Modern biometric identification methods
Recently, on Habré there are many articles on Google systems for identification of persons. To be honest, from many of them it carries journalism and, to put it mildly, incompetence. And I wanted to write a good article on biometrics, but it’s not in the first one! There are a couple of quite good articles on biometrics on Habré - but they are rather short and incomplete. Here I will try to briefly outline the general principles of biometric identification and the modern achievements of mankind in this matter. Including in the identification of persons.
The article has a sequel , which, in fact, is its primal.
As a basis for the article, a joint publication with a colleague in a journal ( BDI, 2009 ) will be used, revised for modern realities. Colleagues while Habré is not, but he supported the publication of the revised article here. At the time of publication, the article was a brief overview of the modern market of biometric technologies, which we conducted for ourselves before putting forward our product. The value judgments about applicability put forward in the second part of the article are based on the opinions of people who used and introduced the products, as well as on the opinions of people engaged in the production of biometric systems in Russia and Europe.
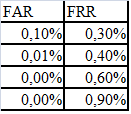
Let's start with the basics. In 95% of cases, biometrics are inherently mathematical statistics. And matstat is an exact science, from which algorithms are used everywhere: in radar and in Bayesian systems. As the two main characteristics of any biometric system, you can take the errors of the first and second kind ). In the theory of radar, they are usually called “false alarm” or “goal skipping”, and in biometrics the most well-established concepts are FAR (False Acceptance Rate) and FRR (False Rejection Rate). The first number describes the probability of a false coincidence of the biometric characteristics of two people. The second is the probability of denial of access by a person who has access. The system is the better, the lower the FRR value for the same FAR values. Sometimes a comparative characteristic EER is used, which determines the point at which the FRR and FAR plots intersect. But it is far from always representative. More details can be found, for example, here .
The following can be noted: if the FAR and FRR are not given in the characteristics of the system in open biometric databases, then so that the manufacturers would not declare its characteristics, this system is most likely incapable or much weaker than its competitors .
But not only FAR and FRR determine the quality of the biometric system. If this were the only way, then the leading technology would be the recognition of people by DNA, for which FAR and FRR tend to zero. But it is obvious that this technology is not applicable at the present stage of human development! We have developed several empirical characteristics to assess the quality of the system. “Counterfeit resistance” is an empirical characteristic that summarizes how easy it is to deceive a biometric identifier. "Resistance to the environment" is a characteristic that empirically assesses the stability of the system under different environmental conditions, such as changes in lighting or room temperature. “Ease of use” shows how difficult it is to use a biometric scanner, whether identification is possible “on the go”. An important feature is the "Speed of operation" and "Cost of the system." Do not forget that the biometric characteristics of a person can change over time, so if it is unstable, this is a significant disadvantage.
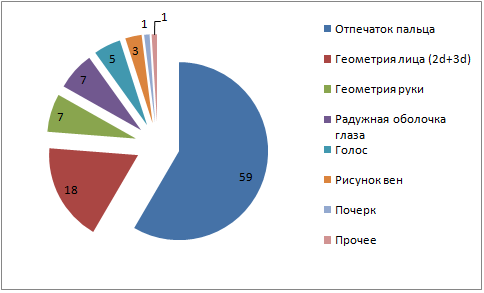
The abundance of biometric methods is amazing. The main methods using static biometric characteristics of a person are identification by papillary pattern on fingers, iris, face geometry, retina, hand vein pattern, hand geometry. There is also a family of methods that use dynamic characteristics: identification by voice, dynamics of handwritten handwriting, heart rate, gait. Below is the distribution of the biometric market a couple of years ago. In every second source, these data fluctuate by 15-20 percent, so this is just an estimate. Also here, under the concept of "hand geometry" lurk two different methods which will be described below.
In the article we will consider only those characteristics that are applicable in access control systems (ACS) or in related tasks. By virtue of their superiority, this is primarily static characteristics. Of the dynamic characteristics at the moment, only voice recognition has at least some statistical significance (comparable to the worst static algorithms FAR ~ 0.1%, FRR ~ 6%), but only under ideal conditions.
In order to feel the probabilities of FAR and FRR, one can estimate how often false coincidences will occur if you install an identification system at an organization with a staff size of N people. The probability of a false coincidence of the fingerprint obtained by the scanner for a database of N fingerprints is FAR ∙ N. And every day, about N people pass through the access control point too. Then the probability of an error per working day is FAR ∙ (N ∙ N). Of course, depending on the goals of the identification system, the probability of an error per unit of time can vary greatly, but if we accept a valid one error during the working day, then:
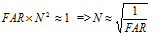 (one)
(one)
Then we obtain that the stable operation of the identification system with FAR = 0.1% = 0.001 is possible with a staff size of N≈30.
')
Today, the concept of "biometric algorithm" and "biometric scanner" are not necessarily interrelated. The company can produce these items one by one, or together. The greatest differentiation of scanner manufacturers and software manufacturers has been achieved on the papillary finger pattern biometrics market. The smallest 3D face scanner on the market. In fact, the level of differentiation largely reflects the development and saturation of the market. The more choice - the more subjects worked out and perfected. Different scanners have a different set of abilities. Basically, it is a set of tests for checking whether a biometrics object is forged or not. For finger scanners, this can be a bump test or temperature check, for eye scanners it can be a pupil accommodation check, for face scanners, a face movement.
Scanners greatly influence the FAR and FRR statistics. In some cases, these figures may change tenfold, especially in real conditions. Usually, the characteristics of the algorithm are given for some “ideal” base, or just for a well-suited one, where blurred and blurred frames are thrown out. Only a few algorithms honestly indicate both the base and the full FAR / FRR output for it.
And now more in detail about each of the technologies.

