Connecting a GPS receiver to a laptop and creating a GPS tracker
Many travel lovers have long started to use GPS-devices during their leisure time.
Someone uses navigators to move from one locality to another on the nearest highway / road, using, as a rule, navigation programs with vector maps. And someone prefers a more extreme pastime, getting from point A to point B on the nearest way in off-road cars. For the latter, vector maps are not so important, here the main thing is to know the features of the topography of the nearest terrain, and navigation programs with raster maps attached to the coordinates are used.
I set a goal to connect an external GPS receiver to a laptop, on which you can install various programs for working with vector and raster maps in order to get a convenient tool for planning a route and viewing your current location. At the same time, I wanted to transfer GPS data to the server so that my location could be tracked remotely (improvised GPS tracker).
So, if you are interested in this topic, welcome to the topic.
What we have :
A certain software should be installed on the laptop:
On the PDA, additional applications should also be installed:
1) GPSGate.
First, we will achieve the transfer of a GPS signal from an external device to a laptop.
Here the scheme will be simple:
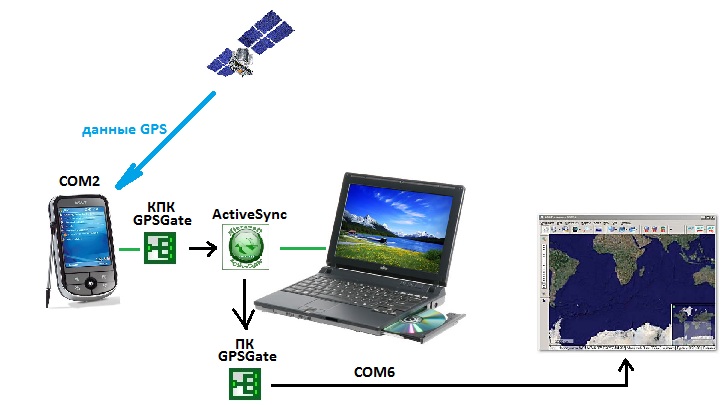
')
We now turn from theory to practice.
Configure GSP Receiver
We assume that the GPSGate program is already installed on our PDA.
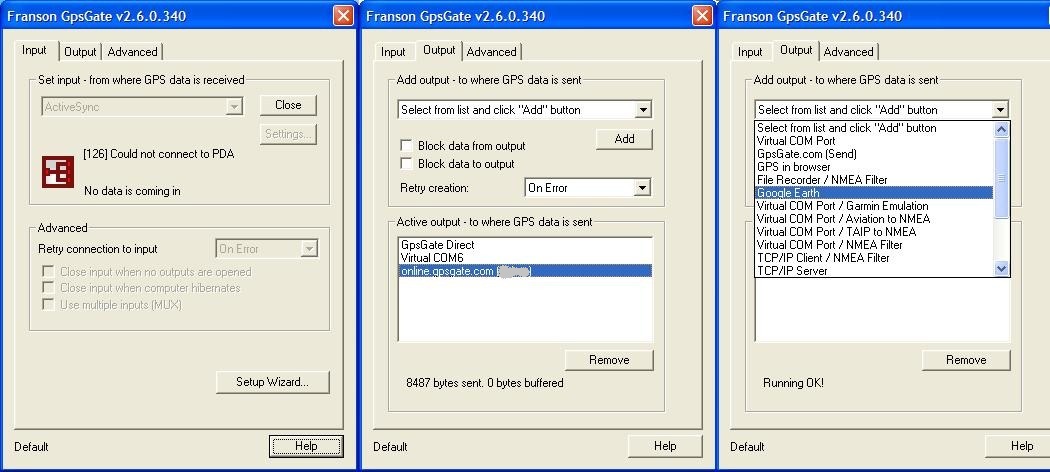
We make the program settings :
If the procedures for receiving and transmitting coordinates are successful, the icon on the panel lights up in green. If the device is ready, but the coordinates have not yet been received (satellites are not caught) - the program tag is lit in yellow.
Now we have achieved the transfer of the GPS signal from the PDA to the laptop.
