And again about topological sorting ...
Greetings to all readers of Habr! Having decided to write this article, I found a lot of materials on Habré on graphs and, in particular, on topological sorting . For example, the theoretical part is described in some detail and examples of basic algorithms are given. Therefore, I will not repeat, but I will tell you about the practical scope of Topological sorting , or rather, I want to share my personal experience of using this method in the development of DevExpress products. From the article, the motives and reasons for using this algorithm will become clear. At the end I will give our variant of the implementation of the algorithm for sorting dependent objects.
Scope of the sorting algorithm in DevExpress
In a previous article, we talked about the XtraScheduler scheduler and its print extension. It includes a report designer working with visual elements. When designing in the designer of the appearance of the printed form, it is necessary to establish links between the visual elements of the report on the principle of "master-slave". These dependencies should determine how data is transferred between items. For internal implementation, this implies the formation of the correct printing priority of these objects.
')
The elements were inherently oriented graph of objects, since The options of these controls uniquely determined the direction of the dependency by specifying a reference to the main object.
The topological sorting algorithm could not be better suited to build dependent objects in the correct order before printing, analyzing the connections between them. In addition, the dependent controls for printing used the rendering data of the main controls. Therefore, the algorithm was also applied to the organization of internal data caching objects containing the main data iterator object and its associated subordinate list.
Where else did we apply the algorithm?
A little later, in the XtraRichEdit project , when developing import and export styles for documents in RTF and DOC formats, it also became necessary to get the objects containing dependencies between them in the correct order. The described algorithm was generalized and successfully applied in this case.
Algorithm-T
Let us turn to our implementation of the sorting algorithm. It is based on the described Algorithm-T from the book “The Art of Programming” by Donald Knuth (Volume 1, Chapter 2.2.3). Therefore, you can read about the details of the algorithm in the original; here I will only provide an algorithm for a general understanding of the idea.
Why did we choose this algorithm? Just let me quote the author a little.
“The analysis of the algorithm T can be easily performed using Kirchhoff’s law. Using this law, the execution time can be estimated approximately using the formula c1 * m + c2 * n, where m is the number of relations introduced, n is the number of objects, and c1 and c2 are constants. A faster algorithm for solving this problem is simply impossible to imagine! ”
The implemented algorithm is located in the DevExpress.Data.dll assembly in the Algorithms class, which along with the topological sorting contains a number of other useful algorithms.
namespace DevExpress.Utils { public static class Algorithms { public static IList<T> TopologicalSort<T>(IList<T> sourceObjects, IComparer<T> comparer) { TopologicalSorter<T> sorter = new TopologicalSorter<T>(); return sorter.Sort(sourceObjects, comparer); } } Using the algorithm is extremely simple. It is enough to call the static class method, passing it the necessary parameters. An example call is as follows:
protected virtual IList<XRControl> SortControls(List<XRControl> sourceControls) { return Algorithms.TopologicalSort<XRControl>(sourceControls, new ReportViewControlComparer()); } You can do without calling a static method by explicitly creating an instance of the sorter object.
The source code of the sorter class that implements the algorithm will be given at the end of the article.
As can be seen from the parameters, in addition to the list of objects, a specialized comparer is passed to the method. If it is not specified, the default object will be used. In practice, the comparator object is usually specified, since it determines the comparison logic, which can be based on the properties of the compared objects. In addition, such an object can implement several IComparer interfaces simultaneously for several inherited types.
As an example of such a class, I will give our ReportViewControlComparer, which is used in the XtraScheduler.Reporting library:
public class ReportViewControlComparer : IComparer<XRControl>, IComparer<ReportViewControlBase> { #region IComparer<XRControl> Members public int Compare(XRControl x, XRControl y) { return CompareCore(x as ReportRelatedControlBase, y as ReportViewControlBase); } #endregion #region IComparer<ReportViewControlBase> Members public int Compare(ReportViewControlBase x, ReportViewControlBase y) { return CompareCore(x as ReportRelatedControlBase, y); } #endregion int CompareCore(ReportRelatedControlBase slave, ReportViewControlBase master) { if (slave != null && master != null) { if (slave.LayoutOptionsHorizontal.MasterControl == master || slave.LayoutOptionsVertical.MasterControl == master) return 1; } return 0; } } Application example
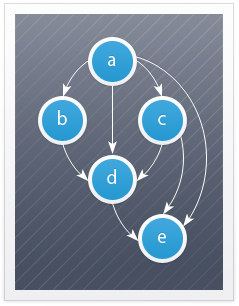
To demonstrate the operation of the algorithm, create a console application. As an example of a graph, we take a simple graph of 5 nodes (see the figure at the beginning of the article).
G = ({a, b, c, d, e}, {(a, b), (a, c), (a, d), (a, e), (b, d), (c, d ), (c, e), (d, e)})
To represent the graph, a simple class will be used that defines a node with a list of other nodes associated with it.