Dactyloscopy (fingerprint recognition) is the most developed to date biometric method of personal identification. The catalyst for the development of the method was its widespread use in forensic science of the 20th century.
Each person has a unique papillary fingerprint pattern, thanks to which identification is possible. Typically, algorithms use characteristic points on fingerprints: the end of the pattern line, the branching of the line, single points. Additionally, information on the morphological structure of the fingerprint is used: the relative position of the closed lines of the papillary pattern, the “arched” and spiral lines. The features of the papillary pattern are converted into a unique code that preserves the information content of the fingerprint image. And it is the “fingerprint codes” that are stored in the database used for searching and comparing. The time for transferring a fingerprint image to a code and its identification usually does not exceed 1s, depending on the size of the base. The time spent on the offering of a hand is not taken into account.
As a source of data on FAR and FRR, we used the VeriFinger SDK statistical data obtained using the DP U.are.U fingerprint scanner. Over the past 5-10 years, the recognition characteristics on the finger is not much stepped forward, so that the figures show a good average of modern algorithms. The algorithm itself VeriFinger several years won the international competition "International Fingerprint Verification Competition", where finger recognition algorithms competed.
The characteristic value of FAR for the fingerprint recognition method is 0.001%.
From formula (1), we obtain that stable operation of the identification system with FAR = 0.001% is possible with a staff size of N≈300.
The advantages of the method. High accuracy - statistical indicators of the method are better than indicators of identification methods by face, voice, and painting. Low cost fingerprint scanning devices. Simple enough procedure for scanning a print.
Disadvantages: papillary fingerprint pattern is very easily damaged by small scratches, cuts. People who use scanners in enterprises with a staff of several hundred people claim a high degree of scanning failure. Many of the scanners are inadequately related to dry skin and do not let in old people. When communicating at the last MIPS exhibition, the security chief of a large chemical enterprise said that their attempt to introduce finger scanners at the enterprise (scanners of various systems were tried) failed - the minimal impact of chemical reagents on employees' fingers caused scanner security systems to fail - the scanners declared fingers fake. There is also a lack of security against forgery of the print image, partly due to the widespread use of the method. Of course, not all scanners can be deceived by methods from the Destroyers of Legends, but still. For some people with “inappropriate” fingers (features of body temperature, humidity) the probability of access denial may reach 100%. The number of such people varies from fractions of percent for expensive scanners to ten percent for inexpensive ones.
Of course, it is worth noting that a large number of shortcomings are caused by the prevalence of the system, but these shortcomings are taking place and they appear very often.
At the moment, fingerprint recognition systems occupy more than half of the biometric market. Many Russian and foreign companies are engaged in the production of access control systems based on the method of fingerprint identification. Due to the fact that this direction is one of the oldest, it has received the most widespread and is by far the most developed. Fingerprint scanners have come a really long way to improvement. Modern systems are equipped with various sensors (temperature, pressing force, etc.), which increase the degree of protection against fakes. Every day the systems are becoming more comfortable and compact. In fact, the developers have already reached a certain limit in this area, and there is no place to develop the method. In addition, most companies produce ready-made systems that are equipped with everything you need, including software. Integrators in this area simply do not need to assemble the system themselves, since it is unprofitable and will take more time and effort than to buy a ready-made and already inexpensive system, the more the choice will be really wide.
Among the foreign companies engaged in fingerprint recognition systems, SecuGen can be mentioned (USB scanners for PCs, scanners that can be installed in enterprises or embedded in locks, SDKs, and software for connecting the system to a computer); Bayometric Inc. (fingerprint scanners, TAA / Access control systems, fingerprint SDKs, embedded fingerprint modules); DigitalPersona, Inc. (USB-scanners, SDK). In Russia, the following companies work in this area: BioLink (fingerprint scanners, biometric access control devices, software); Sonda (fingerprint scanners, biometric access control devices, SDK); SmartLok (fingerprint scanners and modules), etc.
The iris of the eye is a unique characteristic of a person. The drawing of the iris is formed in the eighth month of intrauterine development, finally stabilizes at the age of about two years and practically does not change during life, except as a result of severe injuries or abrupt pathologies. The method is one of the most accurate among biometric methods.
The system of identification by the iris is logically divided into two parts: an image capture device, its primary processing and transfer to a calculator, and a calculator that compares the image with images in the database, and sends a command to allow the actuator to execute.
The time of primary image processing in modern systems is about 300-500 ms, the speed of comparing the resulting image with the base is 5000-150000 comparisons per second on a regular PC. This comparison speed does not impose restrictions on the use of the method in large organizations when used in access systems. When using specialized calculators and search optimization algorithms, it becomes even possible to identify a person among the inhabitants of the whole country.
I can immediately reply that I am somewhat biased and have a positive attitude towards this method, since it was in this field that we launched our startup. A small self-praise will be devoted to the paragraph at the end.
The characteristics of the FAR and FRR for the iris are best in the class of modern biometric systems (with the possible exception of the method of recognition by the retina). The article presents the characteristics of the iris recognition library of our algorithm - the EyeR SDK, which correspond to the VeriEye algorithm tested using the same bases. The bases of the company CASIA obtained by their scanner were used.
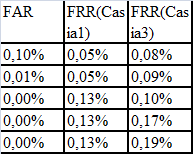
The characteristic value of FAR is 0.00001%.
According to the formula (1) N≈3000 - the number of staff of the organization, in which the identification of the employee is quite stable.
Here it is worth noting an important feature that distinguishes the system of recognition by the iris from other systems. In the case of using a resolution camera of 1.3 MP, you can capture two eyes on a single frame. Since the FAR and FRR probabilities are statistically independent probabilities, when recognizing by two eyes, the FAR value will be approximately equal to the square of the FAR value for one eye. For example, for FAR 0.001% when using two eyes, the probability of a false tolerance will be 10-8%, with FRR only two times higher than the corresponding FRR value for one eye with FAR = 0.001%.
The advantages of the method. Statistical reliability of the algorithm. Capturing the image of the iris can be done at a distance of several centimeters to several meters, while physical contact of the person with the device does not occur. The iris is protected from damage - and therefore will not change over time. It is also possible to use a high number of anti-counterfeiting methods.
Disadvantages of the method. The price of a system based on the iris is higher than the price of a system based on finger recognition or face recognition. Low availability of ready-made solutions. Any integrator who comes to the Russian market today and says “give me a ready-made system” will most likely break off. Most of them are expensive turnkey systems installed by large companies such as Iridian or LG.
At present, the specific weight of iris-based identification technologies in the global biometric market is, according to various estimates, from 6 to 9 percent (while fingerprint recognition technologies occupy more than half of the market). It should be noted that from the very beginning of the development of this method, its strengthening in the market slowed down the high cost of equipment and components necessary to assemble an identification system. However, with the development of digital technology, the cost of a separate system began to decline.
The leader in software development in this area is Iridian Technologies.
The entrance to the market to a large number of manufacturers was limited by the technical complexity of the scanners and, as a result, their high cost, as well as the high price of software due to the Iridian’s monopoly position in the market. These factors allowed only large companies to develop in the field of iris recognition, most likely already engaged in the production of some components suitable for the identification system (high-resolution optics, miniature cameras with infrared illumination, etc.). Examples of such companies are LG Electronics, Panasonic, OKI. They entered into a contract with Iridian Technologies, and as a result of joint work, the following identification systems appeared: Iris Access 2200, BM-ET500, OKI IrisPass. Later, improved models of systems emerged due to the technical capabilities of these companies to develop independently in this area. It should be said that the above companies have also developed their own software, but as a result, Iridian Technologies software is preferred in the finished system.
In the Russian market, products of foreign companies prevail. Although that can be bought with difficulty. For a long time, the firm Papilon assured everyone that they have iris recognition. But even representatives of RosAtom - their direct purchaser, for whom they made the system, say that this is not true. At some point, some other Russian company appeared that made iris scanners. Now I do not remember the name. They bought the algorithm from someone, maybe from the same VeriEye. The scanner itself was a system of 10-15 years old, not at all contactless.
In the last year, a couple of new manufacturers entered the world market due to the expiration of the primary patent for recognizing a person by the eyes. The greatest trust among them, in my opinion, deserves AOptix. At least their previews and documentation does not cause suspicion. The second company is SRI International. Even at first glance, a person engaged in iris recognition systems, their videos seem to be quite false. Although I would not be surprised if in reality they are able to do something. Both that and that system does not show data on FAR and FRR, and also, apparently, is not protected from fakes.
There are many methods of recognition on the geometry of the face. All of them are based on the fact that the facial features and the shape of the skull of each person are individual. This area of biometrics seems attractive to many, because we get to know each other first and foremost by the face. This area is divided into two areas: 2-D recognition and 3-D recognition. Each of them has advantages and disadvantages, but much also depends on the scope and requirements for a particular algorithm.
In short, I will talk about 2-d and move on to one of the most interesting methods for today - 3-d.
