Usability testing step by step or HCD design evaluation
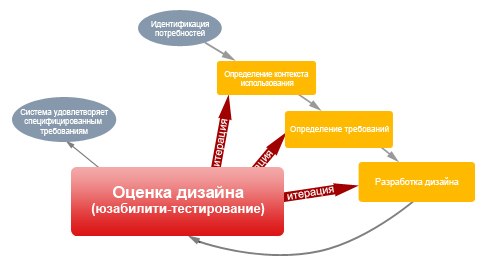
According to the HCD standard (Site: ISO 9241-210: Human-centered design ) there is a design evaluation stage, it is in it that high-quality usability testing can be conducted.
Write this article made me problems that arose during my usability testing. I hope I will help someone more accurately determine when to apply usability testing and how to avoid some issues during its implementation.
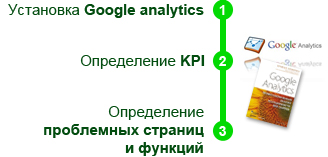 In the case of an already developed site, the question of conducting usability testing arises when you feel or discover that something is wrong with the site. In any case, you need to install Google analytics (book: Google Analytics. Professional analysis of website traffic ) or another service for analyzing site visits. I will not talk about why such a service should be installed, since the topic has long been exhausted and does not recommend installing such services only lazy. After installing Google analytics, you already have specific data on visitor statistics, entry and exit points for site visitors and other information.
In the case of an already developed site, the question of conducting usability testing arises when you feel or discover that something is wrong with the site. In any case, you need to install Google analytics (book: Google Analytics. Professional analysis of website traffic ) or another service for analyzing site visits. I will not talk about why such a service should be installed, since the topic has long been exhausted and does not recommend installing such services only lazy. After installing Google analytics, you already have specific data on visitor statistics, entry and exit points for site visitors and other information.
The next step should be the definition of KPI (Wikipedia: Key Performance Indicators - key performance indicators ). It is necessary to analyze what is important for business, to determine the goals that should be achieved by the sites.
Example: for someone it may be orders of the goods, for someone to address through the feedback form with any questions, etc.
')
If up to this point the recommendations were mandatory, then in any case these steps will help in the development and promotion of the site, then there are recommendations, if you really understand that the site is not effective.
The third step is to directly identify the problem pages and functions. Simply conducting usability testing is ineffective, it is necessary to understand where problems arise, on which page, with which function, and then conduct testing to determine what is wrong on the page and how to solve it. Again, Google analytics will help, here you can determine which pages users are leaving, which pages are ignored, and which functions are not used.
 So, at the moment it has already been determined that the site needs redesign, found pages and functions with which users have problems. It remains the case for small - to understand why users have problems and how to fix them.
So, at the moment it has already been determined that the site needs redesign, found pages and functions with which users have problems. It remains the case for small - to understand why users have problems and how to fix them.
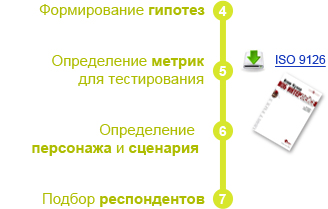
The fourth step should be the formation of hypotheses about what is wrong with the page, and on this basis, it is necessary to determine the metrics (Wikipedia: ISO 9126 - Evaluation of a software product ) for which the functions will be tested (there is an expert assessment method in which the expert advances hypotheses to improve the site interface and, on the basis of them, the site is being redesigned, however, it is possible to check whether this hypothesis is true, only by the result of the introduction of changes, which entails a large cost of error).
Example: using Google analytics, we have determined that users enter the registration page, but it does not pass. Perhaps users can not understand what information to enter in the field or do not know what to do next, after filling in the fields. Therefore, we need to test this page against the metrics of system message clarity and operational sequence.
After determining the metrics by which we will test the problem areas on the site, it is necessary to determine the character and the scenario of work (the book: Alan Cooper on the interface. Basics of interaction design ), which will be used for usability testing. This step is necessary to attract the right respondents and select a job for usability testing. If you miss this point, the respondent who is not the target user can successfully pass the problem area, and the user who actually uses this page will have really big problems. The result will be a redesign of the interface without data, and the problem will remain. Exact definition of the script will help give the respondent the right task. That is, if the task is to buy a mobile phone, and the respondent will not register at all (and we are testing the registration), then usability testing is useless.
Note: choose a scenario so that problem areas are tested as much as possible.
Next comes the selection of respondents based on the selected character. The more the respondent matches the portrait of the character, the better. A sufficient number of respondents - 5-8 people. In choosing the quantity, I base myself on the recommendation of Jacob Nielsen and my own experience.
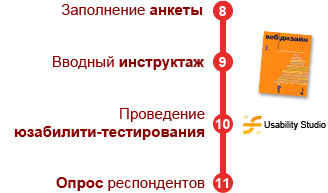 Immediately before the usability testing itself, let the respondent fill out a questionnaire to check that the selected characteristics match the selected character and respondent. Conduct an introductory briefing, during which describe the context of the site's use and the task (books: Web Design: Steve Krug's book, or “don't make me think!” ).