public class GraphNode { List<GraphNode> linkedNodes = new List<GraphNode>(); object id; public GraphNode(object id) { this.id = id; } public List<GraphNode> LinkedNodes { get { return linkedNodes; } } public object Id { get { return id; } } } The code for the application itself is shown below:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { DoDXTopologicalSort(); } private static void DoDXTopologicalSort() { GraphNode[] list = PrepareNodes(); Console.WriteLine("DX Topological Sorter"); Console.WriteLine(new string('-', 21)); Console.WriteLine("Nodes:"); GraphNode[] list = PrepareNodes(); PrintNodes(list); IComparer<GraphNode> comparer = new GraphNodeComparer(); IList<GraphNode> sortedNodes = DevExpress.Utils.Algorithms.TopologicalSort<GraphNode>(list, comparer); Console.WriteLine("Sorted nodes:"); PrintNodes(sortedNodes); Console.Read(); } static GraphNode[] PrepareNodes() { GraphNode nodeA = new GraphNode("A"); GraphNode nodeB = new GraphNode("B"); GraphNode nodeC = new GraphNode("C"); GraphNode nodeD = new GraphNode("D"); GraphNode nodeE = new GraphNode("E"); nodeA.LinkedNodes.AddRange(new GraphNode[] { nodeB, nodeC, nodeE }); nodeB.LinkedNodes.Add(nodeD); nodeC.LinkedNodes.AddRange(new GraphNode[] { nodeD, nodeE }); nodeD.LinkedNodes.Add(nodeE); return new GraphNode[] { nodeD, nodeA, nodeC, nodeE, nodeB }; } static void PrintNodes(IList<GraphNode> list) { for (int i = 0; i < list.Count; i++) { string s = string.Empty; if (i > 0) s = "->"; s += list[i].Id.ToString(); Console.Write(s); } Console.WriteLine("\r\n"); } } Directly connections of the graph are set in the PrepareNodes method. In this case, dependencies are created arbitrarily.
To compare the nodes, we also need the GraphNodeComparer class.
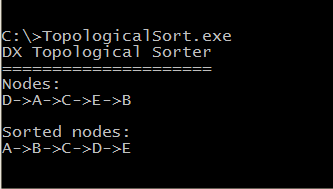
public class GraphNodeComparer : IComparer<GraphNode> { public int Compare(GraphNode x, GraphNode y) { if (x.LinkedNodes.Contains(y)) return -1; if (y.LinkedNodes.Contains(x)) return 1; return 0; } } After launching the application, we will get a sorted list of nodes and the console will display
A-> B-> C-> D-> E.
The result of the program is shown in the figure below:
Sorter source code
As I promised above, I provide the code for the implementation of the topological sorting algorithm.
namespace DevExpress.Utils.Implementation {
#region TopologicalSorter
public class TopologicalSorter<T> {
#region Node
public class Node {
int refCount;
Node next;
public Node( int refCount, Node next) {
this .refCount = refCount;
this .next = next;
}
public int RefCount { get { return refCount; } }
public Node Next { get { return next; } }
}
#endregion
#region Fields
int [] qLink;
Node[] nodes;
IList<T> sourceObjects;
IComparer<T> comparer;
#endregion
#region Properties
protected internal Node[] Nodes { get { return nodes; } }
protected internal int [] QLink { get { return qLink; } }
protected IComparer<T> Comparer { get { return comparer; } }
protected internal IList<T> SourceObjects { get { return sourceObjects; } }
#endregion
protected IComparer<T> GetComparer() {
return Comparer != null ? Comparer : System.Collections. Generic .Comparer<T>.Default;
}
protected bool IsDependOn(T x, T y) {
return GetComparer().Compare(x, y) > 0;
}
public IList<T> Sort(IList<T> sourceObjects, IComparer<T> comparer) {
this .comparer = comparer;
return Sort(sourceObjects);
}
public IList<T> Sort(IList<T> sourceObjects) {
this .sourceObjects = sourceObjects;
int n = sourceObjects.Count;
if (n < 2)
return sourceObjects;
Initialize(n);
CalculateRelations(sourceObjects);
int r = FindNonRelatedNodeIndex();
IList<T> result = ProcessNodes(r);
return result.Count > 0 ? result : sourceObjects;
}
protected internal void Initialize( int n) {
int count = n + 1;
this .qLink = new int [count];
this .nodes = new Node[count];
}
protected internal void CalculateRelations(IList<T> sourceObjects) {
int n = sourceObjects.Count;
for ( int y = 0; y < n; y++) {
for ( int x = 0; x < n; x++) {
if (!IsDependOn(sourceObjects[y], sourceObjects[x]))
continue ;
int minIndex = x + 1;
int maxIndex = y + 1;
QLink[maxIndex]++;
Nodes[minIndex] = new Node(maxIndex, Nodes[minIndex]);
}
}
}
protected internal int FindNonRelatedNodeIndex() {
int r = 0;
int n = SourceObjects.Count;
for ( int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
if (QLink[i] == 0) {
QLink[r] = i;
r = i;
}
}
return r;
}
protected virtual IList<T> ProcessNodes( int r) {
int n = sourceObjects.Count;
int k = n;
int f = QLink[0];
List <T> result = new List <T>(n);
while (f > 0) {
result.Add(sourceObjects[f - 1]);
k--;
Node node = Nodes[f];
while (node != null ) {
node = RemoveRelation(node, ref r);
}
f = QLink[f];
}
return result;
}
Node RemoveRelation(Node node, ref int r) {
int suc_p = node.RefCount;
QLink[suc_p]--;
if (QLink[suc_p] == 0) {
QLink[r] = suc_p;
r = suc_p;
}
return node.Next;
}
}
#endregion
* This source code was highlighted with Source Code Highlighter .findings
If necessary, in a specific order of processing objects that are dependent on each other, they can be pre-ordered by applying the topological sorting algorithm. As a result, the correct sequence of objects and the execution of actions on them are constructed.
The proposed algorithm provides the following advantages:
- the use of generalization (generic), i.e. It can be used to sort objects of various types.
- the ability to set your class Comparer, that is, it allows you to implement different logic for comparing objects.
- linearity algorithm, non-recursive algorithm
An example with source text is available here .
I hope this material will be useful to you in future projects.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/116812/
All Articles