2-D face recognition is one of the most statistically ineffective biometrics methods. It appeared a long time ago and was used mainly in forensic science, which contributed to its development. Later computer interpretations of the method appeared, as a result of which it became more reliable, but, of course, it was inferior and more and more inferior to other biometric methods of personal identification every year. Currently, due to poor statistics, it is used in multimodal or, as it is also called, cross biometrics, or in social networks.
For FAR and FRR, data for VeriLook algorithms are used. Again, for modern algorithms, it has very ordinary characteristics. Sometimes algorithms with FRR of 0.1% are zipped with a similar FAR, but the bases for which they were obtained are very doubtful (cut out background, the same facial expression, the same hairstyle, lighting).
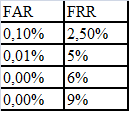
The characteristic value of FAR is 0.1%.
From the formula (1) we get N≈30 - the number of staff of the organization, in which the identification of the employee is quite stable.
As can be seen, the statistical indicators of the method are quite modest: this eliminates the advantage of the method that it is possible to carry out hidden surveys of people in crowded places. It's funny to watch a regular project on detecting criminals through video cameras installed in crowded places financed a couple of times a year. Over the past ten years, the statistical characteristics of the algorithm have not improved, and the number of such projects has grown. Although, it is worth noting that the algorithm is quite suitable for leading a person in a crowd through many cameras.
The advantages of the method. With 2-D recognition, unlike most biometric methods, expensive equipment is not required. With appropriate equipment, recognition is possible at considerable distances from the camera.
Disadvantages. Low statistical confidence. There are requirements for lighting (for example, it is not possible to register the faces of people entering from the street on a sunny day). For many algorithms unacceptability of any external interference, such as glasses, a beard, some elements of hair. Be sure to frontal image of the face, with very small deviations. Many algorithms do not take into account possible changes in facial expressions, that is, the expression must be neutral.
The implementation of this method is a rather difficult task. Despite this, there are currently many methods for 3-D facial recognition. Methods can not be compared with each other, as they use different scanners and databases. far from all of them give out FAR and FRR, completely different approaches are used.
Transitional from 2-d to 3-d method is a method that implements the accumulation of information about a person. This method has better characteristics than the 2d method, but just like it uses only one camera. When the subject enters the database, the subject turns its head and the algorithm connects the image together, creating a 3d template. And when recognition is used several frames of the video stream. This method rather refers to the experimental and implementation for access control systems I have never seen.
The most classic method is the template projection method. It consists in the fact that a grid is projected onto the object (person). Next, the camera takes pictures at a speed of tens of frames per second, and the resulting images are processed by a special program. The beam falling on a curved surface is bent - the greater the curvature of the surface, the stronger the bending of the beam. Initially, this used a source of visible light supplied through the "blinds". Then the visible light was replaced by infrared, which has several advantages. Usually, at the first stage of processing, images are discarded, in which faces are not visible at all or there are foreign objects that interfere with identification. A 3-D model of the face is restored on the images obtained, on which unnecessary interferences (hairstyle, beard, mustache, and glasses) are highlighted and removed. Then the model is analyzed - anthropometric features are singled out, which ultimately are recorded in a unique code entered into the database. Image capture and processing time is 1-2 seconds for the best models.
Also gaining popularity is the method of 3-d recognition by the image obtained from several cameras. An example of this is Vocord with its 3d scanner. This method gives positioning accuracy, according to the developers' assertions, above the template projection method. But, until I see FAR and FRR at least on their own base - I won’t believe it !!! But it is already being developed for 3 years, and the movements at the exhibitions are not yet visible.
The complete data on FRR and FAR for algorithms of this class are not explicitly given on manufacturers' websites. But for the best Bioscript models (3D EnrolCam, 3D FastPass), working according to the template projection method with FAR = 0.0047%, the FRR is 0.103%.
It is believed that the statistical reliability of the method is comparable to the reliability of the fingerprint identification method.
The advantages of the method. No need to contact the scanning device. Low sensitivity to external factors, both on the person himself (appearance of glasses, beard, change of hairstyle), and in his environment (light, turn of the head). High level of reliability comparable to fingerprint identification.
Disadvantages of the method. The high cost of equipment. Commercially available systems outperformed even iris scanners. Changes in facial expressions and disturbances on the face worsen the statistical reliability of the method. The method is not yet well developed, especially in comparison with the long-used fingerprinting, which complicates its widespread use.
Face recognition by geometry is referred to as “three large biometrics” along with fingerprint and iris recognition. It must be said that this method is quite common, and so far it is given preference over recognition by the iris. The specific weight of face recognition technology in the total volume of the global biometric market can be estimated at between 13-18 percent. In Russia, this technology also shows a greater interest than, for example, in iris identification. As mentioned earlier, there are many 3-D recognition algorithms. Most companies prefer to develop ready-made systems, including scanners, servers and software. However, there are those who offer the consumer only the SDK. Today we can mention the following companiesinvolved in the development of this technology: Geometrix, Inc. (3D facial scanners, software), Genex Technologies (3D facial scanners, software) in the USA, Cognitec Systems GmbH (SDK, special calculators, 2D cameras) in Germany, Bioscrypt (3D facial scanners, software) is a subsidiary of the American company L- 1 Identity Solutions.
In Russia, Artec Group companies (3D face scanners and software) are working in this direction - a company headquartered in California, and development and production are carried out in Moscow. Also, several Russian companies own 2D face recognition technology - Vocord, ITV, etc.
In the field of 2D face recognition, software is the main subject of development, since conventional cameras are great at capturing face images. The solution to the problem of recognizing the image of a face has to some extent come to a standstill — for several years now, the statistical indicators of the algorithms have practically not improved. In this area there is a systematic "work on the bugs."
3D face recognition is now a much more attractive area for developers. A lot of teams work in it and regularly hear about new discoveries. Many works are in a state of "about to release." But so far the market has only old offers; in recent years, the choice has not changed.
One of the interesting points that I sometimes think about and which Habre might answer: will there be enough kinect to create such a system? Projects to pull out a 3d model of a person through him are quite possible.
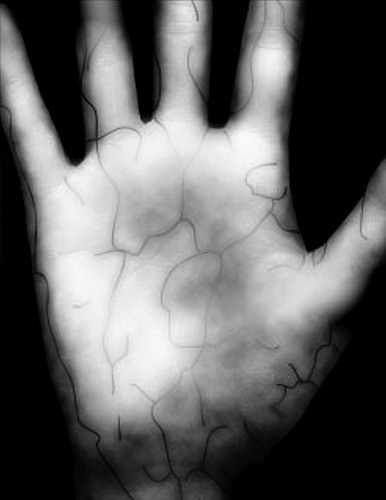
This is a new technology in the field of biometrics, its widespread use began just 5-10 years ago. An infrared camera takes pictures of the outside or inside of the arm. The pattern of veins is formed due to the fact that blood hemoglobin absorbs IR radiation. As a result, the degree of reflection is reduced, and veins are visible on the camera as black lines. A special program based on the data obtained creates a digital convolution. No human contact with the scanning device is required.
The technology is comparable in reliability with the recognition of the iris of the eye, somewhat superior to it, but somewhat inferior.
FRR and FAR values are given for the Palm Vein scanner. According to the developer, with a FAR of 0.0008%, the FRR is 0.01%. No firm gives a more accurate graph for several values.
The advantages of the method. No need to contact the scanning device. High accuracy - the statistics of the method are comparable with the indications of the iris. Hidden characteristics: in contrast to all of the above - this characteristic is very difficult to get from a person "on the street", for example, having photographed him with a camera.
Disadvantages of the method. The scanner's illumination by sunlight and the rays of halogen bulbs is unacceptable. Some age-related diseases, such as arthritis, greatly worsen FAR and FRR. The method is less studied in comparison with other static methods of biometrics.
Recognition of the pattern of the veins of the hand is a fairly new technology, and therefore its share on the world market is small and amounts to about 3%. However, this method is becoming increasingly interesting. The fact is that, being fairly accurate, this method does not require such expensive equipment as, for example, face recognition or iris recognition methods. Now many companies are developing in this area. For example, on the request of the British company TDSi, software was developed for a palm vein biometric reader PalmVein, represented by Fujitsu. The scanner itself was developed by Fujitsu primarily to combat financial fraud in Japan.
The following companies, Veid Pte, also work in the field of vein identification. Ltd.(scanner, software), Hitachi VeinID (scanners)
In Russia, the companies involved in this technology, I do not know.
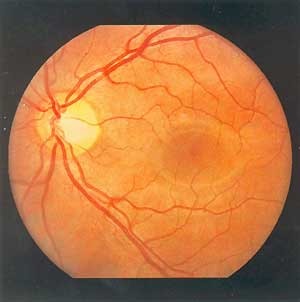
Until recently, it was believed that the most reliable method of biometric identification and authentication of identity is a method based on scanning the retina. It contains the best features of identification by the iris and veins of the hand. The scanner reads the capillary pattern on the surface of the retina. The retina has a fixed structure, unchanged in time, except as a result of the disease, for example, cataracts.
Retinal scanning is performed using low-intensity infrared light directed through the pupil to the blood vessels at the back of the eye. Retinal scanners are widely used in access control systems for highly sensitive objects, since they have one of the lowest rates of denial of access for registered users and there is almost no mistaken access authorization.
Unfortunately, a number of difficulties arise when using this method of biometrics. The scanner here is a very complex optical system, and a person must not move for a considerable time while the system is pointing, which causes discomfort.
According to the company EyeDentify for the scanner ICAM2001 with FAR = 0.001%, the FRR value is 0.4%.
Benefits. High level of statistical reliability. Due to the low prevalence of systems, there is little likelihood of developing a way to "deceive" them.
Disadvantages.Difficult to use system with high processing time. High system cost. The absence of a broad market offer and, as a consequence, an insufficient intensity of development of the method.

