Radio signal modulation
 In the comments to the article "Signal quality criteria in WiMax networks", zlyoha lamented the lack of articles describing the physical side of information transfer via radio channel.
In the comments to the article "Signal quality criteria in WiMax networks", zlyoha lamented the lack of articles describing the physical side of information transfer via radio channel.We decided to correct this omission and write a cycle of posts about wireless data transfer.
In the first of them, we will talk about the main aspect of information transmission by means of a radio signal - modulation.
Modulation (lat. Modulatio - dimension) is the process of changing one or several parameters of a high-frequency carrier wave according to the law of a low-frequency information signal.
The transmitted information is embedded in the control signal, and the role of information carrier is performed by a high-frequency oscillation, called carrier.
Modulation can be done by changing the amplitude, phase, or frequency of the high frequency carrier.
This technique has several important advantages:
- Allows you to generate a radio signal that will have properties corresponding to the properties of the carrier frequency. About the properties of waves of different frequency ranges can be read, for example, here .
- Allows you to use small antennas, because the size of the antenna must be proportional to the wavelength.
- Allows you to avoid interference with other radio signals.
The data stream transmitted in WiMax networks corresponds to a frequency in the region of 11 kHz. If we try to transmit this low-frequency signal through the air, we need an antenna of the following sizes:
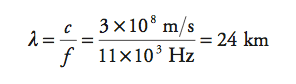
An antenna 24 kilometers long does not seem comfortable enough to use.
If we transmit this signal superimposed on a 2.5 GHz carrier frequency (the frequency used in the Yota WiMax), then we will need a 12 cm antenna.
Analog Modulation.
Before proceeding directly to digital modulation, I will give a picture illustrating analog AM (amplitude) and FM (frequency) modulation, which will refresh many school knowledge:

source signal
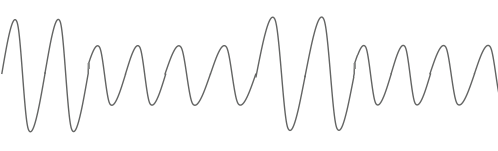
AM (amplitude modulation)
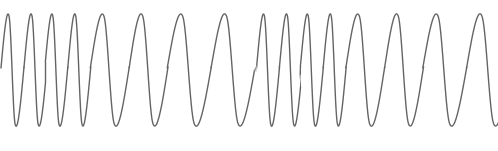
FM (frequency modulation)
')
Digital modulation and its types.
In digital modulation, the analog carrier signal is modulated with a digital bitstream.
There are three fundamental types of digital modulation (or encryption) and one hybrid:
- ASK - Amplitude shift keying (Amplitude binary modulation).
- FSK - Frequency shift keying (Frequency Binary Modulation).
- PSK - Phase shift keying (Phase shift modulation).
- ASK / PSK.
I will mention that there is a tradition in Russian radio terminology to use the term "manipulation" to modulate a digital signal.
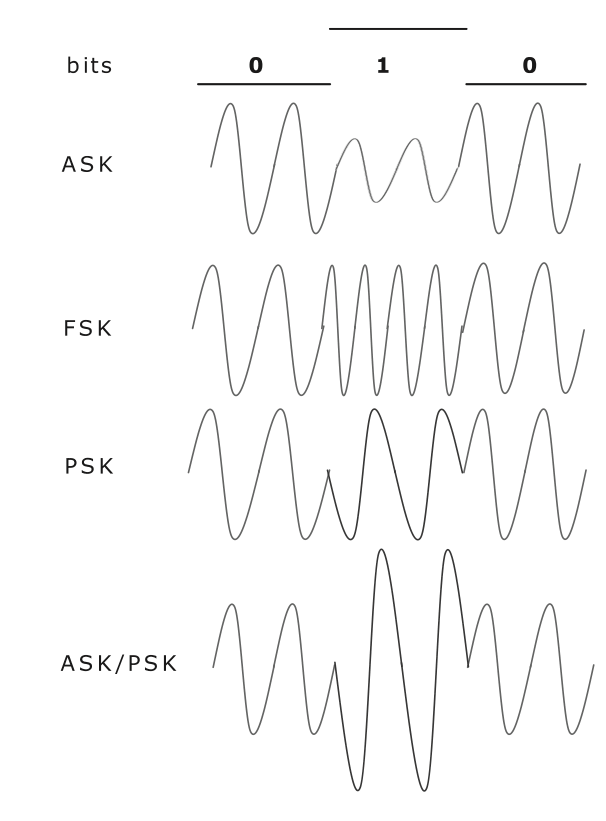
In the case of amplitude shuffling, the signal amplitude for a logical zero can be (for example) two times smaller than the logical one and one.
Frequency modulation in a similar way represents a logical unit interval with a greater frequency than zero.
Phase ciphering represents “0” as a signal without a shift, and “1” as a signal with a shift.
Yes, here we are dealing with a “phase shift” :)
Each of the schemes has its strengths and weaknesses.
- ASK is good in terms of bandwidth efficiency, but prone to distortion in the presence of noise and not efficient enough in terms of power consumption.
- FSK - exactly the opposite, is energy efficient, but does not effectively use the frequency band.
- PSK is good in both aspects.
- ASK / PSK - a combination of two schemes. It allows even better use of the frequency band.
The simplest PSK scheme (shown in the figure) has its own name - Binary phase-shift keying. A single phase shift between “0” and “1” is used - 180 degrees, half the period.
There are also QPSK and 8-PSK:
QPSK uses 4 different phase shifts (by quarter period) and can encode 2 bits per symbol (01, 11, 00, 10). 8-PSK uses 8 different phase shifts and can encode 3 bits per symbol.
More here
One of the particular implementations of the ASK / PSK scheme called QAM - Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM). This is a method of combining two AM signals in one channel. with a quarter-period difference in the phase (hence the word quadrature arises.) Higher QAM levels are based on the same principles as PSK. If you are interested in details, you can easily find them on the net.
Theoretical bandwidth efficiency:
| Format | Efficiency (bps / Hz) |
| Bpsk | one |
| QPSK | 2 |
| 8-PSK | 3 |
| 16-QAM | four |
| 32-QAM | five |
| 64-QAM | 6 |
| 256-QAM | eight |
The more complex the modulation scheme, the more detrimental effects on it are distortions during transmission, and the smaller the distance from the base station at which the signal can be successfully received.
Theoretically, PSK and QAM schemes of a higher level are possible, but in practice there are too many errors when using them.
Now that we have covered the main points, you can write what modulation schemes are used in WiMax networks.
Signal modulation in WiMax networks.
WiMax uses “dynamic adaptive modulation”, which allows the base station to choose between bandwidth and maximum distance to the receiver. To increase the range, the base station can switch between 64-QAM, 16-QAM and QPSK.
Conclusion
I hope that I managed to strike a balance between the popularity of presentation and technical content. If this article is claimed, I will continue to work in this direction. WiMax technology has many nuances that you can talk about.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/119047/
All Articles