What does digg work on
We’ve already told you what MySpace works on and how Google’s data centers are organized , and now let's take a look at smaller projects like digg . There is nothing particularly unique and made “by special order”, as in the first two cases, but still interesting.
At launch, the project was hosted on a single Linux server with Apache 1.3 and PHP 4.x. MySQL 4.0, MyISAM tables and MySQL built-in search were used to manage the databases. The developers specifically tried to use as many open source products as possible to ensure the rapid development of the project without financial difficulties. In addition to the above, free packages ImageMagick, Ispell, prototype / scriptaculous, and others have found use. Soon another was added to one server and the project began to grow rapidly.
With the advent of the second server, MyISAM tables had to be supplemented with InnoDB tables. After the appearance of the third server, Apache 2.x and master-slave replication systems were installed in MySQL, they started using memcached, switched to PHP 5.x and hired a database administrator.
Now the digg server system consists of two relatively independent clusters. Separate PHP servers that are behind their load balancer interact with MySQL servers and generate pages in real time.
')

An important role in the process of generating pages is assigned to the memcached caching module, which greatly reduces the load on the servers. In order to increase the efficiency of its work on the specific content of social media, an additional program code was written specifically for the site digg.
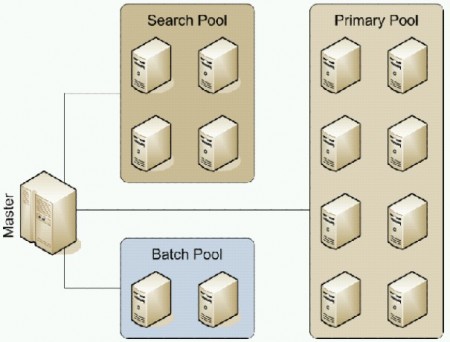
The MySQL server group is divided into specialized clusters: main, search, and operational.
It is clear that in such a situation, you can resort to the separation of the database (sharding). This approach has both advantages and disadvantages. The advantages of sharding include increased performance and improved manageability / customizability of the DBMS, and disadvantages include increased PHP load, complicated programming and loss of SQL support. Although MySQL supports several types of sharding, digg does not use any of them, because all of these technologies, according to the developers, were rather raw at that time.
Today, digg databases are a rather heterogeneous structure from MySQL versions 5.0.22, 5.0.27, 5.0.30 and 5.0.32, there is also MySQL 4.1 to support Cacti. The installation and maintenance of databases is carried out through the Debian operating system.
For online OLTP transaction processing, InnoDB tables are used (they also recover faster after hardware failures), and for analytical OLAP processing, MyISAM tables (faster loading and updating of versions).
The growth of digg has reached such a stage that a whole series of new problems related to the scaling of the infrastructure have faced the engineers. Buying and installing all large amounts of RAM has ceased to bring effect.
via Presentation from the conference MySQL UC 2007
At launch, the project was hosted on a single Linux server with Apache 1.3 and PHP 4.x. MySQL 4.0, MyISAM tables and MySQL built-in search were used to manage the databases. The developers specifically tried to use as many open source products as possible to ensure the rapid development of the project without financial difficulties. In addition to the above, free packages ImageMagick, Ispell, prototype / scriptaculous, and others have found use. Soon another was added to one server and the project began to grow rapidly.
With the advent of the second server, MyISAM tables had to be supplemented with InnoDB tables. After the appearance of the third server, Apache 2.x and master-slave replication systems were installed in MySQL, they started using memcached, switched to PHP 5.x and hired a database administrator.
Now the digg server system consists of two relatively independent clusters. Separate PHP servers that are behind their load balancer interact with MySQL servers and generate pages in real time.
')

An important role in the process of generating pages is assigned to the memcached caching module, which greatly reduces the load on the servers. In order to increase the efficiency of its work on the specific content of social media, an additional program code was written specifically for the site digg.
The MySQL server group is divided into specialized clusters: main, search, and operational.

It is clear that in such a situation, you can resort to the separation of the database (sharding). This approach has both advantages and disadvantages. The advantages of sharding include increased performance and improved manageability / customizability of the DBMS, and disadvantages include increased PHP load, complicated programming and loss of SQL support. Although MySQL supports several types of sharding, digg does not use any of them, because all of these technologies, according to the developers, were rather raw at that time.
Today, digg databases are a rather heterogeneous structure from MySQL versions 5.0.22, 5.0.27, 5.0.30 and 5.0.32, there is also MySQL 4.1 to support Cacti. The installation and maintenance of databases is carried out through the Debian operating system.
For online OLTP transaction processing, InnoDB tables are used (they also recover faster after hardware failures), and for analytical OLAP processing, MyISAM tables (faster loading and updating of versions).
The growth of digg has reached such a stage that a whole series of new problems related to the scaling of the infrastructure have faced the engineers. Buying and installing all large amounts of RAM has ceased to bring effect.
via Presentation from the conference MySQL UC 2007
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/11168/
All Articles