This method is quite common 10 years ago and what has happened from criminalistics in recent years has been waning. It is based on obtaining the geometric characteristics of the hands: finger lengths, palm width, etc. This method, like the retina of the eye, is dying, and since it has much lower characteristics, we will not even introduce its full description.
It is sometimes considered that geometric recognition methods are used in vein recognition systems. But on sale, we have never seen such clearly stated. And besides, often when recognizing through the veins, only a palm is taken, while when recognizing by geometry, a finger is taken.
At the time, we have developed a good recognition algorithm for the eyes. But at that time such a high-tech thing in this country was not needed, and in the bourgeois (where we were invited after the very first article) - I didn’t want to go. But suddenly, after a year and a half, investors were found who wanted to build a “biometric portal” for themselves - a system that would eat 2 eyes and use the color component of the iris (which the investor had a world patent for). Actually now we are doing it. But this is not an article about self-praise, it is a brief lyrical digression. If anyone is interested there is a little bit of information, and sometime in the future, when we enter the market (or not), I will write a few words about the vicissitudes of a biometric project in Russia.
Even in the class of static biometric systems there is a large selection of systems. Which one to choose? It all depends on the security requirements. The most statistically reliable and tamper-resistant access systems are the iris and vein access systems. On the first of them there is a wider market of offers. But this is not the limit. Biometric identification systems can be combined to achieve astronomical accuracy. The cheapest and easiest to use, but with good statistics, are fingertip tolerance systems. The admission on 2D to the person is convenient and cheap, but has limited scope of applications because of bad statistical indicators.
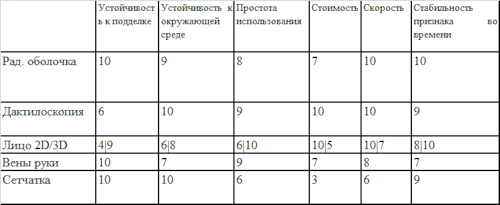
Consider the characteristics that each of the systems will have: resistance to forgery, resistance to the environment, ease of use, cost, speed, stability of the biometric feature over time. We place the estimates from 1 to 10 in each graph. The closer the score to 10, the better the system in this respect. Principles for the selection of ratings were described at the very beginning of the article.
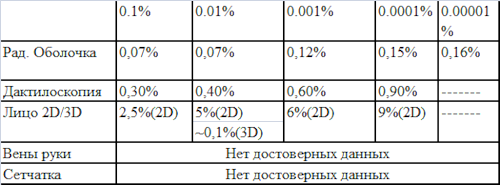
Also consider the ratio of FAR and FRR for these systems. This ratio determines the effectiveness of the system and the breadth of its use.
It is worth remembering that for the iris you can increase the accuracy of the system almost quadratically, without loss for time, if you complicate the system by making it into two eyes. For the dactyloscopic method - by combining several fingers, and recognizing by veins, by combining two hands, but this improvement is possible only with an increase in time spent working with a person.
Summarizing the results for the methods, it can be said that for medium and large objects, as well as for objects with maximum safety requirements, the iris should be used as a biometric access and, possibly, recognition by the veins of the hands. For facilities with up to several hundred personnel, fingerprint access will be optimal. The recognition systems for 2D face images are very specific. They may be required in cases where recognition requires a lack of physical contact, but it is not possible to install the iris control system. For example, if it is necessary to identify a person without his participation, a hidden camera, or an outdoor detection camera, but this is possible only with a small number of subjects in the database and a small stream of people filmed by the camera.
Some manufacturers, such as Neurotechnology, have demo versions of biometrics methods available on the site, which they can do, so you can easily plug them in and play. For those who decide to delve into the problem more seriously, I can advise the only book I saw in Russian - the “Guide to Biometrics” by R.M. Ball, J.H. Connel, S. Pankanti. There are many algorithms and their mathematical models. Not everything is complete and not everything corresponds to modernity, but the base is not bad and inclusive.
In this opus, I did not go into the problem of authentication, but only affected the identification. In principle, from the characteristics of FAR / FRR and the possibility of falsification, all conclusions on the issue of authentication suggest themselves.
The article has a sequel , which, in fact, is its primal.
As a basis for the article, a joint publication with a colleague in a journal ( BDI, 2009 ) will be used, revised for modern realities. Colleagues while Habré is not, but he supported the publication of the revised article here. At the time of publication, the article was a brief overview of the modern market of biometric technologies, which we conducted for ourselves before putting forward our product. The value judgments about applicability put forward in the second part of the article are based on the opinions of people who used and introduced the products, as well as on the opinions of people engaged in the production of biometric systems in Russia and Europe.
general information
Let's start with the basics. In 95% of cases, biometrics are inherently mathematical statistics. And matstat is an exact science, from which algorithms are used everywhere: in radar and in Bayesian systems. As the two main characteristics of any biometric system, you can take the errors of the first and second kind ). In the theory of radar, they are usually called “false alarm” or “goal skipping”, and in biometrics the most well-established concepts are FAR (False Acceptance Rate) and FRR (False Rejection Rate). The first number describes the probability of a false coincidence of the biometric characteristics of two people. The second is the probability of denial of access by a person who has access. The system is the better, the lower the FRR value for the same FAR values. Sometimes a comparative characteristic EER is used, which determines the point at which the FRR and FAR plots intersect. But it is far from always representative. More details can be found, for example, here .
The following can be noted: if the FAR and FRR are not given in the characteristics of the system in open biometric databases, then so that the manufacturers would not declare its characteristics, this system is most likely incapable or much weaker than its competitors .
But not only FAR and FRR determine the quality of the biometric system. If this were the only way, then the leading technology would be the recognition of people by DNA, for which FAR and FRR tend to zero. But it is obvious that this technology is not applicable at the present stage of human development! We have developed several empirical characteristics to assess the quality of the system. “Counterfeit resistance” is an empirical characteristic that summarizes how easy it is to deceive a biometric identifier. "Resistance to the environment" is a characteristic that empirically assesses the stability of the system under different environmental conditions, such as changes in lighting or room temperature. “Ease of use” shows how difficult it is to use a biometric scanner, whether identification is possible “on the go”. An important feature is the "Speed of operation" and "Cost of the system." Do not forget that the biometric characteristics of a person can change over time, so if it is unstable, this is a significant disadvantage.
The abundance of biometric methods is amazing. The main methods using static biometric characteristics of a person are identification by papillary pattern on fingers, iris, face geometry, retina, hand vein pattern, hand geometry. There is also a family of methods that use dynamic characteristics: identification by voice, dynamics of handwritten handwriting, heart rate, gait. Below is the distribution of the biometric market a couple of years ago. In every second source, these data fluctuate by 15-20 percent, so this is just an estimate. Also here, under the concept of "hand geometry" lurk two different methods which will be described below.

