OFDM - digital modulation technology in WiMax and LTE networks
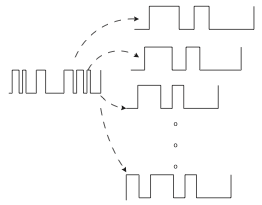 We present the second article from the cycle of posts about wireless data transfer.
We present the second article from the cycle of posts about wireless data transfer.In the comments to the first of them: “Modulation of the radio signal”, the respected nerudo advised to talk about such an important point as OFDM. What we do with pleasure and do.
What is OFDM?
OFDM (Eng. Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing - orthogonal frequency division multiplexing)')
This is a modulation scheme using multiple carriers. The channel is divided into several subchannels or subcarrier (the Russian analogue “subcarrier” seems a little ridiculous to me, I will try to avoid this word, using where necessary “auxiliary carrier”)
In OFDM, a high-speed data stream is converted into several parallel bit streams of lower speed, each of which is modulated by its own individual carrier.
All this multitude of carriers is transmitted simultaneously.
The main advantage of OFDM is that the duration of the symbol in the auxiliary carrier is significantly longer compared to the propagation delay than in traditional modulation schemes. This makes OFDM much more resistant to intersymbol interference (ISI, intersymbol interference).
ISI - Intersymbol Interference
Intersymbol interference is a form of signal distortion caused by the effect of one symbol on another. This effect is observed in both wired and wireless data transmission systems.
The master's thesis of your humble servant was just devoted to the fight against intersymbol interference
 , therefore I will explain on the example of the cable line. The cable is a distributed RC-chain, and the high-frequency components of the signal in it are subject to attenuation. The most critical case is a single one after a series of zeros or a single zero after one:
, therefore I will explain on the example of the cable line. The cable is a distributed RC-chain, and the high-frequency components of the signal in it are subject to attenuation. The most critical case is a single one after a series of zeros or a single zero after one: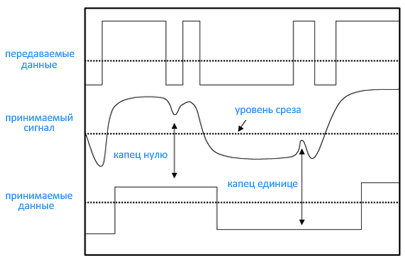
When data is transmitted “over the air”, there is no RC component, but another mechanism is activated, leading to the same effect. It is called multipath.
Due to this effect, the wireless signal from the transmitter reaches the receiver through several different paths. The reasons for this reflection (for example, from buildings) are refraction (refraction when passing through treetops) and atmospheric effects.
Since all paths are of different lengths, and some of the effects described above lead to a signal delay, as a result, different versions of the signal will come to the receiver at different times. Due to the overlap of all these signals, the resulting signal will be distorted.
I will take an example of signal distortion in multipath from Wikipedia.
Source signal:
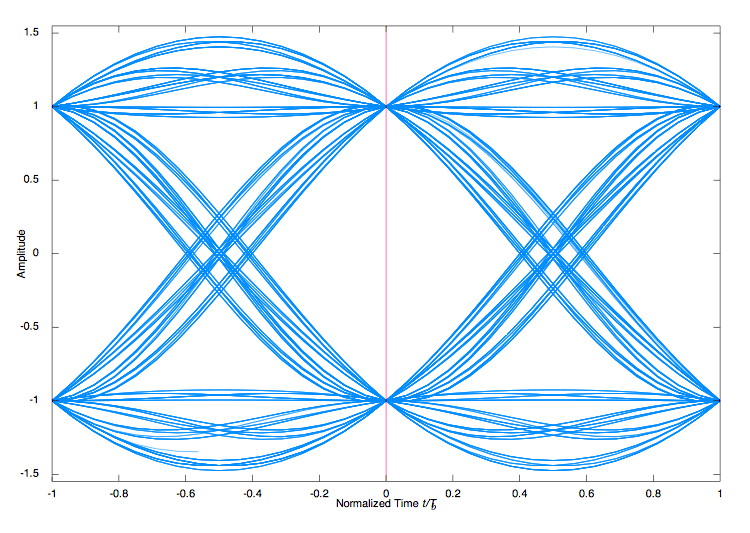
Signal affected by multipath:

Perhaps a respected person at the sight of these pictures made a surprised face. Now I will explain.
This is the so-called eye diagram. It is built very simply: all sources of interaction or signals are superimposed on each other. By “eye” is meant an area in the middle that is shaped like an eye. In the first picture, “the eye is wide open
t ", on the second" eyes narrowed. " If the "eye closes" or is less than a certain value, then such a signal can no longer be accepted.
It is intuitively clear that the higher the signal frequency, the smaller the “eye” will be.
The key principle of OFDM is the use of a guard interval. This is possible due to the fact that the length of each character is long enough.
I will give an example from the English-language Wikipedia:
“If someone transmits a million characters per second using a one-way modulation wirelessly, then the length of each character will be one microsecond or less. This results in certain synchronization requirements and the need to suppress multipath interference. If the same million characters per second is distributed among a thousand subchannels, the duration of each character can be increased by three orders of magnitude (i.e., to one millisecond) at approximately the same throughput. Suppose that we can insert a guard interval equal to 1/8 of the character's duration between each character. Intersymbol interference can be tolerated if the time between the reception of the first and last echo is shorter than the guard interval (ie, 125 microseconds). This corresponds to a maximum difference of 37.5 kilometers between the signal path length.
Another advantage is resistance to frequency-dependent attenuation. This type of attenuation can have a very negative effect on multipath signal propagation, especially if the source and receiver are not in direct view. With OFDM modulation, data is distributed among multiple auxiliary carriers, therefore, information affected in several subchannels can be recovered using the ECC.
In conclusion, I will give the most well-known data transmission standards in which this principle is used:
- ADSL (wired data transmission)
- DVB-T
- WiMAX
- LTE
PS: Why?
In the comments to the first article there was a question, what exactly is this “opening of the habrow university”.
I will answer here. Yota is one of the largest in the world and the first in Russia wireless 4G mobile Internet operator. In Moscow, St. Petersburg, Sochi, Ufa and Krasnodar, access is now provided using WiMax technology.
In our blog, we decided to bring the basics of this technology to a wide range of people.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/119319/
All Articles