Blockers of all time
In the fall of 2007, a new type of malware appeared in the Runet’s open space — extortion programs. This type of fraud went online before, but only in Russia it gained immense popularity. The ease of receiving money from its victims has become a fruitful soil. If at first we used rather exotic forms of payment (for example, VKontakte, Yandex Money, etc.), which ordinary users were not very familiar with, then the fraudsters later switched to simpler and more understandable ways: sending SMS to short numbers and transferring money to phone numbers. The two most popular forms of payment are well known even to people who rarely deal with computers. It is this fact, as well as simplicity and anonymity during the registration of short numbers that played a decisive role in the mass character that the extortionists acquired.

The technical side of the ransomware also did not stand still. If initially they were very simple programs written “on the knee”, then after a few years, the blockers were very technologically sophisticated products with protection against analysis, protection against detection, technology of network worms, encryption, etc. etc.
The technologies, through which fraudsters were going to demand money from users, were also developed. If initially the system was blocked entirely, and the user received information about a technical failure, then later more advanced social engineering technologies were used.
Here are just some of them:
1) Partial locking of the system (for example, a window that is placed on top of the third screen) - working with such a computer is possible, but very uncomfortable;
2) Demonstration of adult content - designed for children with dad computers;
3) Demonstration of content containing perversion elements - designed for adults;
etc.
It is absolutely useless to pay fraudsters: sending an expensive SMS (or even several) does not guarantee at all that the victim will receive the promised unlock code. With the replenishment of the account through the payment terminal, the situation is no better - there is simply no identification number on the check to which the extortionists refer. By sending money, the user sponsors new developments, from which he himself suffers later (according to our data, on average, users get infected more than 1 time).
')
In our work, we constantly encounter extortionists and decided to create our own hit parade, highlighting, in our opinion, the most interesting ones in the following nominations:
The most difficult
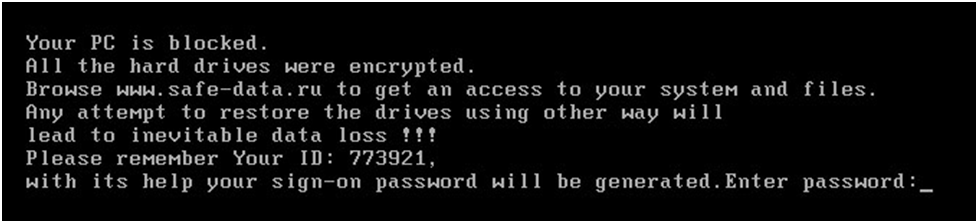
This blocker is unique in that it infects the MBR. He has not gained much popularity. We can say that he was more of a concept.
In May 2011, a second MBR blocker appeared, gaining more and more popularity.
The most popular
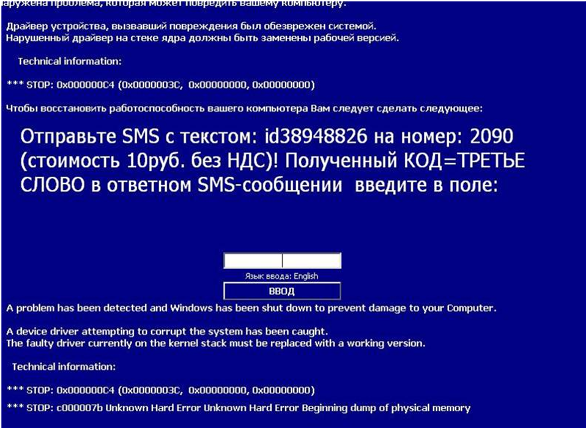
MOST MASS, MOST PROFITABLE Blocker of all times and peoples. In June 2010, new blockers of this family came out literally once an hour. The epidemic stopped only after law enforcement agencies detained members of this criminal group.