In the article we will consider only those characteristics that are applicable in access control systems (ACS) or in related tasks. By virtue of their superiority, this is primarily static characteristics. Of the dynamic characteristics at the moment, only voice recognition has at least some statistical significance (comparable to the worst static algorithms FAR ~ 0.1%, FRR ~ 6%), but only under ideal conditions.
In order to feel the probabilities of FAR and FRR, one can estimate how often false coincidences will occur if you install an identification system at an organization with a staff size of N people. The probability of a false coincidence of the fingerprint obtained by the scanner for a database of N fingerprints is FAR ∙ N. And every day, about N people pass through the access control point too. Then the probability of an error per working day is FAR ∙ (N ∙ N). Of course, depending on the goals of the identification system, the probability of an error per unit of time can vary greatly, but if we accept a valid one error during the working day, then:
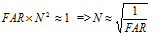 (one)
(one)Then we obtain that the stable operation of the identification system with FAR = 0.1% = 0.001 is possible with a staff size of N≈30.
')
Biometric scanners
Today, the concept of "biometric algorithm" and "biometric scanner" are not necessarily interrelated. The company can produce these items one by one, or together. The greatest differentiation of scanner manufacturers and software manufacturers has been achieved on the papillary finger pattern biometrics market. The smallest 3D face scanner on the market. In fact, the level of differentiation largely reflects the development and saturation of the market. The more choice - the more subjects worked out and perfected. Different scanners have a different set of abilities. Basically, it is a set of tests for checking whether a biometrics object is forged or not. For finger scanners, this can be a bump test or temperature check, for eye scanners it can be a pupil accommodation check, for face scanners, a face movement.
Scanners greatly influence the FAR and FRR statistics. In some cases, these figures may change tenfold, especially in real conditions. Usually, the characteristics of the algorithm are given for some “ideal” base, or just for a well-suited one, where blurred and blurred frames are thrown out. Only a few algorithms honestly indicate both the base and the full FAR / FRR output for it.
And now more in detail about each of the technologies.
Fingerprints

