Measuring speech intelligibility: a formant approach
Formants are areas in the spectrum of the sound of speech where the concentration of energy is maximum. The formant approach was first proposed in 1929 by D. Collard. He firmly held his position until the 70s, until a modulation approach was proposed, allowing to take into account not only noise, but also reverberation interference, echo and nonlinear distortion.
Over the 80 years of its existence, the formant approach has gained many adherents and modifications, but the foreign version of the formant method, known as the articulation index (AI), has become the most common. We will come to it, having considered the version of N. B. Pokrovsky and the modern domestic method of measuring speech intelligibility based on it.
According to this method, the entire analyzed frequency range is divided into several adjacent bands, within each of which the formant density probability, speech and noise spectra are approximately considered constant. Articulation legibility is the sum of the formant clearances of each band:
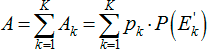
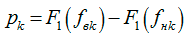
K is the number of adjacent bands;
p k - the probability of the formant stay in the k -th frequency band;
F 1 (f) is the probability distribution function of formants;
f ok is the center frequency of the band;
f Nk - the lower limiting frequency of the band;
f VK - upper limit frequency of the band;
P (E ' k ) is the coefficient of speech perception, otherwise the probability of the absence of speech masking by noise.
')
The rate of speech perception depends on the difference in the levels of the formant spectrum and the interference spectrum. With sufficiently high noise levels, this is the signal-to-noise ratio in each of the frequency bands.
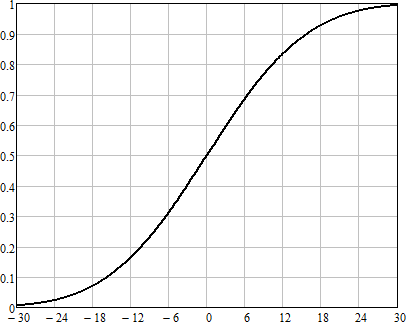
Frankly, the speech perception coefficient curve for each frequency band is different, however, in the method of N. B. Pokrovsky they were also asked not to pay attention to it and use any one curve to simplify the calculations. Methodical error on the face.
Of course, for a full description of the Pokrovsky method, it is necessary to cite at least another method for constructing perceptual coefficients, a number of formulas and observations, however, since this is not the purpose of this article, we will move on.
The modern Russian method was proposed in 2000 by Ya. I. Zheleznyak, Yu. K. Makarov and A. A. Khorev. In fact, he repeats the N. B. Pokrovsky method with the only difference that signal analysis is performed in five octave frequency bands . It is also assumed to automate the calculations, which required an approximation of the measured values by analytical ratios.
As before, articulation intelligibility is determined by the expression:

Analytical ratios:
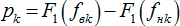
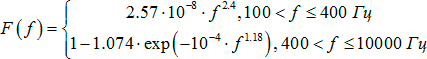
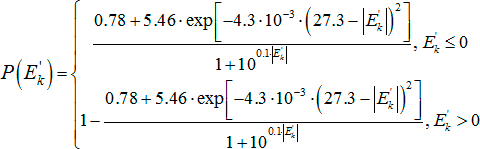
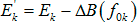
E ' k - effective level of sensation of formant in the frequency band;
E k - effective sensation level of the speech signal in the frequency band, with a relatively large noise level equal to the signal-to-noise ratio SNR;
∆B (f) is the difference between the average speech spectrum and formant spectrum;

D sk and D nk are the signal and noise dispersions, respectively;
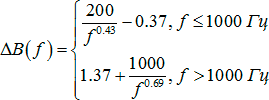
Verbal intelligibility is calculated using the formant:
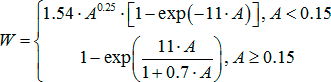
V. L. Kargashin expressed the opinion that this version should be improved, namely:
The above is present in the AI method.
The use of the articulation index was proposed by G. Fletcher in 1940. There are two versions of this method:
Consider this method for twenty equal-articulation bands. Speech intelligibility is determined by the same formula:

However, since the calculations are made in twenty bands, the formula above takes the form:
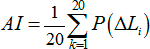
∆L i - the difference between peak speech level and effective masking noise level
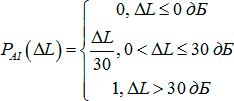
In this way
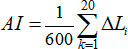
It may be asked whether we have the right to approximate the coefficient of perception by such a linear relationship? We have, since the result obtained using the curves according to Pokrovsky will be the same averaged as the result obtained with the approximation by a linear dependence.