Immediately before the usability testing itself, let the respondent fill out a questionnaire to check that the selected characteristics match the selected character and respondent. Conduct an introductory briefing, during which describe the context of the site's use and the task (books: Web Design: Steve Krug's book, or “don't make me think!” ).
Example of a task: in search of a new mobile phone, you, through a search engine, visited this site. Find the phone you need (also ask the respondent to describe the phone they will be looking for).
Conducting the most usability testing (program: Usability Studio ) is not as it seems a difficult task. You need a laptop with a camera and several programs to record the movement of users and record actions from the screen. Ask the respondent to comment on all his actions and emotions. As practice shows, he will do it in such a way (and this is not surprising, because even at home, users often like to scold or, on the contrary, groom different forms and other elements on websites).
After completing the test, ask the respondent about his impression, what difficulties he encountered and what he found uncomfortable. I do not recommend using the survey data as a law to change everything that he does not like. Users need to listen, but very suspicious of his subjective opinion. It is better if, based on the survey results, a hypothesis emerged about the need to change the interfaces, add another item to the list of problem areas and test it in the next iteration.
 Next, you need to view the collected video materials, analyze the results of usability testing and determine the requirements for the interface for redesign (book: Web-design. Usability of Web-sites ). Changes that will be made on the basis of certain requirements should be checked at the next usability testing. The number of such iterations should largely depend on the objectives and budget allocated for the redesign of the site.
Next, you need to view the collected video materials, analyze the results of usability testing and determine the requirements for the interface for redesign (book: Web-design. Usability of Web-sites ). Changes that will be made on the basis of certain requirements should be checked at the next usability testing. The number of such iterations should largely depend on the objectives and budget allocated for the redesign of the site.
Examples: add hints to the registration form, highlight the purchase button, add a “platform” field to the phone's selection form using parameters, etc.
If the design was carried out according to the ISO 9241-210 standard, then usability testing should not be a costly and time consuming process in connection with the prepared analytical framework. The main stages of usability testing when designing a site from scratch remain the same as described above, except for some aspects:
The main problem that I encountered in usability testing in this case is the testing of static design, and not a full-fledged site. In fact, it is better to test the imposed and even programmed site, but the price of iteration into the design will be already high. The earlier the problem is found in the interface, the lower the cost of fixing it. How to conduct a full usability testing of static images? The solution to this problem was Axure. The cheapest and most successful way was to artificially place links to a static picture of the site design and generate it into an HTML page. This method makes it possible to test the site without spending resources even on layout. Of course, in the generated pages there is almost no functionality, it is displayed only in a certain form, but to identify more problems this is enough.
I do not consider the quantitative usability testing option, since it allows to determine the overall ergonomics of the interface, but it does not allow to determine what problems arise, why and how to fix them.
PS I am waiting for constructive criticism about the proposed solution of quality usability testing of the design, since I have never seen such a solution. If you have any suggestions how to conduct a full-fledged high-quality usability testing cheaply and angrily, then I will be glad to read it.

Write this article made me problems that arose during my usability testing. I hope I will help someone more accurately determine when to apply usability testing and how to avoid some issues during its implementation.
Site redesign
When is it worth usability testing and what precedes it?
 In the case of an already developed site, the question of conducting usability testing arises when you feel or discover that something is wrong with the site. In any case, you need to install Google analytics (book: Google Analytics. Professional analysis of website traffic ) or another service for analyzing site visits. I will not talk about why such a service should be installed, since the topic has long been exhausted and does not recommend installing such services only lazy. After installing Google analytics, you already have specific data on visitor statistics, entry and exit points for site visitors and other information.
In the case of an already developed site, the question of conducting usability testing arises when you feel or discover that something is wrong with the site. In any case, you need to install Google analytics (book: Google Analytics. Professional analysis of website traffic ) or another service for analyzing site visits. I will not talk about why such a service should be installed, since the topic has long been exhausted and does not recommend installing such services only lazy. After installing Google analytics, you already have specific data on visitor statistics, entry and exit points for site visitors and other information.The next step should be the definition of KPI (Wikipedia: Key Performance Indicators - key performance indicators ). It is necessary to analyze what is important for business, to determine the goals that should be achieved by the sites.
Example: for someone it may be orders of the goods, for someone to address through the feedback form with any questions, etc.
')
If up to this point the recommendations were mandatory, then in any case these steps will help in the development and promotion of the site, then there are recommendations, if you really understand that the site is not effective.
The third step is to directly identify the problem pages and functions. Simply conducting usability testing is ineffective, it is necessary to understand where problems arise, on which page, with which function, and then conduct testing to determine what is wrong on the page and how to solve it. Again, Google analytics will help, here you can determine which pages users are leaving, which pages are ignored, and which functions are not used.
Preparing for usability testing
 So, at the moment it has already been determined that the site needs redesign, found pages and functions with which users have problems. It remains the case for small - to understand why users have problems and how to fix them.