Dactyloscopy (fingerprint recognition) is the most developed to date biometric method of personal identification. The catalyst for the development of the method was its widespread use in forensic science of the 20th century.
Each person has a unique papillary fingerprint pattern, thanks to which identification is possible. Typically, algorithms use characteristic points on fingerprints: the end of the pattern line, the branching of the line, single points. Additionally, information on the morphological structure of the fingerprint is used: the relative position of the closed lines of the papillary pattern, the “arched” and spiral lines. The features of the papillary pattern are converted into a unique code that preserves the information content of the fingerprint image. And it is the “fingerprint codes” that are stored in the database used for searching and comparing. The time for transferring a fingerprint image to a code and its identification usually does not exceed 1s, depending on the size of the base. The time spent on the offering of a hand is not taken into account.
Statistical characteristics of the method
As a source of data on FAR and FRR, we used the VeriFinger SDK statistical data obtained using the DP U.are.U fingerprint scanner. Over the past 5-10 years, the recognition characteristics on the finger is not much stepped forward, so that the figures show a good average of modern algorithms. The algorithm itself VeriFinger several years won the international competition "International Fingerprint Verification Competition", where finger recognition algorithms competed.

The characteristic value of FAR for the fingerprint recognition method is 0.001%.
From formula (1), we obtain that stable operation of the identification system with FAR = 0.001% is possible with a staff size of N≈300.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
The advantages of the method. High accuracy - statistical indicators of the method are better than indicators of identification methods by face, voice, and painting. Low cost fingerprint scanning devices. Simple enough procedure for scanning a print.
Disadvantages: papillary fingerprint pattern is very easily damaged by small scratches, cuts. People who use scanners in enterprises with a staff of several hundred people claim a high degree of scanning failure. Many of the scanners are inadequately related to dry skin and do not let in old people. When communicating at the last MIPS exhibition, the security chief of a large chemical enterprise said that their attempt to introduce finger scanners at the enterprise (scanners of various systems were tried) failed - the minimal impact of chemical reagents on employees' fingers caused scanner security systems to fail - the scanners declared fingers fake. There is also a lack of security against forgery of the print image, partly due to the widespread use of the method. Of course, not all scanners can be deceived by methods from the Destroyers of Legends, but still. For some people with “inappropriate” fingers (features of body temperature, humidity) the probability of access denial may reach 100%. The number of such people varies from fractions of percent for expensive scanners to ten percent for inexpensive ones.
Of course, it is worth noting that a large number of shortcomings are caused by the prevalence of the system, but these shortcomings are taking place and they appear very often.
Market situation
At the moment, fingerprint recognition systems occupy more than half of the biometric market. Many Russian and foreign companies are engaged in the production of access control systems based on the method of fingerprint identification. Due to the fact that this direction is one of the oldest, it has received the most widespread and is by far the most developed. Fingerprint scanners have come a really long way to improvement. Modern systems are equipped with various sensors (temperature, pressing force, etc.), which increase the degree of protection against fakes. Every day the systems are becoming more comfortable and compact. In fact, the developers have already reached a certain limit in this area, and there is no place to develop the method. In addition, most companies produce ready-made systems that are equipped with everything you need, including software. Integrators in this area simply do not need to assemble the system themselves, since it is unprofitable and will take more time and effort than to buy a ready-made and already inexpensive system, the more the choice will be really wide.
Among the foreign companies engaged in fingerprint recognition systems, SecuGen can be mentioned (USB scanners for PCs, scanners that can be installed in enterprises or embedded in locks, SDKs, and software for connecting the system to a computer); Bayometric Inc. (fingerprint scanners, TAA / Access control systems, fingerprint SDKs, embedded fingerprint modules); DigitalPersona, Inc. (USB-scanners, SDK). In Russia, the following companies work in this area: BioLink (fingerprint scanners, biometric access control devices, software); Sonda (fingerprint scanners, biometric access control devices, SDK); SmartLok (fingerprint scanners and modules), etc.
Iris

The iris of the eye is a unique characteristic of a person. The drawing of the iris is formed in the eighth month of intrauterine development, finally stabilizes at the age of about two years and practically does not change during life, except as a result of severe injuries or abrupt pathologies. The method is one of the most accurate among biometric methods.
The system of identification by the iris is logically divided into two parts: an image capture device, its primary processing and transfer to a calculator, and a calculator that compares the image with images in the database, and sends a command to allow the actuator to execute.
The time of primary image processing in modern systems is about 300-500 ms, the speed of comparing the resulting image with the base is 5000-150000 comparisons per second on a regular PC. This comparison speed does not impose restrictions on the use of the method in large organizations when used in access systems. When using specialized calculators and search optimization algorithms, it becomes even possible to identify a person among the inhabitants of the whole country.
I can immediately reply that I am somewhat biased and have a positive attitude towards this method, since it was in this field that we launched our startup. A small self-praise will be devoted to the paragraph at the end.
Statistical characteristics of the method
The characteristics of the FAR and FRR for the iris are best in the class of modern biometric systems (with the possible exception of the method of recognition by the retina). The article presents the characteristics of the iris recognition library of our algorithm - the EyeR SDK, which correspond to the VeriEye algorithm tested using the same bases. The bases of the company CASIA obtained by their scanner were used.

The characteristic value of FAR is 0.00001%.
According to the formula (1) N≈3000 - the number of staff of the organization, in which the identification of the employee is quite stable.
Here it is worth noting an important feature that distinguishes the system of recognition by the iris from other systems. In the case of using a resolution camera of 1.3 MP, you can capture two eyes on a single frame. Since the FAR and FRR probabilities are statistically independent probabilities, when recognizing by two eyes, the FAR value will be approximately equal to the square of the FAR value for one eye. For example, for FAR 0.001% when using two eyes, the probability of a false tolerance will be 10-8%, with FRR only two times higher than the corresponding FRR value for one eye with FAR = 0.001%.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
The advantages of the method. Statistical reliability of the algorithm. Capturing the image of the iris can be done at a distance of several centimeters to several meters, while physical contact of the person with the device does not occur. The iris is protected from damage - and therefore will not change over time. It is also possible to use a high number of anti-counterfeiting methods.
Disadvantages of the method. The price of a system based on the iris is higher than the price of a system based on finger recognition or face recognition. Low availability of ready-made solutions. Any integrator who comes to the Russian market today and says “give me a ready-made system” will most likely break off. Most of them are expensive turnkey systems installed by large companies such as Iridian or LG.
Market situation
At present, the specific weight of iris-based identification technologies in the global biometric market is, according to various estimates, from 6 to 9 percent (while fingerprint recognition technologies occupy more than half of the market). It should be noted that from the very beginning of the development of this method, its strengthening in the market slowed down the high cost of equipment and components necessary to assemble an identification system. However, with the development of digital technology, the cost of a separate system began to decline.
The leader in software development in this area is Iridian Technologies.
The entrance to the market to a large number of manufacturers was limited by the technical complexity of the scanners and, as a result, their high cost, as well as the high price of software due to the Iridian’s monopoly position in the market. These factors allowed only large companies to develop in the field of iris recognition, most likely already engaged in the production of some components suitable for the identification system (high-resolution optics, miniature cameras with infrared illumination, etc.). Examples of such companies are LG Electronics, Panasonic, OKI. They entered into a contract with Iridian Technologies, and as a result of joint work, the following identification systems appeared: Iris Access 2200, BM-ET500, OKI IrisPass. Later, improved models of systems emerged due to the technical capabilities of these companies to develop independently in this area. It should be said that the above companies have also developed their own software, but as a result, Iridian Technologies software is preferred in the finished system.
In the Russian market, products of foreign companies prevail. Although that can be bought with difficulty. For a long time, the firm Papilon assured everyone that they have iris recognition. But even representatives of RosAtom - their direct purchaser, for whom they made the system, say that this is not true. At some point, some other Russian company appeared that made iris scanners. Now I do not remember the name. They bought the algorithm from someone, maybe from the same VeriEye. The scanner itself was a system of 10-15 years old, not at all contactless.
In the last year, a couple of new manufacturers entered the world market due to the expiration of the primary patent for recognizing a person by the eyes. The greatest trust among them, in my opinion, deserves AOptix. At least their previews and documentation does not cause suspicion. The second company is SRI International. Even at first glance, a person engaged in iris recognition systems, their videos seem to be quite false. Although I would not be surprised if in reality they are able to do something. Both that and that system does not show data on FAR and FRR, and also, apparently, is not protected from fakes.
Face Recognition
There are many methods of recognition on the geometry of the face. All of them are based on the fact that the facial features and the shape of the skull of each person are individual. This area of biometrics seems attractive to many, because we get to know each other first and foremost by the face. This area is divided into two areas: 2-D recognition and 3-D recognition. Each of them has advantages and disadvantages, but much also depends on the scope and requirements for a particular algorithm.
In short, I will talk about 2-d and move on to one of the most interesting methods for today - 3-d.
2-D face recognition