B p peak - peak level of speech;
B W - effective noise level;
P p - peak factor - the ratio of the peak value of the level to the mean square;
E - effective sensation level of speech signal
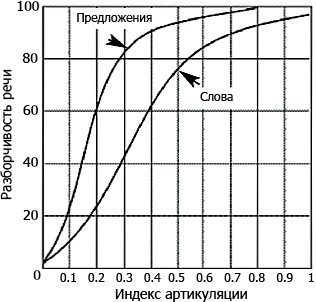
Recalculation of the articulation index into verbal and phrasal intelligibility is carried out according to the schedule:
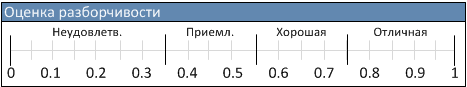
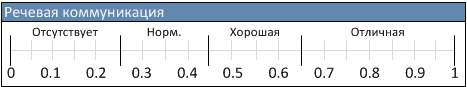
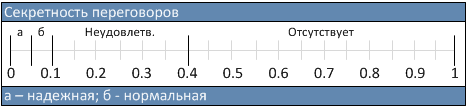
Various estimates for the articulation index are presented below:
The method takes into account:
The method does not apply:
Over the 80 years of its existence, the formant approach has gained many adherents and modifications, but the foreign version of the formant method, known as the articulation index (AI), has become the most common. We will come to it, having considered the version of N. B. Pokrovsky and the modern domestic method of measuring speech intelligibility based on it.
Pokrovsky method
According to this method, the entire analyzed frequency range is divided into several adjacent bands, within each of which the formant density probability, speech and noise spectra are approximately considered constant. Articulation legibility is the sum of the formant clearances of each band:
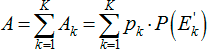
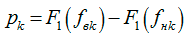
K is the number of adjacent bands;
p k - the probability of the formant stay in the k -th frequency band;
F 1 (f) is the probability distribution function of formants;
f ok is the center frequency of the band;
f Nk - the lower limiting frequency of the band;
f VK - upper limit frequency of the band;
P (E ' k ) is the coefficient of speech perception, otherwise the probability of the absence of speech masking by noise.
')
The rate of speech perception depends on the difference in the levels of the formant spectrum and the interference spectrum. With sufficiently high noise levels, this is the signal-to-noise ratio in each of the frequency bands.

Frankly, the speech perception coefficient curve for each frequency band is different, however, in the method of N. B. Pokrovsky they were also asked not to pay attention to it and use any one curve to simplify the calculations. Methodical error on the face.
Of course, for a full description of the Pokrovsky method, it is necessary to cite at least another method for constructing perceptual coefficients, a number of formulas and observations, however, since this is not the purpose of this article, we will move on.
Almost AI
The modern Russian method was proposed in 2000 by Ya. I. Zheleznyak, Yu. K. Makarov and A. A. Khorev. In fact, he repeats the N. B. Pokrovsky method with the only difference that signal analysis is performed in five octave frequency bands . It is also assumed to automate the calculations, which required an approximation of the measured values by analytical ratios.
| f 0 Hz | 250 | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | 4,000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∆f, Hz | 180 ... 355 | 355 ... 710 | 710 ... 1400 | 1400 ... 2800 | 2800 ... 5600 |
| ∆f is the frequency band; f 0 - the average frequency of the band | |||||
As before, articulation intelligibility is determined by the expression:

Analytical ratios:
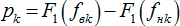
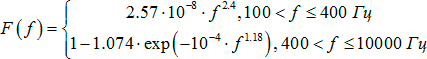
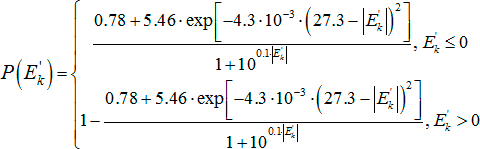
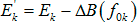
E ' k - effective level of sensation of formant in the frequency band;
E k - effective sensation level of the speech signal in the frequency band, with a relatively large noise level equal to the signal-to-noise ratio SNR;
∆B (f) is the difference between the average speech spectrum and formant spectrum;

D sk and D nk are the signal and noise dispersions, respectively;
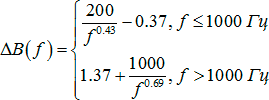
Verbal intelligibility is calculated using the formant:
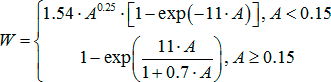
V. L. Kargashin expressed the opinion that this version should be improved, namely:
- you need to add another analysis bandwidth with a center frequency of 8 kHz;
- the possibility of settlement in the one-third octave bands should be implemented;
- it is desirable to approximate the coefficient of perception more simple function
The above is present in the AI method.
AI
The use of the articulation index was proposed by G. Fletcher in 1940. There are two versions of this method:
- for twenty equally-divided lanes;
- for six octave or fifteen three-octave bands
Consider this method for twenty equal-articulation bands. Speech intelligibility is determined by the same formula:

However, since the calculations are made in twenty bands, the formula above takes the form:
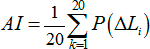
∆L i - the difference between peak speech level and effective masking noise level
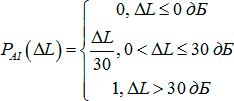
In this way
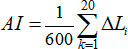
It may be asked whether we have the right to approximate the coefficient of perception by such a linear relationship? We have, since the result obtained using the curves according to Pokrovsky will be the same averaged as the result obtained with the approximation by a linear dependence.

B p peak - peak level of speech;
B W - effective noise level;
P p - peak factor - the ratio of the peak value of the level to the mean square;
E - effective sensation level of speech signal
Recalculation of the articulation index into verbal and phrasal intelligibility is carried out according to the schedule:

Various estimates for the articulation index are presented below:



The method takes into account:
- the effect of reverberation noise;
- the influence of the frequency response of the transmission path;
- the non-stationary nature of the masking noise, if its duty cycle or the on / off time is known;
- clipping effect;
The method does not apply:
- if the speech signal is affected by several different types of interference;
- in the case of mixed reception of the signal from the speaker and loudspeaker
Basement
- Acoustic examination of speech communication channels. Monograph / Didkovsky V.S., Didkovskaya M.V., Prodeus A.N. - Kiev, 2008. 420.
- electrovoice.com.ua
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/128213/
All Articles