Labs ROUTE: EIGRP
EIGRP Lab | EIGRP Lab - Answers
 Hello! Today I want to share with the respected community the labs that helped me in preparing for the ROUTE exam from the new track CCNP, as well as thoughts and impressions from the exam. Due to the fact that there is a lot of material and lab, it will be necessary to break it all up into portions and spread them one by one. Today I propose to talk about CCNP version 6 in general, about the ROUTE exam and look at the EIGRP labs that I used to prepare for the exam.
Hello! Today I want to share with the respected community the labs that helped me in preparing for the ROUTE exam from the new track CCNP, as well as thoughts and impressions from the exam. Due to the fact that there is a lot of material and lab, it will be necessary to break it all up into portions and spread them one by one. Today I propose to talk about CCNP version 6 in general, about the ROUTE exam and look at the EIGRP labs that I used to prepare for the exam.
Interested - welcome under the cat!
By changing the CCNP last summer, Cisco had several goals. In addition to technology upgrades, CCNP was supposed to be a real “bridge” between CCNA and CCIE. CCNP version 5 was closer to CCNA than CCIE - it still contained all the phrases “more about OSPF you can read through the link” and “more details about this protocol feature are described in the CCIE course”. And in it, as in CCNA, there were many topics that are not directly related to routing and switching.
')
As a result, as the beloved Jeremy Chara tells us all about his students, the average person received the CCNP, looked at the CCIE and saw the abyss in front of him. His hands fell and he lost faith in the fact that all the material that separated the CCNP from the CCIE is generally possible to learn.
Changing CCNP, Cisco has taken into account this fact. Almost everything that does not concern Routing & Switching is excluded from the course - it is excluded and transferred to the appropriate areas of Professional certificates. VoIP has become part of CCNP Voice, Wi-Fi is part of CCNP Wireless and so on. The remnants of the former luxury in the course now relate to access technologies and VPN, being a brief overview rather than a full-fledged topic.
But the switching and routing required to build an enterprise network is fully covered. You will no longer see a Cisco EIGRP or OSPF referral site — from a technological point of view, the course covers these protocols from beginning to end. CCNP has become more complex and more specialized. Now it only includes switching and routing, but in this direction - R & S - it really is halfway from CCNA to CCIE.
Of all three new CCNP exams, ROUTE, the heir to the BSCN, is the most voluminous and the most difficult. It is included in several certification tracks: CCNP, CCDP and CCIP, covering Interior Gateway Routing Protocols completely, giving the basics of BGP and familiarizing the reader with IPv6 at a sufficient level to understand the operation of routing using it. Official Certification Guide to prepare for ROUTE - a book in more than 900 pages of text, plus it is very desirable to study the Foundation Learning Guide - another 700 pages.
And, of course, practice.
I was preparing for the exam mainly using GNS3. I have a home lab with real Cisco Systems equipment, but in my opinion GNS3 is more convenient. Functionally, the lab in GNS3 is no different from the labs on real hardware. GNS3 is more convenient in terms of viewing traffic - you don’t have to suffer from port mirroring if you want to see the traffic on the link. And besides, GNS3 is always with you, wherever you are - at work, on a business trip, on vacation. If you want to experiment with your routers, all you need is a laptop and GNS3.
The exam is difficult, but it is very, very good! True. Of course, there are several ambiguous and damp questions, there are glitches with simlets (of course, symlets of such level!), But the exam itself is just perfect! There are no obvious questions at all. Head-on questions in the style of “what is the maximum length of a 100BASE-T segment” - literally a couple of pieces. The absolute majority of questions are scripts. The questions are formulated in the style of “we already believe that you know the theory of OSPF and EIGRP, you tell us better, what would happen if you add one link to this topology? And if you fix the team here like this? And if you make this change here? But in such a topology and with such a configuration, what will be in the routing table? ”
Simlets are especially good. They no longer contain items that need to be fulfilled, as was the case in CCNA. Now the script is a rather abstract description of customer requirements. No items. Just a text. How to build the configuration so that it satisfies these requirements is already up to you. Moreover, there are several options for solving the problem. Which one is more correct - this, as I understand it, should be decided by each person on the exam independently.
The first time I failed my ROUTE. It is because of the simlet. Some of their glitches took too much time, and one of them, I suspect, I did not count because of the peculiarities of the implementation. After the exam, I wrote to the Cisco Certification Support Community, where their experts promptly requested a test from VUE, looked at the results, agreed with my arguments, and issued a voucher for a free retake. Truly, this is really a company with the principle of work “Customer as a Strategy” :-) Therefore, I would recommend you describe the glitches of simlets encountered in the comments, and if you suspect that you could not count the points for the correct answer, feel free to write in Cisco, it's a pleasure to deal with them.
