Malicious programs - 2010: annual report
 The past 2010 can be called the heyday of online fraud. The attackers invented and implemented dozens of schemes for obtaining illegal income, and the malware itself has fallen on hundreds of millions of computers.
The past 2010 can be called the heyday of online fraud. The attackers invented and implemented dozens of schemes for obtaining illegal income, and the malware itself has fallen on hundreds of millions of computers.So, the rating of fraudulent tools - 2010.
Attention, traffic!
I propose to begin this review with the main ten types of "malware" for 2010.
')
10 place - Psevdoslugi
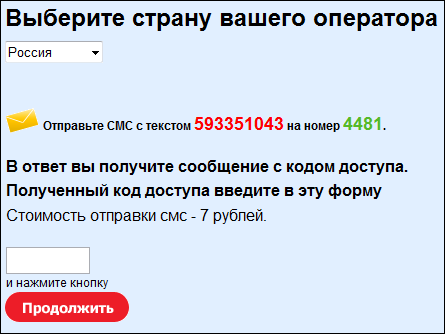
Scammers report that the cost of SMS - 7 rubles. The real cost of some operators is almost 43 times more than the fraudsters announced on the site.
In the past year, many users in the vastness of the Web have repeatedly seen an offer to get access to interesting and, in most cases, illegal content. For example, malefactors suggested to get access to sites with pornographic content, or to read personal messages of any user of social networks. Payment for such “information” in 99% of cases is an SMS message, which, according to the attackers, will cost ten cents, and in fact such a message costs an average of $ 4. Some systems are organized in such a way that by sending one SMS, the user receives a notification stating that in order to gain access to the selected service, you need to send 2 more messages. The pretext may be different. For example, sending the first message to gain access to a porn site comes the question, they say, "If you really turned 18, send an SMS with the code ***** to the number ****." So fraudsters can get an uninformed user from $ 12 to $ 20. The quality of such services is often questionable. Moreover, often the promised is a banal bluff - the user loses money without receiving any content. Links to sites on which such a scheme of fraud is used, usually spread through advertising banner networks through sites with free content.
9th place - False archives
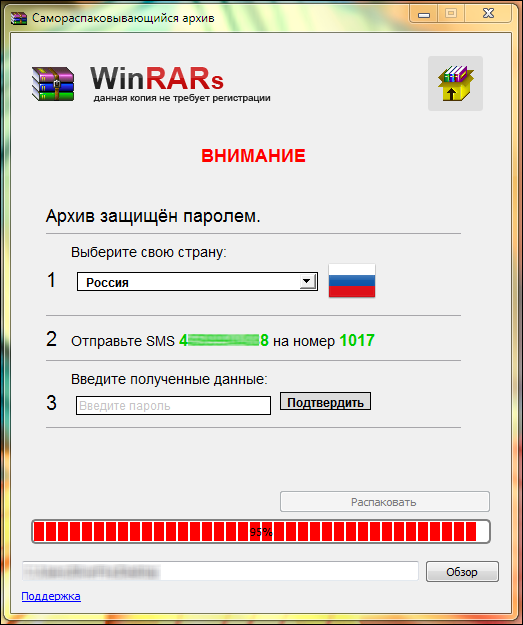
About the cost of SMS says nothing, but here is the real cost .
Malefactors create fake (fake) torrent trackers or file storages from which it is possible to download popular or rare content. These resources appear in the first lines of popular queries in search engines. Using such a resource, the victim receives an allegedly self-extracting archive for downloading, which contains the desired information. In reality, the “archive” is an executable file (* .exe) , the interface and the icon are very similar to the self-extracting archive. The difference of this archive from the present is that in the process of "unpacking" at a certain point the user is informed that in order to complete the process it is necessary to pay some amount of money. In fact, the user is deceived twice - he sends money to attackers and does not receive any useful information. Archives do not contain anything other than the visual shell and garbage, and their size (apparently, to put down the vigilance of users) can reach 70 MB or more.
8th place - boot blockers
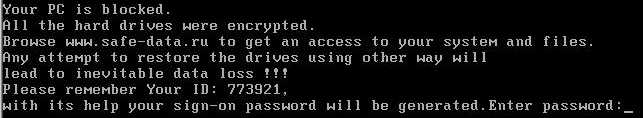
In November 2010, the spread of the blocker was recorded, which during infection is registered in the boot area of the hard disk, thereby blocking the loading of the operating system used. When the computer is turned on, the user's screen displays information with the requirements of the attackers. The developers of this particular “malware” require $ 100 for the key.
7 - IM client startup blockers

Again, the price does not say anything, but here is the real price .
For several months in 2010, attackers distributed a malicious program that blocked the launch of popular instant messaging clients. The users of ICQ, QIP and Skype were hit. The IM client was replaced with malware similar in interface, in which the user was informed at startup that his account was blocked for sending spam, and for restoring access to the corresponding service, an SMS message must be sent, of course, to a paid number.