So, at the moment it has already been determined that the site needs redesign, found pages and functions with which users have problems. It remains the case for small - to understand why users have problems and how to fix them.The fourth step should be the formation of hypotheses about what is wrong with the page, and on this basis, it is necessary to determine the metrics (Wikipedia: ISO 9126 - Evaluation of a software product ) for which the functions will be tested (there is an expert assessment method in which the expert advances hypotheses to improve the site interface and, on the basis of them, the site is being redesigned, however, it is possible to check whether this hypothesis is true, only by the result of the introduction of changes, which entails a large cost of error).
Example: using Google analytics, we have determined that users enter the registration page, but it does not pass. Perhaps users can not understand what information to enter in the field or do not know what to do next, after filling in the fields. Therefore, we need to test this page against the metrics of system message clarity and operational sequence.
After determining the metrics by which we will test the problem areas on the site, it is necessary to determine the character and the scenario of work (the book: Alan Cooper on the interface. Basics of interaction design ), which will be used for usability testing. This step is necessary to attract the right respondents and select a job for usability testing. If you miss this point, the respondent who is not the target user can successfully pass the problem area, and the user who actually uses this page will have really big problems. The result will be a redesign of the interface without data, and the problem will remain. Exact definition of the script will help give the respondent the right task. That is, if the task is to buy a mobile phone, and the respondent will not register at all (and we are testing the registration), then usability testing is useless.
Note: choose a scenario so that problem areas are tested as much as possible.
Next comes the selection of respondents based on the selected character. The more the respondent matches the portrait of the character, the better. A sufficient number of respondents - 5-8 people. In choosing the quantity, I base myself on the recommendation of Jacob Nielsen and my own experience.
Conduct usability testing
 Immediately before the usability testing itself, let the respondent fill out a questionnaire to check that the selected characteristics match the selected character and respondent. Conduct an introductory briefing, during which describe the context of the site's use and the task (books: Web Design: Steve Krug's book, or “don't make me think!” ).
Immediately before the usability testing itself, let the respondent fill out a questionnaire to check that the selected characteristics match the selected character and respondent. Conduct an introductory briefing, during which describe the context of the site's use and the task (books: Web Design: Steve Krug's book, or “don't make me think!” ).Example of a task: in search of a new mobile phone, you, through a search engine, visited this site. Find the phone you need (also ask the respondent to describe the phone they will be looking for).
Conducting the most usability testing (program: Usability Studio ) is not as it seems a difficult task. You need a laptop with a camera and several programs to record the movement of users and record actions from the screen. Ask the respondent to comment on all his actions and emotions. As practice shows, he will do it in such a way (and this is not surprising, because even at home, users often like to scold or, on the contrary, groom different forms and other elements on websites).
After completing the test, ask the respondent about his impression, what difficulties he encountered and what he found uncomfortable. I do not recommend using the survey data as a law to change everything that he does not like. Users need to listen, but very suspicious of his subjective opinion. It is better if, based on the survey results, a hypothesis emerged about the need to change the interfaces, add another item to the list of problem areas and test it in the next iteration.
Processing usability testing data
 Next, you need to view the collected video materials, analyze the results of usability testing and determine the requirements for the interface for redesign (book: Web-design. Usability of Web-sites ). Changes that will be made on the basis of certain requirements should be checked at the next usability testing. The number of such iterations should largely depend on the objectives and budget allocated for the redesign of the site.
Next, you need to view the collected video materials, analyze the results of usability testing and determine the requirements for the interface for redesign (book: Web-design. Usability of Web-sites ). Changes that will be made on the basis of certain requirements should be checked at the next usability testing. The number of such iterations should largely depend on the objectives and budget allocated for the redesign of the site.Examples: add hints to the registration form, highlight the purchase button, add a “platform” field to the phone's selection form using parameters, etc.
Site designing
If the design was carried out according to the ISO 9241-210 standard, then usability testing should not be a costly and time consuming process in connection with the prepared analytical framework. The main stages of usability testing when designing a site from scratch remain the same as described above, except for some aspects:
- Hypothesis formation
- Definition of metrics for testing
- Defining characters and scenarios
- Selection of respondents
- Filling in the form
- Induction training
- Conduct usability testing
- Survey of respondents
- Results analysis
- Determine requirements for site design
The main problem that I encountered in usability testing in this case is the testing of static design, and not a full-fledged site. In fact, it is better to test the imposed and even programmed site, but the price of iteration into the design will be already high. The earlier the problem is found in the interface, the lower the cost of fixing it. How to conduct a full usability testing of static images? The solution to this problem was Axure. The cheapest and most successful way was to artificially place links to a static picture of the site design and generate it into an HTML page. This method makes it possible to test the site without spending resources even on layout. Of course, in the generated pages there is almost no functionality, it is displayed only in a certain form, but to identify more problems this is enough.
I do not consider the quantitative usability testing option, since it allows to determine the overall ergonomics of the interface, but it does not allow to determine what problems arise, why and how to fix them.
PS I am waiting for constructive criticism about the proposed solution of quality usability testing of the design, since I have never seen such a solution. If you have any suggestions how to conduct a full-fledged high-quality usability testing cheaply and angrily, then I will be glad to read it.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/124462/
All Articles