Geolocation and usability
 From the translator. With the development of mobile Internet, geolocation services have become widespread. By running the application in a smartphone, you can get information about the routes of public transport, the schedule of sessions in the nearest cinema, the addresses of the nearest shops and restaurants, etc. The interest of users to such services is growing. In this regard, it is interesting to consider the geolocation services in terms of ergonomics and usability. We offer our readers a translation of an article on this topic, written by specialists from the French company Usaddict. We hope that this publication will initiate a productive discussion on the specifics of ergonomics and design of geolocation services.
From the translator. With the development of mobile Internet, geolocation services have become widespread. By running the application in a smartphone, you can get information about the routes of public transport, the schedule of sessions in the nearest cinema, the addresses of the nearest shops and restaurants, etc. The interest of users to such services is growing. In this regard, it is interesting to consider the geolocation services in terms of ergonomics and usability. We offer our readers a translation of an article on this topic, written by specialists from the French company Usaddict. We hope that this publication will initiate a productive discussion on the specifics of ergonomics and design of geolocation services.Social services based on geolocation, augmented reality or even simple mobile applications that take into account the spatial location of the user: all these innovations require developers to be particularly ingenious in order to become truly user-friendly.
Geolocation simplifies the use of many web services, especially those designed for new generation mobile phones (iPhones and other smartphones). Therefore, in modern mobile devices there are such functions as GPS navigation (information about geographic coordinates - latitude, longitude and altitude) and compass (orientation to the cardinal points).
One of the goals of geolocation is to search for objects in the immediate environment of the user. The first thing to mention here is the GoogleMaps mobile app. It is installed by default on most smartphones and allows the user to determine both their location and the location of any object. It is possible to integrate the application with a list of phone contacts.
')
A careful study of the interface can catch the following interesting points:
- The blue dot shows the current location, and the red dot shows the destination.
- Object names are given in a black frame, which is different in color from the main part of the map.
- The blue arrow (in the right part of the frame) means the transition to reading the exact address, and the red icon - to the panoramic street view (StreetView).
- On the toolbar located at the bottom of the screen, there is an icon (imperceptible), clicking on which you can change the visualization method (standard plan, satellite view, mixed view) and even add traffic elements.

Some sites offer interesting geolocation-based services. So, Allocine, a movie news site, uses the iPhone’s features to facilitate access to its own services. One has only to touch the screen twice - and the user can find out which cinemas are located next to him. Another click - and you can get information about the time of the next sessions.
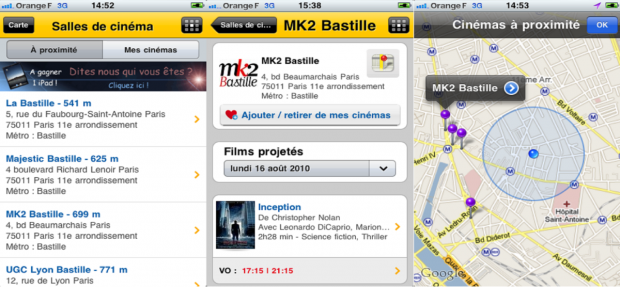
Interactive maps are becoming more widespread, but their presence is not necessarily for geolocation.
The SeLoger website offers an application for smartphones, through which a user can get information about properties offered for sale or rental on a certain street (as well as in a certain area or even in the whole city) - all without a map. However, the geolocation capabilities in this application are not fully exploited: by clicking on the Autour de vous icon (“Around you”), the user will not be able to get information about real estate objects in the area of his direct location.

The mobile version of SeLoger , however, is characterized by insufficient navigation convenience: in order to switch from the first image to the last one, you need to scroll through 4 screens.
Practical recommendations
- When developing geolocation services, consider the size of the buttons of the mobile device. This will help ensure the accuracy of the cursor.
- The number of screens is better to be kept to the minimum necessary for the user to solve the most common tasks.
Geolocation in social networks
Geolocation capabilities have recently been actively used in social networks. There was even a special term - "geolocation social networks" (English Location-Based Social Networks, abbreviated LBSN). Members of such networks can inform others about their location (by simply pressing a mobile device button). You can also receive information about objects located in a particular area. Examples of such services include FourSquare , Gowalla , Whrrl , Brightkite, or Loopt . Using geolocation, you can filter the information received and leave only relevant to the current location.

Augmented Reality
Another area for using geolocation capabilities is augmented reality that allows you to add virtual elements to images of existing objects. In the latest models of smartphones there is a function that allows you to determine the point at which the camera of the phone is pointed. Special applications allow you to visualize the route to the nearest metro station ( MetroParis ), a supermarket or restaurant ( AroundMe ), tourist information ( Wikitude ).


But many users note that the interface of such applications is far from perfect: pointers take up too much screen space and overlap each other.

Recommendations
- To the arrangement of elements on the screen is required to show increased attention. It is advisable not to overlap.
- The amount of information displayed on the screen should be reduced to the most necessary minimum.
Final notes and recommendations
Geolocation is becoming more widespread and is of considerable interest from the point of view of ergonomics.
Before implementing geolocation services, you need to seriously think about goals and results. The introduction of any innovation is not a tribute to fashion, but an attempt to solve real-life problems.
The emergence of Google applications ( Google Maps Navigation ) and Facebook ( Places ) will have a major impact on the market. Hopefully, the further development of geolocation services will be marked by improved ergonomic performance and usability.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/120556/
All Articles