6 place - Pseudo antivirus
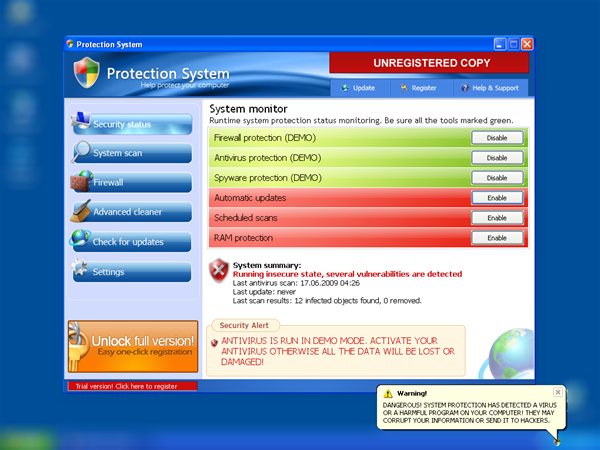
Pseudo-antivirus programs look similar to antivirus software, and often their design resembles several antivirus products at once. But these malware have nothing to do with antivirus programs. Once installed into the system, such “antiviruses” immediately report that the system is supposedly infected (partly true), and to treat the system it is necessary to purchase a paid version of the antivirus program. In some cases, they threaten to remove all information from the hard disk or make the computer unusable.
5th place - Redirectors on malicious and fraudulent sites
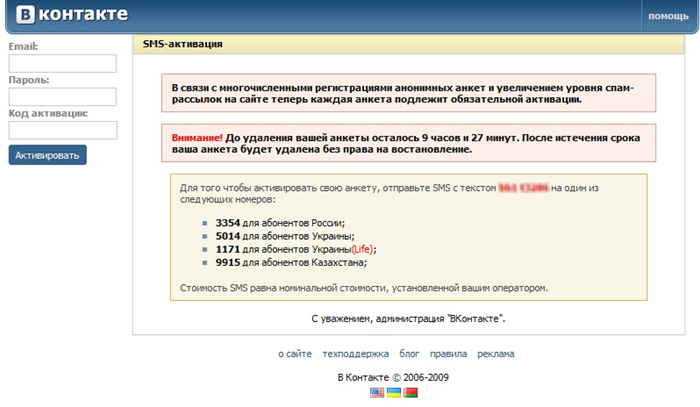
The price is written quite cleverly, but here is the real cost .
These malicious programs are created by hackers to modify the system hosts file so that when you try to access a popular site (for example, one of the popular social networks), a fake site with a design similar to the original one appears in the Internet browser. Usually, access to most search engines is blocked in order to deprive the user of the opportunity to "crack down" with the virus. In this case, with the user under various pretexts will be required money. The most popular requirements of fraudsters are: the user must send an SMS to unblock access to the social network; the user must send an SMS to confirm that he is not a bot; etc. However, some viruses change the path to the hosts file in the registry, thus reducing the likelihood that the average user will cope with the malware.
4th place - Redirectors to a local web server
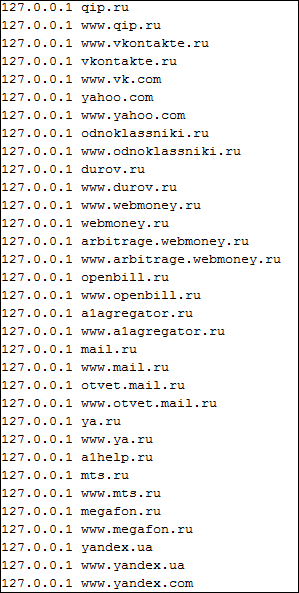
Unlike the type described above, these malicious programs, after infecting the system, redirect the user to the pages that the web server locally installed on the computer generates. In this case, the attackers make it easy for them to find a hoster that does not remove the malicious website from their addresses until the victim’s computer is infected. It is also possible to redirect to 127.0.0.1 in order to block access to some resources without installing a local web server.
3rd place - data encryption
In 2010, many new modifications of encryption Trojans appeared, the purpose of which are user documents. After the Trojan encrypts documents, it displays information that it is necessary to send money to the attackers for decoding. In the overwhelming majority of cases, virologists promptly develop utilities with which to decipher user data, but since it is not always possible and the attackers require significant amounts of money to decrypt, Trojan.Encoder is in third place in our dozens.
2 place - Windows blockers
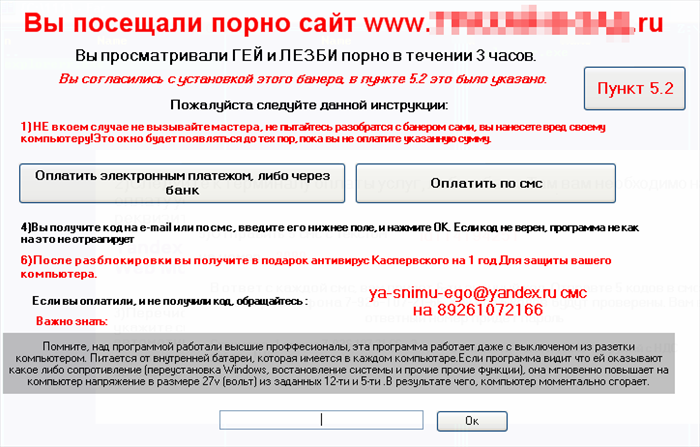
The second place is taken by the classic Windows blockers, which have been keeping users and anti-virus companies in suspense since the fall of 2009. Windows blockers include malware that displays a window (blocking other windows) with the requirements of attackers. Thus, the user is deprived of the opportunity to work at the computer until he pays for unlocking. The variety of such blockers, as well as pretexts of fraudsters, is shocking - from demands to pay a fine for using pirated software to claims for paying for ordered porn content.
