PSNR and SSIM or how to work with images under C
 In this article I will touch on the basic principles of how to work with images. For this, I chose the OpenCV library . It is distributed for free, so download it is not difficult.
In this article I will touch on the basic principles of how to work with images. For this, I chose the OpenCV library . It is distributed for free, so download it is not difficult.When I was given the task of learning to write two metrics to assess the difference between the two pictures, in particular, the quality of the modified from the original, I was of course all this embarrassed a bit. Knowledge in programming was, to put it mildly, not very big, after all, it was only a freshman. Fortunately, what library to choose said in advance, so that this work arose. But how to use it was already an order of magnitude more difficult, everything that I was basically able to dig on the Internet was in English, even though I know it at the level that I can read those. literature, due to the enormity of the library itself, was not enough. Well, what was possible, what functions and how to use, I could then clarify with the teacher. All that was needed was to understand how to access the image itself, in particular, individual pixels of the image. Anyone interested, welcome under cat.
PSNR / SSIM
To begin with, what is it PSNR and SSIM . As Wikipedia tells us. PSNR, the peak signal-to-noise ratio, is most often used to measure the level of distortion when compressing images. And we will find it so. In this case, everything will depend on the bit depth of the image.
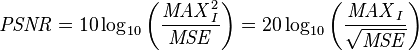
')
Where MSE is the standard deviation

SSIM is considered more complex, and was created to more accurately determine the difference between the two images, so to speak. The peculiarity is that it always lies in the interval from -1 to 1, and when its value is 1, it means that we have two identical pictures. The general formula is

Here
 (x) average value for the first picture,
(x) average value for the first picture,  (y) this is for the second,
(y) this is for the second, 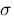 (x) the standard deviation for the first picture, and accordingly
(x) the standard deviation for the first picture, and accordingly 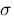 (y) for the second,
(y) for the second, 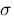 (x, y) is already a covariance. I will remind her to be
(x, y) is already a covariance. I will remind her to be 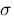 (x, y) =
(x, y) = 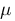 (x, y) -
(x, y) - 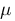 (x) *
(x) * 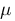 (y). We continue C1 and C2, the correction factors that we need because of the smallness of the denominator. Moreover, they are equal to the square of the number, equal to the number of colors corresponding to a given image bit depth multiplied by 0.01 and 0.03, respectively.
(y). We continue C1 and C2, the correction factors that we need because of the smallness of the denominator. Moreover, they are equal to the square of the number, equal to the number of colors corresponding to a given image bit depth multiplied by 0.01 and 0.03, respectively.Code
I repent, my programming style is probably not very good, but do not judge me harshly, I don’t have so much experience and I promise to improve it all the time. For the purposes of this article, I will limit myself to parsing only the SSIM metrics. First you need to have Visual Studio at hand. Here I simply managed to understand how to add the initially selected library to the project. You need to add the header files, and the files themselves to the newly created project. In more detail it is written here .
To explain my written code, I will bet on its commenting on the go. The code is not too long, so it can be understood. Well, let's get started.
Pointers to pictures we get.
IplImage* img1 = cvvLoadImage("before.bmp"); IplImage* img2 = cvvLoadImage("after.bmp"); Bitness can be determined
img->depth That is quite simple.To find the desired values, I wrote a couple of its functions. To find
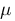 (x), that is, the mean value . In fact, we work with a picture as with a two-dimensional array. Even here, the resulting value will need to be divided by the size of the image, found as follows:
(x), that is, the mean value . In fact, we work with a picture as with a two-dimensional array. Even here, the resulting value will need to be divided by the size of the image, found as follows: (img->width)*(img->height) double avg(IplImage* img){ unsigned char* ptr; int x,y,b=0,g=0,r=0,col=0; for(x=0;x<=img->width;x++){ for(y=0;y<=img->height;y++){ ptr=(uchar*)(img->imageData+y*img->widthStep); // b=ptr[3*x]; g=ptr[3*x+1]; // r=ptr[3*x+2]; // b - blue, r - red, g - green col+=b+g+r; }} return col/3.00; } The standard deviation is so, here we have to, among other things, transfer the previously obtained average values.
double var(IplImage* img, double mu){ //variance unsigned char* ptr; int x,y,b=0,g=0,r=0; double col=0; for(x=0;x<=img->width;x++){ for(y=0;y<=img->height;y++){ ptr=(uchar*)(img->imageData+y*img->widthStep); b=ptr[3*x]; col+=(abs(1.0*b-mu))*(abs(1.0*b-mu)); g=ptr[3*x+1]; col+=(abs(1.0*g-mu))*(abs(1.0*g-mu)); r=ptr[3*x+2]; col+=(abs(1.0*r-mu))*(abs(1.0*r-mu)); }} return col; } And the covariance is like this:
double cov(IplImage* img1,IplImage* img2,double mu1,double mu2){ //covariance unsigned char* ptr; int x,y,b1=0,g1=0,r1=0,b2=0,g2=0,r2=0; double col=0; for(x=0;x<=img1->width;x++){ for(y=0;y<=img1->height;y++){ ptr=(uchar*)(img1->imageData+y*img1->widthStep); b1=ptr[3*x]; g1=ptr[3*x+1]; r1=ptr[3*x+2]; ptr=(uchar*)(img2->imageData+y*img2->widthStep); b2=ptr[3*x]; g2=ptr[3*x+1]; r2=ptr[3*x+2]; col+=(b1-mu1)*(b2-mu2)+(g1-mu1)*(g2-mu2)+(r1-mu2)*(r2-mu2); }} return col; } In fact, we only need to substitute the values obtained in the above formula. Just do not forget to release the memory.
cvReleaseImage(&img1); cvReleaseImage(&img2); PS
Download the library itself you can here . A lot of interesting things about OpenCV here (thanks to ZlodeiBaal ). Also in the future I would like to write an article similar to this one, but already about working with video and using other libraries.Who has any questions or errors, or just want to praise the author, write, be sure to answer.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/126848/
All Articles