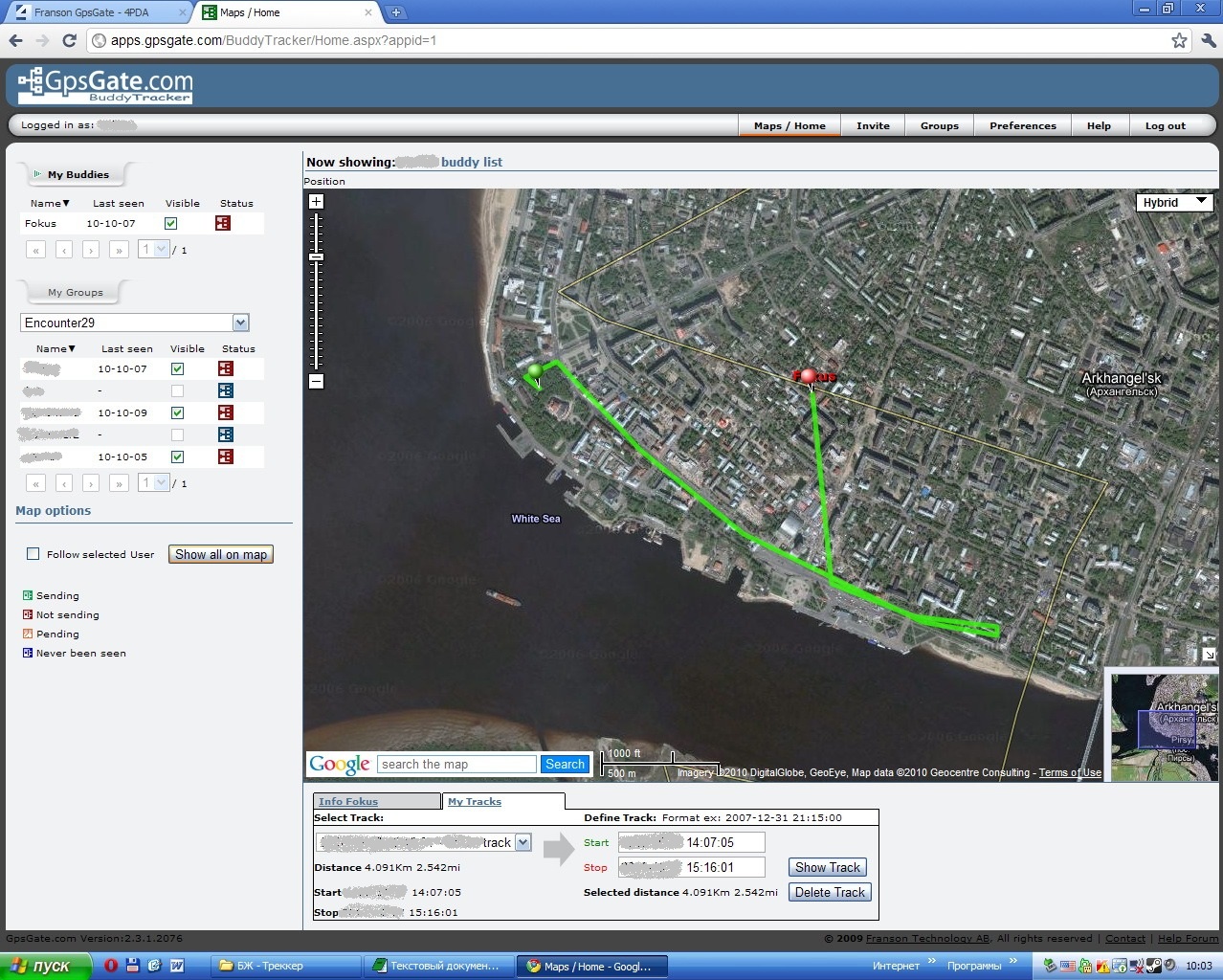
Here you can also duplicate the transfer of the GPS signal to the GPSGate server, in order to monitor your position (preliminary registration on the website is necessary)
To do this, on the " Output " tab, add the item " gpsgate.com (Send) " and in the settings for connecting to the server specify your login / password on gpsgate.com . Data transmission from the PDA to the server will be carried out by means of cellular communication. If you have a 3G modem, you can make similar settings in the program.
GPSGate installed on a laptop.

Go to setting the laptop
It is assumed that there are already installed: ActiveSync, GPSGate and SASPlanet (or Google "Earth").