The exam covers the following features of EIGRP technology:
For preparation I used the following lab:
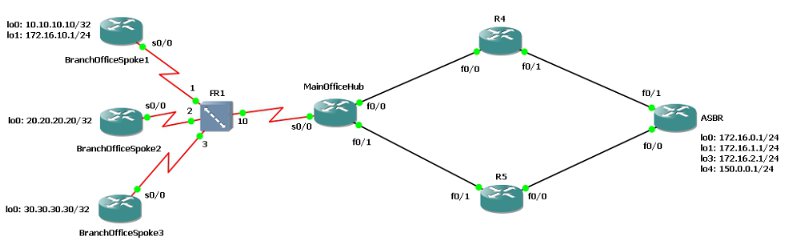
Download GNS3 configs topology here . I used IOS c2600-ipbasek9-mz. If your startup config does not load automatically, apply it manually (right click on the router, startup-config).
Again, I have the official Cisco labs to prepare for ROUTE, but from my point of view it is always more interesting to build the lab myself. In the process of building, a bunch of interesting glitches will surely pop up, which will be curious to tinker with :-)
I am deeply convinced that you can best understand the technology by solving all sorts of bugs (hello to the TSHOOT exam) and looking for information about obscure things on your own, so I’ll suggest you several riddles in this configuration. They can be used to verify whether you know EIGRP at the CCNP level.
I hope the lab will be useful to those who are preparing for CCNP and those who, perhaps, want to refresh some EIGRP features in their memory. In the next topic I will definitely give a brief comment on each of the points.
 Hello! Today I want to share with the respected community the labs that helped me in preparing for the ROUTE exam from the new track CCNP, as well as thoughts and impressions from the exam. Due to the fact that there is a lot of material and lab, it will be necessary to break it all up into portions and spread them one by one. Today I propose to talk about CCNP version 6 in general, about the ROUTE exam and look at the EIGRP labs that I used to prepare for the exam.
Hello! Today I want to share with the respected community the labs that helped me in preparing for the ROUTE exam from the new track CCNP, as well as thoughts and impressions from the exam. Due to the fact that there is a lot of material and lab, it will be necessary to break it all up into portions and spread them one by one. Today I propose to talk about CCNP version 6 in general, about the ROUTE exam and look at the EIGRP labs that I used to prepare for the exam.Interested - welcome under the cat!
CCNP v.6
By changing the CCNP last summer, Cisco had several goals. In addition to technology upgrades, CCNP was supposed to be a real “bridge” between CCNA and CCIE. CCNP version 5 was closer to CCNA than CCIE - it still contained all the phrases “more about OSPF you can read through the link” and “more details about this protocol feature are described in the CCIE course”. And in it, as in CCNA, there were many topics that are not directly related to routing and switching.
')
As a result, as the beloved Jeremy Chara tells us all about his students, the average person received the CCNP, looked at the CCIE and saw the abyss in front of him. His hands fell and he lost faith in the fact that all the material that separated the CCNP from the CCIE is generally possible to learn.
Changing CCNP, Cisco has taken into account this fact. Almost everything that does not concern Routing & Switching is excluded from the course - it is excluded and transferred to the appropriate areas of Professional certificates. VoIP has become part of CCNP Voice, Wi-Fi is part of CCNP Wireless and so on. The remnants of the former luxury in the course now relate to access technologies and VPN, being a brief overview rather than a full-fledged topic.
But the switching and routing required to build an enterprise network is fully covered. You will no longer see a Cisco EIGRP or OSPF referral site — from a technological point of view, the course covers these protocols from beginning to end. CCNP has become more complex and more specialized. Now it only includes switching and routing, but in this direction - R & S - it really is halfway from CCNA to CCIE.
642-902 ROUTE
Of all three new CCNP exams, ROUTE, the heir to the BSCN, is the most voluminous and the most difficult. It is included in several certification tracks: CCNP, CCDP and CCIP, covering Interior Gateway Routing Protocols completely, giving the basics of BGP and familiarizing the reader with IPv6 at a sufficient level to understand the operation of routing using it. Official Certification Guide to prepare for ROUTE - a book in more than 900 pages of text, plus it is very desirable to study the Foundation Learning Guide - another 700 pages.
And, of course, practice.
I was preparing for the exam mainly using GNS3. I have a home lab with real Cisco Systems equipment, but in my opinion GNS3 is more convenient. Functionally, the lab in GNS3 is no different from the labs on real hardware. GNS3 is more convenient in terms of viewing traffic - you don’t have to suffer from port mirroring if you want to see the traffic on the link. And besides, GNS3 is always with you, wherever you are - at work, on a business trip, on vacation. If you want to experiment with your routers, all you need is a laptop and GNS3.