The very first
The first blockers in the open spaces of the Runet used exotic forms of payment, little known to housewives and unassuming design (no nude female and male body). But it all started with them.
The most beautiful

Animated
A blocker that uses an animated gif c mamma (Latin) as a picture, making oscillatory movements. As a payment, the blocker asked to send an SMS to one of the short numbers, among which were present both Russian and Ukrainian, Kazakhstan, Lithuanian and German.

The first non-Russian
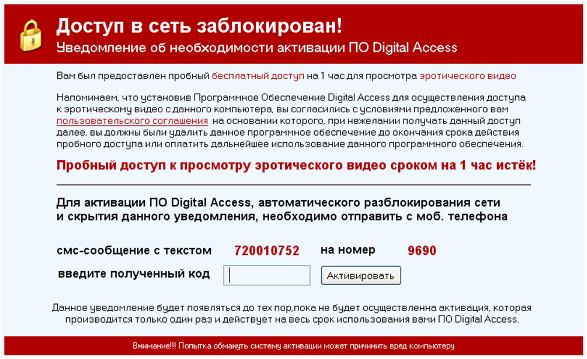
This blocker, which caused the first major epidemic of blockers in runet, came from Ukraine. Initially, SMS to Ukrainian number was accepted as payment.
A characteristic feature of the blockers from this family was the demonstration of the license agreement (!!!) at the first start of the blocker, in which it was reported that the user's computer would be blocked. But who reads these conventions?
In subsequent versions of the blocker, the license agreement, although demonstrated, was rather quickly closed, and the blocker started the installation regardless of the user's actions whether he agreed with the terms or not.
Most harmless
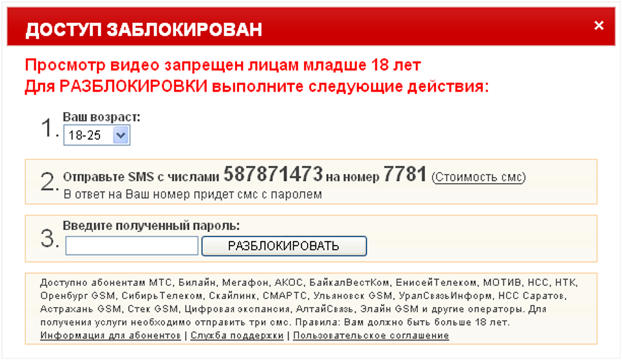
This “blocker” is not a blocker as such. Fraudsters specifically create sites that pretend to be adult sites, and place JavaScript in them that displays the image below in the browser. After the site is created, it is distributed through the banner system. To combat this type of fraud, it is enough just to close the browser and not enter this site in the future, but many users are frightened, believe that their machine has become infected, and are in a hurry to pay money to the extortionists.
Most creative
The first years of development of blockers, the authors approached their creation with a soul. They came across very funny, funny and touching blockers. And only a few years later, the blockers began to rivet like cakes - quickly and quickly, in time to knock down the detections of antivirus products.

Most greedy
Since there was an upper price limit for the cost of SMS (500-600r.), Some blockers began to ask to send 2, and very greedy - 3 SMS.
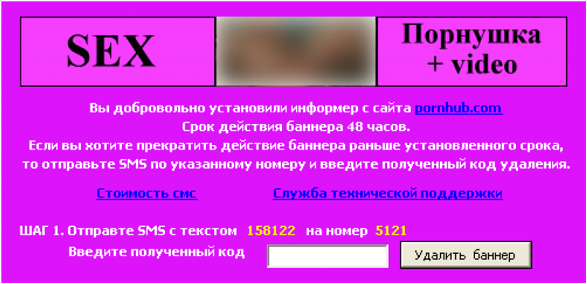
Most arrogant
The peculiarity of this blocker in the big names that he covers.