2-D face recognition is one of the most statistically ineffective biometrics methods. It appeared a long time ago and was used mainly in forensic science, which contributed to its development. Later computer interpretations of the method appeared, as a result of which it became more reliable, but, of course, it was inferior and more and more inferior to other biometric methods of personal identification every year. Currently, due to poor statistics, it is used in multimodal or, as it is also called, cross biometrics, or in social networks.
Statistical characteristics of the method
For FAR and FRR, data for VeriLook algorithms are used. Again, for modern algorithms, it has very ordinary characteristics. Sometimes algorithms with FRR of 0.1% are zipped with a similar FAR, but the bases for which they were obtained are very doubtful (cut out background, the same facial expression, the same hairstyle, lighting).

The characteristic value of FAR is 0.1%.
From the formula (1) we get N≈30 - the number of staff of the organization, in which the identification of the employee is quite stable.
As can be seen, the statistical indicators of the method are quite modest: this eliminates the advantage of the method that it is possible to carry out hidden surveys of people in crowded places. It's funny to watch a regular project on detecting criminals through video cameras installed in crowded places financed a couple of times a year. Over the past ten years, the statistical characteristics of the algorithm have not improved, and the number of such projects has grown. Although, it is worth noting that the algorithm is quite suitable for leading a person in a crowd through many cameras.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
The advantages of the method. With 2-D recognition, unlike most biometric methods, expensive equipment is not required. With appropriate equipment, recognition is possible at considerable distances from the camera.
Disadvantages. Low statistical confidence. There are requirements for lighting (for example, it is not possible to register the faces of people entering from the street on a sunny day). For many algorithms unacceptability of any external interference, such as glasses, a beard, some elements of hair. Be sure to frontal image of the face, with very small deviations. Many algorithms do not take into account possible changes in facial expressions, that is, the expression must be neutral.
3-D face recognition

The implementation of this method is a rather difficult task. Despite this, there are currently many methods for 3-D facial recognition. Methods can not be compared with each other, as they use different scanners and databases. far from all of them give out FAR and FRR, completely different approaches are used.
Transitional from 2-d to 3-d method is a method that implements the accumulation of information about a person. This method has better characteristics than the 2d method, but just like it uses only one camera. When the subject enters the database, the subject turns its head and the algorithm connects the image together, creating a 3d template. And when recognition is used several frames of the video stream. This method rather refers to the experimental and implementation for access control systems I have never seen.
The most classic method is the template projection method. It consists in the fact that a grid is projected onto the object (person). Next, the camera takes pictures at a speed of tens of frames per second, and the resulting images are processed by a special program. The beam falling on a curved surface is bent - the greater the curvature of the surface, the stronger the bending of the beam. Initially, this used a source of visible light supplied through the "blinds". Then the visible light was replaced by infrared, which has several advantages. Usually, at the first stage of processing, images are discarded, in which faces are not visible at all or there are foreign objects that interfere with identification. A 3-D model of the face is restored on the images obtained, on which unnecessary interferences (hairstyle, beard, mustache, and glasses) are highlighted and removed. Then the model is analyzed - anthropometric features are singled out, which ultimately are recorded in a unique code entered into the database. Image capture and processing time is 1-2 seconds for the best models.
Also gaining popularity is the method of 3-d recognition by the image obtained from several cameras. An example of this is Vocord with its 3d scanner. This method gives positioning accuracy, according to the developers' assertions, above the template projection method. But, until I see FAR and FRR at least on their own base - I won’t believe it !!! But it is already being developed for 3 years, and the movements at the exhibitions are not yet visible.
Method statistics
The complete data on FRR and FAR for algorithms of this class are not explicitly given on manufacturers' websites. But for the best Bioscript models (3D EnrolCam, 3D FastPass), working according to the template projection method with FAR = 0.0047%, the FRR is 0.103%.
It is believed that the statistical reliability of the method is comparable to the reliability of the fingerprint identification method.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
The advantages of the method. No need to contact the scanning device. Low sensitivity to external factors, both on the person himself (appearance of glasses, beard, change of hairstyle), and in his environment (light, turn of the head). High level of reliability comparable to fingerprint identification.
Disadvantages of the method. The high cost of equipment. Commercially available systems outperformed even iris scanners. Changes in facial expressions and disturbances on the face worsen the statistical reliability of the method. The method is not yet well developed, especially in comparison with the long-used fingerprinting, which complicates its widespread use.
Market situation
Face recognition by geometry is referred to as “three large biometrics” along with fingerprint and iris recognition. It must be said that this method is quite common, and so far it is given preference over recognition by the iris. The specific weight of face recognition technology in the total volume of the global biometric market can be estimated at between 13-18 percent. In Russia, this technology also shows a greater interest than, for example, in iris identification. As mentioned earlier, there are many 3-D recognition algorithms. Most companies prefer to develop ready-made systems, including scanners, servers and software. However, there are those who offer the consumer only the SDK. Today we can mention the following companiesinvolved in the development of this technology: Geometrix, Inc. (3D facial scanners, software), Genex Technologies (3D facial scanners, software) in the USA, Cognitec Systems GmbH (SDK, special calculators, 2D cameras) in Germany, Bioscrypt (3D facial scanners, software) is a subsidiary of the American company L- 1 Identity Solutions.
In Russia, Artec Group companies (3D face scanners and software) are working in this direction - a company headquartered in California, and development and production are carried out in Moscow. Also, several Russian companies own 2D face recognition technology - Vocord, ITV, etc.
In the field of 2D face recognition, software is the main subject of development, since conventional cameras are great at capturing face images. The solution to the problem of recognizing the image of a face has to some extent come to a standstill — for several years now, the statistical indicators of the algorithms have practically not improved. In this area there is a systematic "work on the bugs."
3D face recognition is now a much more attractive area for developers. A lot of teams work in it and regularly hear about new discoveries. Many works are in a state of "about to release." But so far the market has only old offers; in recent years, the choice has not changed.
One of the interesting points that I sometimes think about and which Habre might answer: will there be enough kinect to create such a system? Projects to pull out a 3d model of a person through him are quite possible.
Vein Recognition

