Comparative performance analysis of PCI-E SSD, SSD and HDD drives
Improving the performance of the disk subsystem is the most pressing issue today. This is due to the fact that HDD, due to its low cost, still occupies a leading position in the mass segment. In more than half of resource-intensive applications, the spindle disks become the bottleneck. In this case, everything depends not on the bandwidth of the SATA interface, but on the physical capabilities of the mechanical components of the magnetic disk. The bandwidth of SATA-II and SATA-III interfaces is 300MB / s and 600MB / s, respectively. And the maximum performance that a regular HDD can provide is not more than 150 MB / s. Therefore, the transition to the SATA-III interface will be justified only for SSD, and not for everyone.
To assess the effectiveness of disk subsystems of different types, the following solutions were chosen for testing:
1. OCZ RevoDrive X2 PCI-E SSD 100Gb

')
2. Plextor PX-128M2S SSD 128Gb

3. Transcend TS64GSSD25S-M SSD 64Gb
4. 4 x Transcend TS64GSSD25S-M RAID-0

5. WD Caviar Green SATA-II HDD 750Gb

6. 4 x WD RE4 1TB 7200RPM RAID-0

The following charts show the performance of solutions in different test modes:


From the test results we can make a series of conclusions:
Testing was carried out in the laboratory DEPO Computers
To assess the effectiveness of disk subsystems of different types, the following solutions were chosen for testing:
1. OCZ RevoDrive X2 PCI-E SSD 100Gb

')
2. Plextor PX-128M2S SSD 128Gb

3. Transcend TS64GSSD25S-M SSD 64Gb
4. 4 x Transcend TS64GSSD25S-M RAID-0

5. WD Caviar Green SATA-II HDD 750Gb

6. 4 x WD RE4 1TB 7200RPM RAID-0

The following charts show the performance of solutions in different test modes:
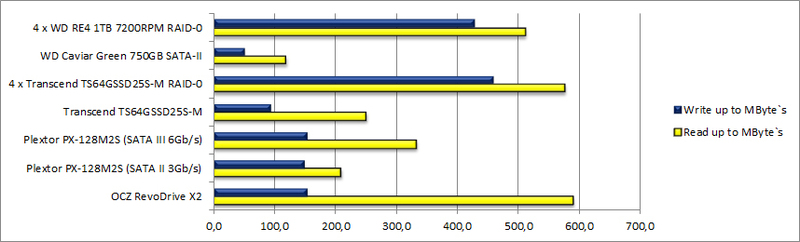
Sequential

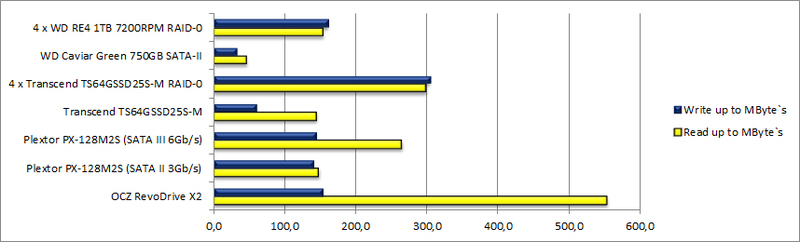
Random, 512KB

Random, 4KB, Queue Depth = 1

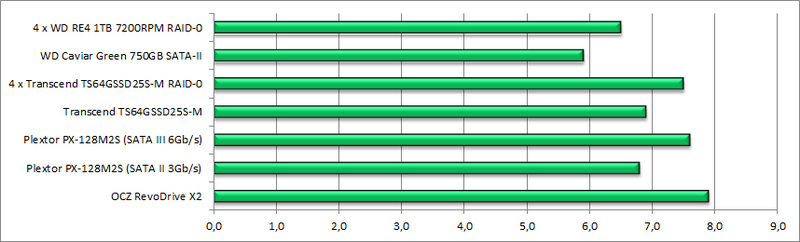
Random, 4KB, Queue Depth = 32

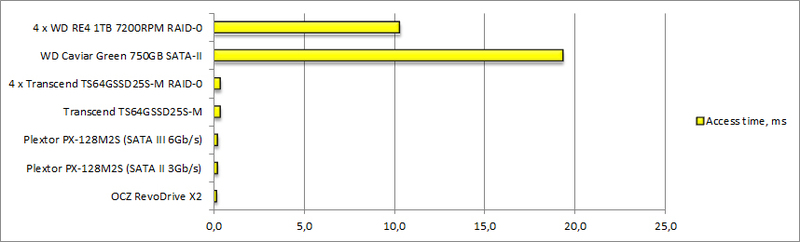
Access time

Windows System Performance Rating

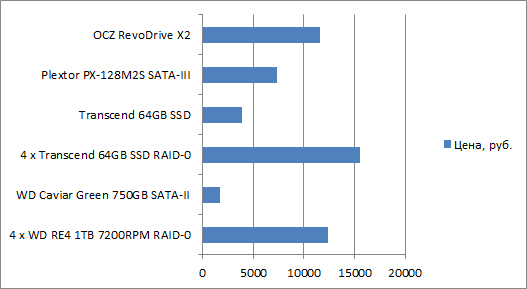
Average solution cost

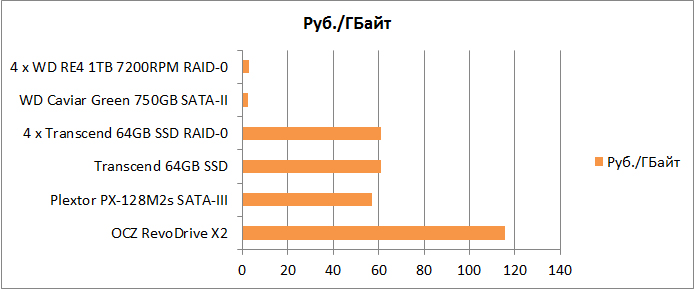
Average cost per gigabyte

From the test results we can make a series of conclusions:
- Obviously, the weak point of spindle disks is random reading / writing of small data blocks.
- It is no less obvious that SSD recordings are not as good as reading: RevoDrive, for example, did not show 690 MBytes / s as stated by the manufacturer. But it is implemented RAID-0 Of the 4 SSD
- If the work requires the sequential recording of large data blocks, then the most effective solution would be a RAID-0 of 4 HDD 7200RPM
- SSD or RAID from SSD is ideal for quick reading. The operating system installed on the OCZ RevoDrive X2 boots in seconds. No wonder - at the peak the reading speed of this device reaches 800 megabytes per second
- The Plextor PX-128M2S, connected via the SATA-III interface, showed results significantly higher than through the SATA-II interface. This is the case when the interface can become a bottleneck
- For maximum efficiency of the disk subsystem, it is best to make it combined. For each task, allocate disks of a certain type and organize RAID for performance and fault tolerance requirements.
Testing was carried out in the laboratory DEPO Computers
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/130466/
All Articles