The most honest
This blocker is interesting because, unlike its colleagues, it honestly states that it is a blocker.
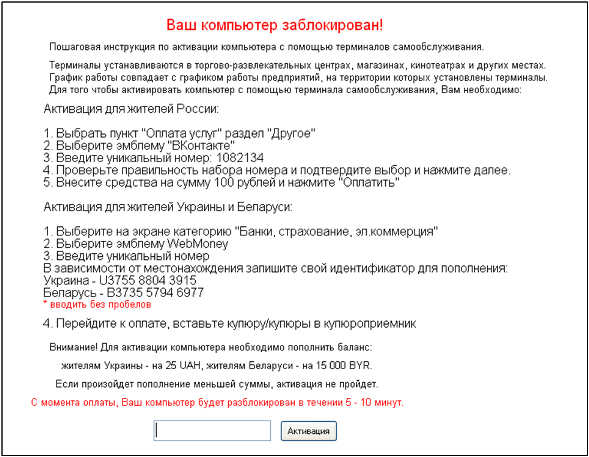
Longest running
This blocker is unique in that it uses a subscription system to enrich its authors. Instead of requiring sending an SMS or transferring money to an account, this blocker requires you to send your phone number. An SMS comes with a deactivation code.
All these innocuous actions pursue one goal - to register a user on a so-called subscription. By entering the deactivation code into the blocker, the user thereby agrees with the terms of the subscription (which, naturally, no one has shown to him). After a subscription, they start to regularly withdraw money from the user's phone (for example, every 3 days for 150 rubles). This method works until the user refuses to subscribe or for a certain time (for example, a week) there are no funds on the phone.
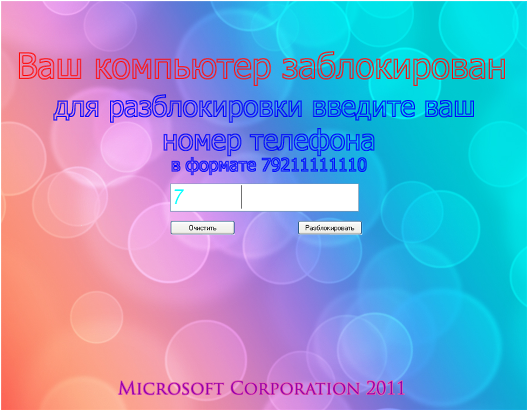
Most brutal
This blocker is characterized by the display of homosexuals.
His second “remarkable” feature is deactivation codes - this is not a meaningless set of characters, but game codes (for example, IDDQD), game characters (KERRIGAN IS SO SEXY), authors of favorite works (FRANK HERBERT), etc.
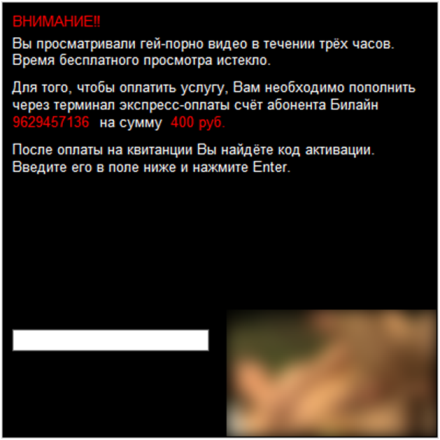
The most detailed ("blond")
This blocker can be called the most detailed in the field of instructions for its deactivation. Since this program does not use SMS as a form of payment, it uses the more exotic “V kontakte” scheme, with which relatively few users are familiar, it provided infected users with very detailed step-by-step instructions on how to transfer money to fraudsters.

The most "Kaspersky"
This blocker impersonates itself as a kind of non-existent product of Kaspersky Lab, Kaspersky Lab Antivirus Online. At one time, it was very popular and literally caused a flurry of letters to the company with the text “If you don’t get enough money, why do you also need this program?” In general, this blocker spoiled a lot of blood to both shift analysts and the PR department.