This is a new technology in the field of biometrics, its widespread use began just 5-10 years ago. An infrared camera takes pictures of the outside or inside of the arm. The pattern of veins is formed due to the fact that blood hemoglobin absorbs IR radiation. As a result, the degree of reflection is reduced, and veins are visible on the camera as black lines. A special program based on the data obtained creates a digital convolution. No human contact with the scanning device is required.
The technology is comparable in reliability with the recognition of the iris of the eye, somewhat superior to it, but somewhat inferior.
FRR and FAR values are given for the Palm Vein scanner. According to the developer, with a FAR of 0.0008%, the FRR is 0.01%. No firm gives a more accurate graph for several values.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
The advantages of the method. No need to contact the scanning device. High accuracy - the statistics of the method are comparable with the indications of the iris. Hidden characteristics: in contrast to all of the above - this characteristic is very difficult to get from a person "on the street", for example, having photographed him with a camera.
Disadvantages of the method. The scanner's illumination by sunlight and the rays of halogen bulbs is unacceptable. Some age-related diseases, such as arthritis, greatly worsen FAR and FRR. The method is less studied in comparison with other static methods of biometrics.
Market situation
Recognition of the pattern of the veins of the hand is a fairly new technology, and therefore its share on the world market is small and amounts to about 3%. However, this method is becoming increasingly interesting. The fact is that, being fairly accurate, this method does not require such expensive equipment as, for example, face recognition or iris recognition methods. Now many companies are developing in this area. For example, on the request of the British company TDSi, software was developed for a palm vein biometric reader PalmVein, represented by Fujitsu. The scanner itself was developed by Fujitsu primarily to combat financial fraud in Japan.
The following companies, Veid Pte, also work in the field of vein identification. Ltd.(scanner, software), Hitachi VeinID (scanners)
In Russia, the companies involved in this technology, I do not know.
Retina

Until recently, it was believed that the most reliable method of biometric identification and authentication of identity is a method based on scanning the retina. It contains the best features of identification by the iris and veins of the hand. The scanner reads the capillary pattern on the surface of the retina. The retina has a fixed structure, unchanged in time, except as a result of the disease, for example, cataracts.
Retinal scanning is performed using low-intensity infrared light directed through the pupil to the blood vessels at the back of the eye. Retinal scanners are widely used in access control systems for highly sensitive objects, since they have one of the lowest rates of denial of access for registered users and there is almost no mistaken access authorization.
Unfortunately, a number of difficulties arise when using this method of biometrics. The scanner here is a very complex optical system, and a person must not move for a considerable time while the system is pointing, which causes discomfort.
According to the company EyeDentify for the scanner ICAM2001 with FAR = 0.001%, the FRR value is 0.4%.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
Benefits. High level of statistical reliability. Due to the low prevalence of systems, there is little likelihood of developing a way to "deceive" them.
Disadvantages.Difficult to use system with high processing time. High system cost. The absence of a broad market offer and, as a consequence, an insufficient intensity of development of the method.
Hand geometry

This method is quite common 10 years ago and what has happened from criminalistics in recent years has been waning. It is based on obtaining the geometric characteristics of the hands: finger lengths, palm width, etc. This method, like the retina of the eye, is dying, and since it has much lower characteristics, we will not even introduce its full description.
It is sometimes considered that geometric recognition methods are used in vein recognition systems. But on sale, we have never seen such clearly stated. And besides, often when recognizing through the veins, only a palm is taken, while when recognizing by geometry, a finger is taken.
A little self-praise
At the time, we have developed a good recognition algorithm for the eyes. But at that time such a high-tech thing in this country was not needed, and in the bourgeois (where we were invited after the very first article) - I didn’t want to go. But suddenly, after a year and a half, investors were found who wanted to build a “biometric portal” for themselves - a system that would eat 2 eyes and use the color component of the iris (which the investor had a world patent for). Actually now we are doing it. But this is not an article about self-praise, it is a brief lyrical digression. If anyone is interested there is a little bit of information, and sometime in the future, when we enter the market (or not), I will write a few words about the vicissitudes of a biometric project in Russia.
findings
Even in the class of static biometric systems there is a large selection of systems. Which one to choose? It all depends on the security requirements. The most statistically reliable and tamper-resistant access systems are the iris and vein access systems. On the first of them there is a wider market of offers. But this is not the limit. Biometric identification systems can be combined to achieve astronomical accuracy. The cheapest and easiest to use, but with good statistics, are fingertip tolerance systems. The admission on 2D to the person is convenient and cheap, but has limited scope of applications because of bad statistical indicators.
Consider the characteristics that each of the systems will have: resistance to forgery, resistance to the environment, ease of use, cost, speed, stability of the biometric feature over time. We place the estimates from 1 to 10 in each graph. The closer the score to 10, the better the system in this respect. Principles for the selection of ratings were described at the very beginning of the article.

Also consider the ratio of FAR and FRR for these systems. This ratio determines the effectiveness of the system and the breadth of its use.

It is worth remembering that for the iris you can increase the accuracy of the system almost quadratically, without loss for time, if you complicate the system by making it into two eyes. For the dactyloscopic method - by combining several fingers, and recognizing by veins, by combining two hands, but this improvement is possible only with an increase in time spent working with a person.
Summarizing the results for the methods, it can be said that for medium and large objects, as well as for objects with maximum safety requirements, the iris should be used as a biometric access and, possibly, recognition by the veins of the hands. For facilities with up to several hundred personnel, fingerprint access will be optimal. The recognition systems for 2D face images are very specific. They may be required in cases where recognition requires a lack of physical contact, but it is not possible to install the iris control system. For example, if it is necessary to identify a person without his participation, a hidden camera, or an outdoor detection camera, but this is possible only with a small number of subjects in the database and a small stream of people filmed by the camera.
Young technique on the note
Some manufacturers, such as Neurotechnology, have demo versions of biometrics methods available on the site, which they can do, so you can easily plug them in and play. For those who decide to delve into the problem more seriously, I can advise the only book I saw in Russian - the “Guide to Biometrics” by R.M. Ball, J.H. Connel, S. Pankanti. There are many algorithms and their mathematical models. Not everything is complete and not everything corresponds to modernity, but the base is not bad and inclusive.
PS
In this opus, I did not go into the problem of authentication, but only affected the identification. In principle, from the characteristics of FAR / FRR and the possibility of falsification, all conclusions on the issue of authentication suggest themselves.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/126144/
All Articles