fields:
Adam7 interlacing perfectly demonstrates a picture from Wikipedia (yes, GIF in the article about PNG):

Signals about the end of the file, the data block of this chunk does not contain anything.
Contains the data encoded according to the compression method field in the header. The decoding algorithm is beyond the scope of this article (however, if desired, it may appear in the following), but it is described quite well (and in Russian) here .
Thus, the simplest PNG file (by the example of ) as follows.
) as follows.

When writing this article, I set myself the task of giving the reader general knowledge about the structure of the PNG file, for a deeper understanding it is recommended to read the specifications .
Topic on habre about the structure of JPEG: habrahabr.ru/blogs/algorithm/102521
Topic on habre about the structure of the GIF: habrahabr.ru/blogs/algorithm/127083
Thank you for your attention, I will be glad to any criticism!
Have you ever wanted to know how PNG files are organized? Not? And I still tell.
The PNG (Portable Network Graphics) format was invented in 1995 to become a replacement for GIF , and as early as 1996, with the release of version 1.0, it was recommended by the W3C as a full-fledged network format. Today PNG is one of the main formats of web graphics.

Under the cat you will find a general description of the structure of the PNG-file, a number of picture schemes, preparation
 in the hex editor, and, of course, the link to the specification.
in the hex editor, and, of course, the link to the specification. Common building
The PNG structure in its most general form is presented in the following figure.

That is, the file consists of a signature and a certain number of blocks (chunks, chunks), each of which carries some information (thanks to KO!). But why the signature can not be considered one of the chunks? Let's see more in detail.
File signature
The signature of the PNG file is always the same, consists of 8 bytes, and is (in hex)
89 50 4E 47 0D 0A 1A 0A
What does this mean?
- 89 is a non-ASCII character. Prevents PNG recognition as a text file and vice versa.
- 50 4E 47 - PNG to ASCII records.
- 0D 0A - CRLF (Carriage-return, Line-feed), DOS-style line feed.
- 1A - stops file output in DOS mode (end-of-file), so that you will not fall out a multi-kilo byte image in text form.
- 0A - LF, Unix-style line feed.
')
Chunks
Chunks are the data blocks that make up a file. Each chunk consists of 4 sections.

Let's sort these sections in order.
Length
Well, everything seems to be clear with length. Just the numeric value of the length of the data block.
Type (name)
With type a bit more interesting. The type is 4 case sensitive ASCII characters. The character registers (the fifth bit in the numeric character entry) in the name of the chunk are not for nothing, these are flags that tell the decoder some additional information.
- The first character register determines whether this chunk is critical (upper case) or auxiliary (lower case). Critical chunks must be recognized by each decoder. If the decoder encounters a critical chunk, the type of which cannot be recognized, it must terminate the execution with an error.
- The second character register defines “publicity” (upper case) or “privacy” (lower case) of the chunk. “Public” chunks - official, documented, recognized by most decoders. But if suddenly you need to encode specific information for some of your needs, then just in the name of the chunk, make the second character small.
- The register of the third character is left for future accomplishments. It is assumed that it will be used to differentiate between different versions of the standard. For versions 1.0 and 1.1, the third character must be large. If it (suddenly!) Turned out to be small, all current decoders should deal with a chunk, just like with any other not recognized (that is, exit with an error if the chunk is critical, or skip otherwise).
- The fourth character register means that editors who cannot recognize it can copy this chunk. If the register is lower, the chunk can be copied, regardless of the degree of modification of the file, otherwise (upper case) it is copied only if no critical chunks were affected by the modification.
For a better understanding, let's look at the flags using the example of a chunk containing text.

Below is a list of chunk types with brief explanations.
Critical chunks
- IHDR - the header of the file, contains basic information about the image. Must be the first chunk.
- PLTE - palette, list of colors.
- IDAT - contains, in fact, the image. Figure can be divided into several IDAT chunks, for streaming. Each file must have at least one IDAT chunk.
- IEND - the final chunk, must be the last in the file.
Auxiliary chunks
- bKGD - this chunk sets the main background color.
- cHRM is used to specify the CIE 1931 color space.
- gAMA - defines gamma.
- hIST - a histogram or the total content of each color in the image can be stored in this chunk.
- iCCP - ICC color profile
- iTXt - contains text in UTF-8, possibly compressed, with an optional language mark. iTXt chunk with the 'XML: com.adobe.xmp' keyword can contain the Extensible Metadata Platform (XMP) .
- pHYs - contains the estimated pixel size and / or aspect ratio of the image.
- sBIT (significant bits) - defines the "color accuracy" (color-accuracy) of the image (black and white, full color, black and white with transparency, etc.), for easier decoding.
- sPLT - offers a palette for use if the full range of colors is not available.
- sRGB indicates the use of the standard sRGB scheme.
- sTER is a stereoscopic image indicator.
- tEXt - can contain text in ISO / IEC 8859-1 format, with one name = value pair for each chunk.
- tIME - stores the date the image was last modified.
- tRNS - contains information about transparency.
- zTXt is compressed text, with the same limitations as tEXt.
More information can be found in the specification.
CRC
CRC-32 checksum. By the way the other day was a topic about counting it in Windows.
Minimal PNG
With the overall structure sorted out. Now analyze the content of the mandatory chunks. But which of them are mandatory (not critical, critical are required to be recognized by the decoder, and not present in each file), and what does the minimal PNG file look like? That's how:

Ihdr
The data block in the IHDR contains the following fields:
- Width, 4 bytes
- Height, 4 bytes
- Bit depth (bit depth), determines the number of bits per sample (not pixel), 1 byte
- Color type, consists of 3 flags 1 (a palette is used), 2 (a color is used, not a monochrome image), and 4 (an alpha channel is present), 1 byte
- Compression method. Currently, only the value 0 is available - deflate compression. If the value is different from 0, the chunk is considered unrecognized, and the decoder reports an error. 1 byte
- Filtering method As in the case of compression, at the moment it can only be zero. 1 byte
- Interlace method. Defines the data transfer order. Currently 2 values are available: 0 (no interlace) and 1 ( Adam7 interlace). 1 byte
Adam7 interlacing perfectly demonstrates a picture from Wikipedia (yes, GIF in the article about PNG):

IEND
Signals about the end of the file, the data block of this chunk does not contain anything.
IDAT
Contains the data encoded according to the compression method field in the header. The decoding algorithm is beyond the scope of this article (however, if desired, it may appear in the following), but it is described quite well (and in Russian) here .
Thus, the simplest PNG file (by the example of
 ) as follows.
) as follows.
Conclusion
When writing this article, I set myself the task of giving the reader general knowledge about the structure of the PNG file, for a deeper understanding it is recommended to read the specifications .
Topic on habre about the structure of JPEG: habrahabr.ru/blogs/algorithm/102521
Topic on habre about the structure of the GIF: habrahabr.ru/blogs/algorithm/127083
Thank you for your attention, I will be glad to any criticism!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/130472/
All Articles