Total:
In the trend, as you can see, the development of social engineering techniques, but the technical idea does not stand still. In any case, we decided that it would be safer to prevent blocking than to treat an already infected computer. And if until now we could offer you only a free utility, support.kaspersky.ru/viruses/deblocker , now we are completing work on a new tool, which we will present in one of the following posts.
 Ivan Tatarinov, senior virus analyst at Kaspersky Lab
Ivan Tatarinov, senior virus analyst at Kaspersky Lab
The technical side of the ransomware also did not stand still. If initially they were very simple programs written “on the knee”, then after a few years, the blockers were very technologically sophisticated products with protection against analysis, protection against detection, technology of network worms, encryption, etc. etc.
The technologies, through which fraudsters were going to demand money from users, were also developed. If initially the system was blocked entirely, and the user received information about a technical failure, then later more advanced social engineering technologies were used.
Here are just some of them:
1) Partial locking of the system (for example, a window that is placed on top of the third screen) - working with such a computer is possible, but very uncomfortable;
2) Demonstration of adult content - designed for children with dad computers;
3) Demonstration of content containing perversion elements - designed for adults;
etc.
It is absolutely useless to pay fraudsters: sending an expensive SMS (or even several) does not guarantee at all that the victim will receive the promised unlock code. With the replenishment of the account through the payment terminal, the situation is no better - there is simply no identification number on the check to which the extortionists refer. By sending money, the user sponsors new developments, from which he himself suffers later (according to our data, on average, users get infected more than 1 time).
')
In our work, we constantly encounter extortionists and decided to create our own hit parade, highlighting, in our opinion, the most interesting ones in the following nominations:
The most difficult
This blocker is unique in that it infects the MBR. He has not gained much popularity. We can say that he was more of a concept.
In May 2011, a second MBR blocker appeared, gaining more and more popularity.

| Verdict: | Trojan-Ransom.Boot.Seftad |
| Date of appearance: | November 2010 |
| Date of epidemic decay: | the epidemic did not cause |
The most popular
MOST MASS, MOST PROFITABLE Blocker of all times and peoples. In June 2010, new blockers of this family came out literally once an hour. The epidemic stopped only after law enforcement agencies detained members of this criminal group.

| Verdict: | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.PinkBlocker |
| Date of appearance: | November 2009 |
| Date of epidemic decay: | august 2010 |
The very first
The first blockers in the open spaces of the Runet used exotic forms of payment, little known to housewives and unassuming design (no nude female and male body). But it all started with them.

| Verdict: | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.BlueScreen |
| Date of appearance: | autumn 2007 |
| Date of epidemic decay: | autumn 2008 |
The most beautiful

| Verdict: | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Gimemo |
| Date of appearance: | March 2011 |
| Date of epidemic decay: | the epidemic did not cause |
Animated
A blocker that uses an animated gif c mamma (Latin) as a picture, making oscillatory movements. As a payment, the blocker asked to send an SMS to one of the short numbers, among which were present both Russian and Ukrainian, Kazakhstan, Lithuanian and German.

| Verdict: | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.XBlocker |
| Date of appearance: | December 2009 |
| Date of epidemic decay: | February 2010 |
The first non-Russian
This blocker, which caused the first major epidemic of blockers in runet, came from Ukraine. Initially, SMS to Ukrainian number was accepted as payment.
A characteristic feature of the blockers from this family was the demonstration of the license agreement (!!!) at the first start of the blocker, in which it was reported that the user's computer would be blocked. But who reads these conventions?
In subsequent versions of the blocker, the license agreement, although demonstrated, was rather quickly closed, and the blocker started the installation regardless of the user's actions whether he agreed with the terms or not.

| Verdict: | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Digitala |
| Date of appearance: | October 2009 |
| Date of epidemic decay: | December 2010 |
Most harmless
This “blocker” is not a blocker as such. Fraudsters specifically create sites that pretend to be adult sites, and place JavaScript in them that displays the image below in the browser. After the site is created, it is distributed through the banner system. To combat this type of fraud, it is enough just to close the browser and not enter this site in the future, but many users are frightened, believe that their machine has become infected, and are in a hurry to pay money to the extortionists.