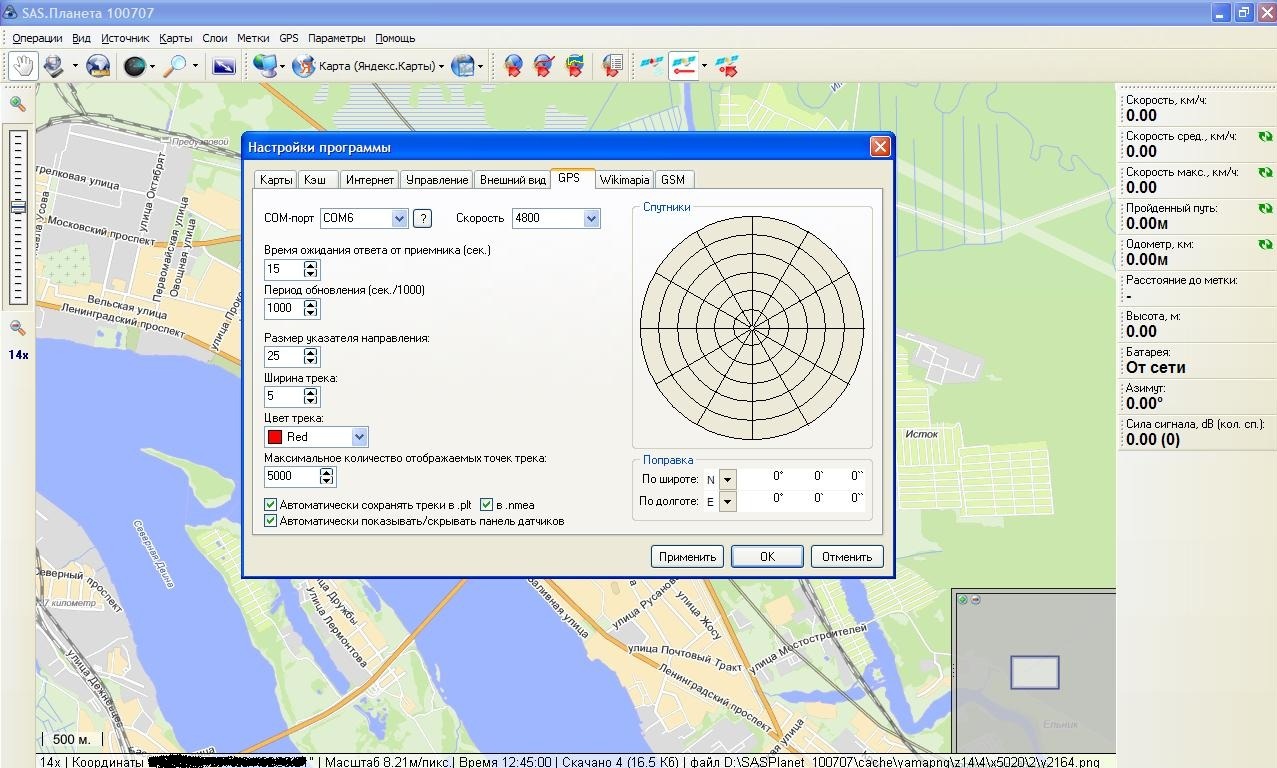
At this basic program settings are over.
SASPlanet has a large number of maps (Yandex, Navitel, Google, etc.)
In the settings in the Source, it is better to specify " Internet + Cache ", then the maps already viewed will be downloaded from the Cache (from the laptop's memory), and new ones from the Internet.
Therefore, it will be more logical, in order to save traffic, to see in advance the largest possible section that you intend to visit on your journey.
What is the result?
We receive a GPS signal to an external device and transfer it to a laptop, where GPS data is processed and we get our current location tied to a raster or vector map in the SASPlanet program (any other similar).
In parallel with this, data on our movement and current location are sent to the server. So You can remotely view our location and route for a specified period of time.
For what?
I use it during team active city games:
1) The headquarters remotely controls and coordinates the movement of all crews at the same time.
2) Navigation programs on a laptop have a wider functionality and visibility than in portable GPS-devices. You can quickly plan and coordinate your route, choose from a variety of maps the most suitable.
Many off-road travelers connect their gps devices with more compact netbooks and use the OziExplorer program with raster topographic maps, which are usually more informative about the terrain.
Lovers of classic tourism will also be more interesting to observe their movement on a large interactive map on which you can see nearby attractions displayed on a Google map.
During the trip, you can share your location with relatives and friends who will be able to trace your route.
Someone uses navigators to move from one locality to another on the nearest highway / road, using, as a rule, navigation programs with vector maps. And someone prefers a more extreme pastime, getting from point A to point B on the nearest way in off-road cars. For the latter, vector maps are not so important, here the main thing is to know the features of the topography of the nearest terrain, and navigation programs with raster maps attached to the coordinates are used.
