Compatible incompatible? Wavelets and Motion Compensation
Hello, dear Habrochane! Today I will tell you about how two seemingly incompatible technologies are combined: wavelet transform imaging technology and motion compensation technology. Of course, the question immediately arises, why is this necessary? It is easy to answer. A major disadvantage of all video compression systems based on wavelets is interframe redundancy, due to which the video sometimes “swells” one and a half times. This disadvantage is significant for simple transformations, and for the commercialized MJPEG-2000, which was called the forerunner of the new era of wavelet video and in general the messiah of the digital world. So, just to get rid of interframe redundancy, we introduce motion compensation into the scheme. This will significantly reduce the flow of information in scenes that are not very saturated with movement, such as a computer warehouse or an empty Louvre hall, which not every tourist comes to, is empty because of the dark time of day. I will answer the second question: why wavelet, but not DCT ? Wavelet can achieve significantly better results with high degrees of video compression. In simple terms, it is much easier to recognize a person on a frame processed with the help of wavelets.

Ready-made solutions offer us something similar, but for good reason they say - “if you want something to be done well, do it yourself”. On the vast majority of video servers, an interframe difference analysis system is implemented. How it works? The second frame is subtracted from the first frame, and if the percentage of discrepancies is small enough - the second frame is not transmitted at all. This is convenient if you survey a room of ten square meters, but if you have one hundred meter shelves of a warehouse in front of you and somewhere in the far corner an attacker in a dark trouser suit has planned something not right - the system may not perceive it. Consider as a hindrance. And will transmit to the monitoring system monitors the same frame again and again. The advantage of this method is its efficiency in terms of the data transmission channel. This is significant if the camera is removed from the monitoring point and the image is not sent via a wired network, but through Wi-Fi, WiMax, GPRS / HSDPA or RadioEthernet.
')
However, back to our sheep. In order to realize motion compensation in video, it is necessary to split the image into blocks. It would seem that this is what MJPEG-2000 relieves of, and it is the absence of the block effect that is imputed to it in the main advantages. This problem is solved, if instead of preprocessing to use post-processing frame. Yes, it will slow down the process, but it has been empirically discovered that even the power of the dense processor from Analog Devices under the loud name ADSP-2183 is enough for 18 frames per second at the current 720p resolution. What then to say about modern processors, economical, cold and fast processors? A similar scheme with some Qualcomm, although it will rise in price by a couple of dozen evergreen units, but will be capable of a full-fledged 720p, and with some modifications at 1080p. So, I present to your attention the scheme:
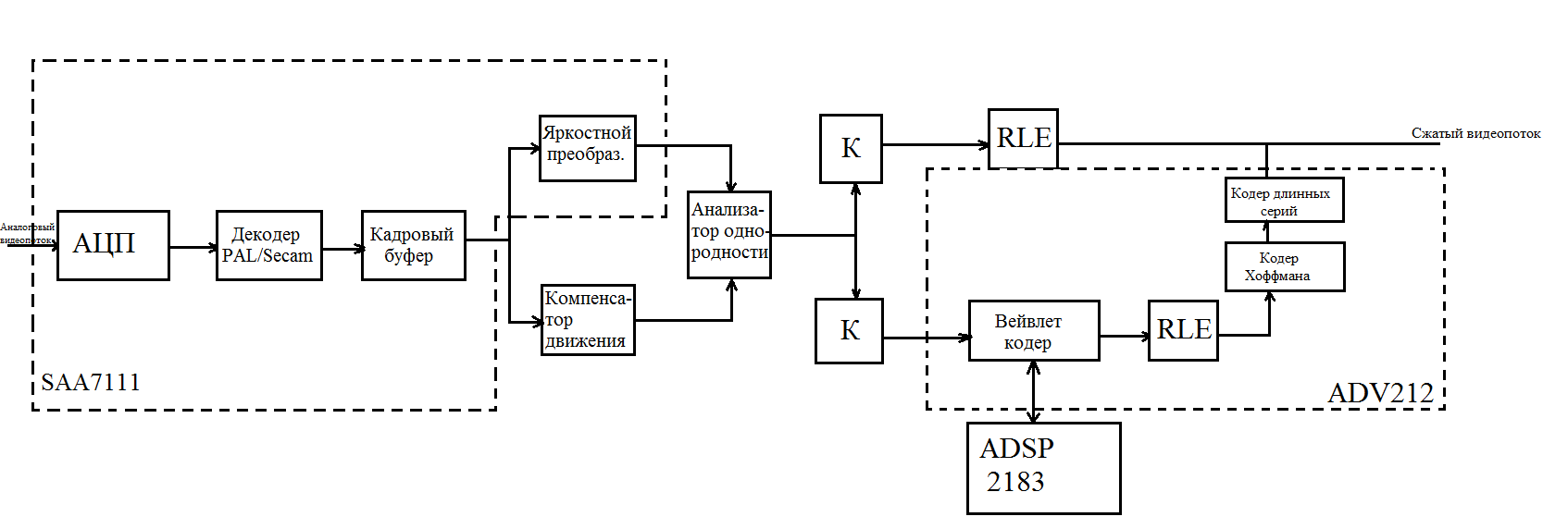
Consider the element base device. ADV212, an extremely successful Analog Devices production model, capable of working with both proprietary wavelet and the open MJPEG-2000 format, was taken as the main codec, and the circuit was created to work with it. The codec shows excellent results and reports that it is ready to compress the image up to 400 times. On my own experience, I assure you that even 300 is no longer what is needed. 250 is our number. The remaining parts were adopted solely because others were not at hand. These are our stars of the evening: the SAA7111 decoder-digitizer from Philips, which is engaged in amplification of low-frequency signals and control of brightness and color levels, and the old ADSP-2183 already mentioned in the article, which simultaneously serves as a motion compensator, homogeneity analyzer, and mathematical mathematical processor.
In total, we received: for an amount in the region of $ 120, along with expenses for the case and conclusions, but without the cost of assembly, we get a working single-channel codec that is cheaper than its competitors for a good hundred US dollars, in the case of China, or even three, in the case of a fashion brand.