The exam is difficult, but it is very, very good! True. Of course, there are several ambiguous and damp questions, there are glitches with simlets (of course, symlets of such level!), But the exam itself is just perfect! There are no obvious questions at all. Head-on questions in the style of “what is the maximum length of a 100BASE-T segment” - literally a couple of pieces. The absolute majority of questions are scripts. The questions are formulated in the style of “we already believe that you know the theory of OSPF and EIGRP, you tell us better, what would happen if you add one link to this topology? And if you fix the team here like this? And if you make this change here? But in such a topology and with such a configuration, what will be in the routing table? ”
Simlets are especially good. They no longer contain items that need to be fulfilled, as was the case in CCNA. Now the script is a rather abstract description of customer requirements. No items. Just a text. How to build the configuration so that it satisfies these requirements is already up to you. Moreover, there are several options for solving the problem. Which one is more correct - this, as I understand it, should be decided by each person on the exam independently.
The first time I failed my ROUTE. It is because of the simlet. Some of their glitches took too much time, and one of them, I suspect, I did not count because of the peculiarities of the implementation. After the exam, I wrote to the Cisco Certification Support Community, where their experts promptly requested a test from VUE, looked at the results, agreed with my arguments, and issued a voucher for a free retake. Truly, this is really a company with the principle of work “Customer as a Strategy” :-) Therefore, I would recommend you describe the glitches of simlets encountered in the comments, and if you suspect that you could not count the points for the correct answer, feel free to write in Cisco, it's a pleasure to deal with them.
EIGRP
The exam covers the following features of EIGRP technology:
- EIGRP timers, neighborhood relationships, neighborhood and network convergence management
- Authorization of neybor in EIGRP
- EIGRP metric, DUAL features, successors and feasible successors
- Default Network Concept
- Route Summarization and Route Filtering
- Bandwidth Control
- Stub routers
- Balancing traffic on routes with different metrics
For preparation I used the following lab:

Download GNS3 configs topology here . I used IOS c2600-ipbasek9-mz. If your startup config does not load automatically, apply it manually (right click on the router, startup-config).
Again, I have the official Cisco labs to prepare for ROUTE, but from my point of view it is always more interesting to build the lab myself. In the process of building, a bunch of interesting glitches will surely pop up, which will be curious to tinker with :-)
I am deeply convinced that you can best understand the technology by solving all sorts of bugs (hello to the TSHOOT exam) and looking for information about obscure things on your own, so I’ll suggest you several riddles in this configuration. They can be used to verify whether you know EIGRP at the CCNP level.
- Why Hub router can not establish EIGRP neighborhood with Spoke 2? Fix it.
- How to view the Hello timer on the Serial0 / 0.202 interface of the MainOfficeHub router? Which team see the Dead timer value?
- Will EIGRP lose its neighborhood with Spoke routers if I change the Hello value of the timer on the Hub router for 5 seconds? And if in 120 seconds? What will be the Dead Timer value for Hub Router, if you put Hello an interval of 5 seconds? How to check it?
- Now the Spoke3 interface of the router and the router's Hub subinterface are located on the network 192.168.101.0/29 and have the addresses .1 and .2, respectively. If I change the address mask of the Spoke interface of the router to / 30, will the EIGRP neighborhood remain?
- 10.10.10.10 and 20.20.20.20 - loopback addresses of the interfaces of the routers Spoke 1 and Spoke 2, respectively. Both networks are visible on the Hub router, but Spoke 1 does not see the network 20.20.20.20, and Spoke 2 does not see 10.10.10.10. At the same time, they see the other networks (for example, the 30.30.30.30 network of the Spoke 3 router) normally. Why is this and how to fix this situation?
- Spoke 1 and Spoke 2 routers are configured as an eigrp stub, but the networks of their loopback interfaces are still announced by the hub router. Why does this happen and how can they not announce anything?
- If the hub router loses the link to the network on 10.10.10.10, where will it send the EIGRP Query and why?
- How much maximum bandwidth to a Spoke 3 link can EIGRP packets take?
- EIGRP authentication is configured between the Hub router and R5, but routers cannot establish a neighborhood. In this case, on the Hub router, the neighborhood with R5 is then installed, then lost. What is the reason for this and how to eliminate it?
- ASBR has an Internet connection through the loopback 4 interface with the address 150.0.0.1/24. It is necessary to announce on EIGRP default route to this network.
- On the Hub router, the summary route is configured for the network 192.168.100.0/22. Why is its metric set to 2169856?
- In connection with the automatic summation of routes, the network of the Loopback 1 interface of the Spoke 1 router and the Loopback network of the 0–3 ASBR routers are announced as the same 172.16.0.0/16 networks. Where do you need to remove the automatic summation, so that all the network routers see them as different networks?
- On the Hub router, traffic balancing is configured on routes with different metrics. The coefficient is variance 2. As can be seen from the EIGRP topology table (and from the diagram), the metrics of the two routes are about 15000 and 16000, but despite this, only one is installed in the routing table. Why did this happen?
I hope the lab will be useful to those who are preparing for CCNP and those who, perhaps, want to refresh some EIGRP features in their memory. In the next topic I will definitely give a brief comment on each of the points.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/125972/
All Articles