1st place - Banking Trojans
The first place in the list of cyber-pests is awarded to bank Trojans. This category of malware includes those that are focused on getting unauthorized access to malicious accounts of individuals and legal entities through remote banking systems. The latter are now rapidly gaining popularity, and criminals are seeking to take advantage of this popularity. Probably, in 2011 we will witness a shift in the sphere of interests of Internet fraudsters from private users to legal entities, on whose accounts much more significant amounts of money are concentrated.
PandaLabs presented its annual report on viral activity.
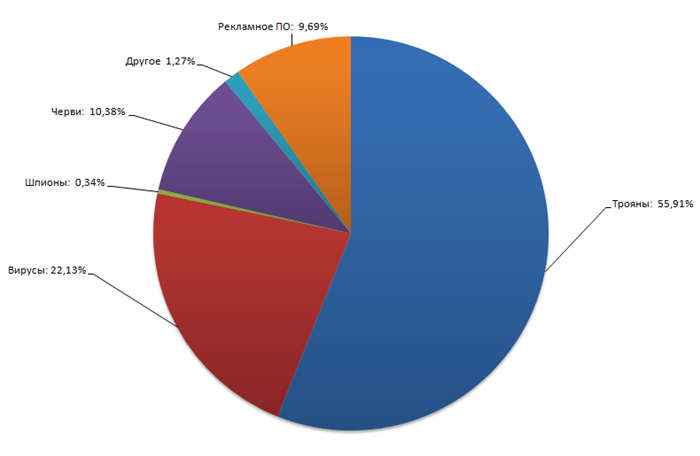
The most popular type of viruses of this year were Trojans.
Analysts note that in 2010, the number of viruses created and spread by cyber-crooks was one third of all viruses that had ever existed. The so-called banking Trojans dominate the ranking of the latest malware, which appeared in 2010 (56% of all new samples). In second place in terms of “popularity” are viruses and worms. The list of the most infected countries was led by Thailand, China, Taiwan, Ukraine and Latvia, with an infection rate in the range of 50-70%.
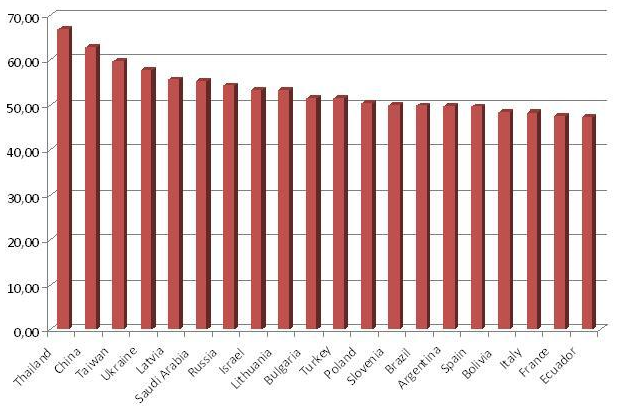
The rating is based on the data obtained through Panda ActiveScan.
As for the most popular methods of infection, in 2010 they became:
- the spread of malware through social networks,
- the creation of fake websites (BlackHat SEO attacks);
- the use of so-called vulnerabilities "zero" day.
During 2010, he continued to actively spread spam, even though some botnets were eliminated (for example, Mariposa and Bredolad ). This saved millions of computers from the threat and, of course, affected the global spam traffic. In 2009, about 95% of all emails turned out to be spam, but in 2010 this figure dropped to about 85%.
2010 can be called the year of the year of cyber crime and cyber wars. Last year, we saw several examples of cyber wars. One of the most striking similar wars was caused by the Stuxnet worm. He managed to infect a nuclear power plant near the city of Bushehr (Iran), which was confirmed by the Iranian authorities.
Another bright cyber war of 2010 is Operation Aurora. The purpose of this attack were the employees of some large transnational corporations. Their work computers were infected by Trojan, who is able to access all confidential information.
2010 also showed us the emergence of a new phenomenon that forever changed the relationship between society and the Internet: cyber protests or so-called hacktivism . This phenomenon has become known through the "Anonymous group." In fact, it is not something completely new, but this time all publications wrote about it. The “Anonymous Group” organized multiple DDoS attacks that brought down the site systems of various copyright protection societies. Thus, this group sought to protect the founder of the site Wikileaks Julian Assange.
It would be desirable to hope that 2011 will manage without dangerous and unpleasant novelties of the world of cyber viruses.
Thanks for attention.
The following materials and sites were used to create the article: 1 , 2 , 3 , 4
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/112070/
All Articles