Ready-made solutions offer us something similar, but for good reason they say - “if you want something to be done well, do it yourself”. On the vast majority of video servers, an interframe difference analysis system is implemented. How it works? The second frame is subtracted from the first frame, and if the percentage of discrepancies is small enough - the second frame is not transmitted at all. This is convenient if you survey a room of ten square meters, but if you have one hundred meter shelves of a warehouse in front of you and somewhere in the far corner an attacker in a dark trouser suit has planned something not right - the system may not perceive it. Consider as a hindrance. And will transmit to the monitoring system monitors the same frame again and again. The advantage of this method is its efficiency in terms of the data transmission channel. This is significant if the camera is removed from the monitoring point and the image is not sent via a wired network, but through Wi-Fi, WiMax, GPRS / HSDPA or RadioEthernet.
')
However, back to our sheep. In order to realize motion compensation in video, it is necessary to split the image into blocks. It would seem that this is what MJPEG-2000 relieves of, and it is the absence of the block effect that is imputed to it in the main advantages. This problem is solved, if instead of preprocessing to use post-processing frame. Yes, it will slow down the process, but it has been empirically discovered that even the power of the dense processor from Analog Devices under the loud name ADSP-2183 is enough for 18 frames per second at the current 720p resolution. What then to say about modern processors, economical, cold and fast processors? A similar scheme with some Qualcomm, although it will rise in price by a couple of dozen evergreen units, but will be capable of a full-fledged 720p, and with some modifications at 1080p. So, I present to your attention the scheme:

Consider the element base device. ADV212, an extremely successful Analog Devices production model, capable of working with both proprietary wavelet and the open MJPEG-2000 format, was taken as the main codec, and the circuit was created to work with it. The codec shows excellent results and reports that it is ready to compress the image up to 400 times. On my own experience, I assure you that even 300 is no longer what is needed. 250 is our number. The remaining parts were adopted solely because others were not at hand. These are our stars of the evening: the SAA7111 decoder-digitizer from Philips, which is engaged in amplification of low-frequency signals and control of brightness and color levels, and the old ADSP-2183 already mentioned in the article, which simultaneously serves as a motion compensator, homogeneity analyzer, and mathematical mathematical processor.
In total, we received: for an amount in the region of $ 120, along with expenses for the case and conclusions, but without the cost of assembly, we get a working single-channel codec that is cheaper than its competitors for a good hundred US dollars, in the case of China, or even three, in the case of a fashion brand.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/126387/
All Articles