| Verdict: | Trojan-Ransom.JS.Smser |
| Date of appearance: | summer 2010 |
| Date of epidemic decay: | to the current time |
Most creative
The first years of development of blockers, the authors approached their creation with a soul. They came across very funny, funny and touching blockers. And only a few years later, the blockers began to rivet like cakes - quickly and quickly, in time to knock down the detections of antivirus products.

| Verdict: | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.ImBlocker |
| Date of appearance: | summer 2008 |
| Date of epidemic decay: | the epidemic did not cause |
Most greedy
Since there was an upper price limit for the cost of SMS (500-600r.), Some blockers began to ask to send 2, and very greedy - 3 SMS.

| Verdict: | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.PinkBlocker |
| Date of appearance: | spring 2010 |
| Date of epidemic decay: | august 2010 |
Most arrogant
The peculiarity of this blocker in the big names that he covers.

| Verdict: | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.ZoBlocker |
| Date of appearance: | N / A |
| Date of epidemic decay: | N / A |
The most honest
This blocker is interesting because, unlike its colleagues, it honestly states that it is a blocker.

| Verdict: | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Honest |
| Date of appearance: | N / A |
| Date of epidemic decay: | the epidemic did not cause |
Longest running
This blocker is unique in that it uses a subscription system to enrich its authors. Instead of requiring sending an SMS or transferring money to an account, this blocker requires you to send your phone number. An SMS comes with a deactivation code.
All these innocuous actions pursue one goal - to register a user on a so-called subscription. By entering the deactivation code into the blocker, the user thereby agrees with the terms of the subscription (which, naturally, no one has shown to him). After a subscription, they start to regularly withdraw money from the user's phone (for example, every 3 days for 150 rubles). This method works until the user refuses to subscribe or for a certain time (for example, a week) there are no funds on the phone.

| Verdict: | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Holotron |
| Date of appearance: | February 2011 |
| Date of epidemic decay: | the epidemic did not cause |
Most brutal
This blocker is characterized by the display of homosexuals.
His second “remarkable” feature is deactivation codes - this is not a meaningless set of characters, but game codes (for example, IDDQD), game characters (KERRIGAN IS SO SEXY), authors of favorite works (FRANK HERBERT), etc.

| Verdict: | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.HmBlocker |
| Date of appearance: | November 2010 |
| Date of epidemic decay: | March 2011 |
The most detailed ("blond")
This blocker can be called the most detailed in the field of instructions for its deactivation. Since this program does not use SMS as a form of payment, it uses the more exotic “V kontakte” scheme, with which relatively few users are familiar, it provided infected users with very detailed step-by-step instructions on how to transfer money to fraudsters.

| Verdict: | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.GiviBlocker |
| Date of appearance: | November 2010 |
| Date of epidemic decay: | the epidemic did not cause |
The most "Kaspersky"
This blocker impersonates itself as a kind of non-existent product of Kaspersky Lab, Kaspersky Lab Antivirus Online. At one time, it was very popular and literally caused a flurry of letters to the company with the text “If you don’t get enough money, why do you also need this program?” In general, this blocker spoiled a lot of blood to both shift analysts and the PR department.

| Verdict: | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Chameleon |
| Date of appearance: | N / A |
| Date of epidemic decay: | N / A |
Total:
In the trend, as you can see, the development of social engineering techniques, but the technical idea does not stand still. In any case, we decided that it would be safer to prevent blocking than to treat an already infected computer. And if until now we could offer you only a free utility, support.kaspersky.ru/viruses/deblocker , now we are completing work on a new tool, which we will present in one of the following posts.
 Ivan Tatarinov, senior virus analyst at Kaspersky Lab
Ivan Tatarinov, senior virus analyst at Kaspersky LabSource: https://habr.com/ru/post/119959/
All Articles