How does the femto network
About the benefits provided by the use of femtocells have already been written on Habré, so in this small note I wanted to talk a little about the architecture of building femto networks on the operator side.
Femtocell (eng. Femtocell) is a low-power and miniature cellular communication station designed to serve a small area (one office or apartment). Connects to the network of the cellular operator through the communication channel, summed up to the user.
The picture below shows the general structure of the femto networks.
')
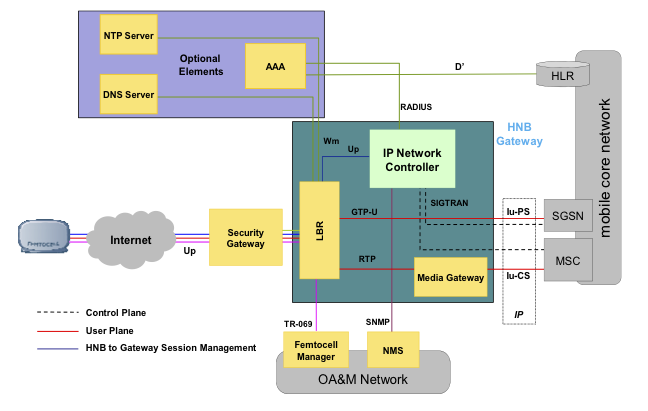
Femto Access Point (FAP) is a user device. The FAP is installed on the territory of the user and is connected to the operator’s network via the user's Internet channel and does not require the user to participate in the initialization and configuration (zero touch plug and play). The access point provides local 3G coverage and allocated capacity in the home or office and allows the user to use all the functionality of their 3G terminal.
Security Gateway (SeGW) - provides secure access to the operator’s network via RAN GW, authentication and establishing IPsec tunnels with an access point.
IP Network Controller (INC) - is a central component of the RAN GW solution, which provides a channel between the mobile operator's network and the RAN GW.
Authentication, Authorization, Accounting (AAA) Server — Provides authentication between the FAP and the HLR using a 3GPP standardized security scheme.
Media Gateway Controller (MGW) - Manages CS streams and interacts with the MSC in the mobile operator's network.
The Load Balancing Router (LBR) is a CISCO router that is used to connect all the gateway elements to each other.
Femtocell Manager - is a platform for managing HNB access points, the number of which can reach several million. With the help of HNB Manager, you can manage the settings of radio parameters, network interfaces, plan and perform software updates, set up access lists in closed groups, and manage the access points in full.
Network Management System (NMS) - allows you to monitor accidents, manage the configuration and performance of the elements of RAN-GW.
DNS server - provides recognition of IP addresses in a closed area of the operator’s network. For example, HNB uses a DNS server to recognize the FQDN of the name of the serving INC site. The DNS server can be separately for each HNB GW or centralized for all HNB requests.
An NTP server is a synchronization source that is required to support synchronization of all HNBs in the event that HNBs cannot synchronize using 2G / 3G signals received via the radio interface. The NTP server can be in each RAN GW or it can be centralized for all RAN GWs.
If some of the abbreviations from the note turned out to be incomprehensible, I recommend reading the article on building UMTS cellular networks .
Femtocell (eng. Femtocell) is a low-power and miniature cellular communication station designed to serve a small area (one office or apartment). Connects to the network of the cellular operator through the communication channel, summed up to the user.
The picture below shows the general structure of the femto networks.
')

Femto Access Point (FAP) is a user device. The FAP is installed on the territory of the user and is connected to the operator’s network via the user's Internet channel and does not require the user to participate in the initialization and configuration (zero touch plug and play). The access point provides local 3G coverage and allocated capacity in the home or office and allows the user to use all the functionality of their 3G terminal.
Security Gateway (SeGW) - provides secure access to the operator’s network via RAN GW, authentication and establishing IPsec tunnels with an access point.
IP Network Controller (INC) - is a central component of the RAN GW solution, which provides a channel between the mobile operator's network and the RAN GW.
Authentication, Authorization, Accounting (AAA) Server — Provides authentication between the FAP and the HLR using a 3GPP standardized security scheme.
Media Gateway Controller (MGW) - Manages CS streams and interacts with the MSC in the mobile operator's network.
The Load Balancing Router (LBR) is a CISCO router that is used to connect all the gateway elements to each other.
Femtocell Manager - is a platform for managing HNB access points, the number of which can reach several million. With the help of HNB Manager, you can manage the settings of radio parameters, network interfaces, plan and perform software updates, set up access lists in closed groups, and manage the access points in full.
Network Management System (NMS) - allows you to monitor accidents, manage the configuration and performance of the elements of RAN-GW.
DNS server - provides recognition of IP addresses in a closed area of the operator’s network. For example, HNB uses a DNS server to recognize the FQDN of the name of the serving INC site. The DNS server can be separately for each HNB GW or centralized for all HNB requests.
An NTP server is a synchronization source that is required to support synchronization of all HNBs in the event that HNBs cannot synchronize using 2G / 3G signals received via the radio interface. The NTP server can be in each RAN GW or it can be centralized for all RAN GWs.
If some of the abbreviations from the note turned out to be incomprehensible, I recommend reading the article on building UMTS cellular networks .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/124610/
All Articles