I set a goal to connect an external GPS receiver to a laptop, on which you can install various programs for working with vector and raster maps in order to get a convenient tool for planning a route and viewing your current location. At the same time, I wanted to transfer GPS data to the server so that my location could be tracked remotely (improvised GPS tracker).
So, if you are interested in this topic, welcome to the topic.
What we have :
- Communicator with GPS
- A laptop
- 3g-modem (can be excluded)
A certain software should be installed on the laptop:
- To synchronize PDAs with PCs (in my case “ActiveSync” - for Windows XP, or “Windows Mobile Device Center” - for Windows 7, Vista) ;
- Navigation programs. For example, OziExplorer (for raster maps) , SASPlanet;
- The program for processing GPS-signal from the receiver.
On the PDA, additional applications should also be installed:
1) GPSGate.
First, we will achieve the transfer of a GPS signal from an external device to a laptop.
Here the scheme will be simple:
- the GPS signal arrives at the PDA through the COM2 hardware port (in my case) ;
- PDA is synchronized with a laptop using ActiveSync;
- Using the GPSGate application installed on the PDA, the GPS signal is redirected from COM2 to the ActiveSync port;
- The GPSGate program installed on the laptop receives a signal from the ActiveSync port and redirects it to the virtual COM port (in my case COM6);
- In the navigation program installed on the laptop, we indicate as the source of the GPS signal our virtual port created in GPSGate.

')
We now turn from theory to practice.
Configure GSP Receiver
We assume that the GPSGate program is already installed on our PDA.
We make the program settings :
- The " Input " tab indicates the hardware port of your GPS receiver. On a PDA, this is usually the COM2 port. You can clarify by going to the Control Panel - External GPS - Equipment .
- The " Output " tab indicates the recipients of the GPS signal.
Here, from the drop-down list, select " ActiveSync " so that the received GPS signal is redirected to the connection port of the PDA and laptop. - You can now select the " Online " menu. The icons should be green (included) , which means that they are currently connected to satellites.
If the procedures for receiving and transmitting coordinates are successful, the icon on the panel lights up in green. If the device is ready, but the coordinates have not yet been received (satellites are not caught) - the program tag is lit in yellow.
Now we have achieved the transfer of the GPS signal from the PDA to the laptop.
Here you can also duplicate the transfer of the GPS signal to the GPSGate server, in order to monitor your position (preliminary registration on the website is necessary)
To do this, on the " Output " tab, add the item " gpsgate.com (Send) " and in the settings for connecting to the server specify your login / password on gpsgate.com . Data transmission from the PDA to the server will be carried out by means of cellular communication. If you have a 3G modem, you can make similar settings in the program.
GPSGate installed on a laptop.

Go to setting the laptop
It is assumed that there are already installed: ActiveSync, GPSGate and SASPlanet (or Google "Earth").
- In the GPSGate settings, select " Input " - ActiveSync (since we will have the ActiveSync source of the GPS signal) ;
- In " Output ", select Virtual COM-Port (The receiver of the GPS signal will be a virtual port, for example, COM-6 );
- In the SASPlanet program settings : Parameters - Program settings - GPS
In the COM port we indicate our Virtual COM-Port COM-6 .


At this basic program settings are over.
SASPlanet has a large number of maps (Yandex, Navitel, Google, etc.)
In the settings in the Source, it is better to specify " Internet + Cache ", then the maps already viewed will be downloaded from the Cache (from the laptop's memory), and new ones from the Internet.
Therefore, it will be more logical, in order to save traffic, to see in advance the largest possible section that you intend to visit on your journey.
What is the result?
We receive a GPS signal to an external device and transfer it to a laptop, where GPS data is processed and we get our current location tied to a raster or vector map in the SASPlanet program (any other similar).
In parallel with this, data on our movement and current location are sent to the server. So You can remotely view our location and route for a specified period of time.

For what?
I use it during team active city games:
1) The headquarters remotely controls and coordinates the movement of all crews at the same time.
2) Navigation programs on a laptop have a wider functionality and visibility than in portable GPS-devices. You can quickly plan and coordinate your route, choose from a variety of maps the most suitable.
Many off-road travelers connect their gps devices with more compact netbooks and use the OziExplorer program with raster topographic maps, which are usually more informative about the terrain.
Lovers of classic tourism will also be more interesting to observe their movement on a large interactive map on which you can see nearby attractions displayed on a Google map.
During the trip, you can share your location with relatives and friends who will be able to trace your route.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/124075/
All Articles