Recommendations on the availability of pages for people with disabilities
Many have heard of the WAI-WCAG (Web Accessibility Initiative Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) recommendations, designed in particular to help users with disabilities (for example, with defects or lack of view).
But, often, it is ignored or sent as a backlog task in the back box. It seems odd, unclaimed, and in principle, what will the blind do on my site?

')
I still try to justify a little "utility" in two words.
First, is the quality . Your service will become more convenient and easy to use.
And, secondly, this is competitiveness - the target audience is snapped up quickly, so finding new niches is a top priority task, any marketer will tell you.
In my case, this is the requirement of the customer. According to Section 508, if I want to sell a product to any US federal agency, I must maintain this standard.
Many will say that they are hardly going to sell something to the US government, but in Russia there is also such a standard (GOST R 52872–2007) and no one guarantees that tomorrow it will not concern you / us.
It should also be noted that if you already follow the principles of correct markup (according to w3c) and optimization for search engines, then you will not need to make any fundamental changes.
Still, I will give a number of recommendations that cover a significant part of the markup elements. They can be noted and boldly used with the next layout.
It is recommended at the beginning of the menu to put a link to go directly to the content. This will make it possible not to follow the same links on each page.
For an example of not applying tags correctly, I’ll give the form of a habrahabr sandbox:
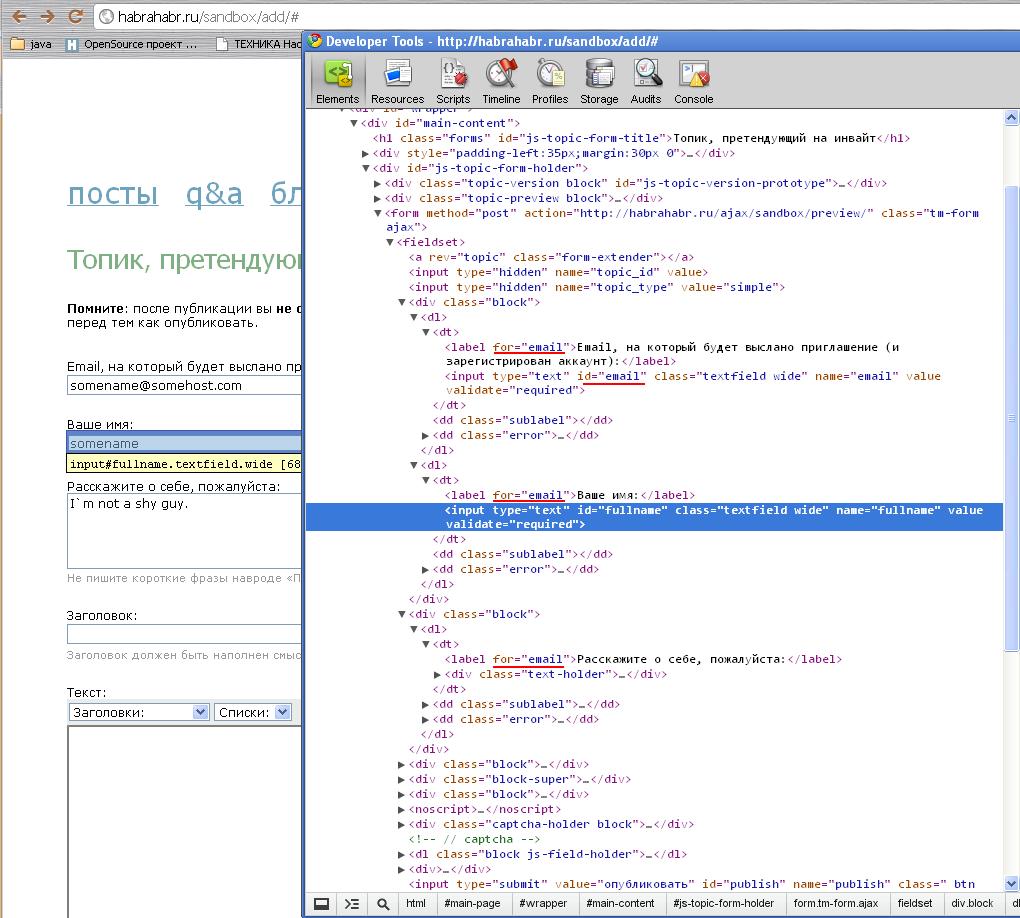
As you can see from the screenshot, three tags are associated with the same input form. Of course, this is most likely a mechanical typo, which will soon be fixed, but this example brings us to an equally important issue of interface testing.
These are the WAVE plug-ins for Firefox and InFocus Toolbar for IE from the SSB Bart Group. Both plugins are free.
There is also a very convenient screen reader JAWS . However, it is paid and it is not so easy to buy it.
PS And most importantly, if you do not know such people, this does not mean that they do not use the Internet. But tomorrow you yourself may be limited in opportunities.
But, often, it is ignored or sent as a backlog task in the back box. It seems odd, unclaimed, and in principle, what will the blind do on my site?

')
I still try to justify a little "utility" in two words.
First, is the quality . Your service will become more convenient and easy to use.
And, secondly, this is competitiveness - the target audience is snapped up quickly, so finding new niches is a top priority task, any marketer will tell you.
In my case, this is the requirement of the customer. According to Section 508, if I want to sell a product to any US federal agency, I must maintain this standard.
Many will say that they are hardly going to sell something to the US government, but in Russia there is also such a standard (GOST R 52872–2007) and no one guarantees that tomorrow it will not concern you / us.
It should also be noted that if you already follow the principles of correct markup (according to w3c) and optimization for search engines, then you will not need to make any fundamental changes.
Still, I will give a number of recommendations that cover a significant part of the markup elements. They can be noted and boldly used with the next layout.
Images:
- If the image carries any information - put the description in the alt attribute;
- If the image is used as a link, use alt to explain where the link leads;
- If you are using images without any information load (spacer.gif for example) leave alt = "" empty.
Tables
- Add the table name to the CAPTION element;
- Describe briefly what information the table contains, and put it in summary ;
- Specify THEAD, TFOOT, TBODY. (And the footer must go to the body of the table TBODY, so that he has time to render before the entire table)
- Use TH to label cells in columns, and TD for data;
- The row cell header is denoted by the scope attribute = "row" . This allows you to associate this cell with all the cells in the TR row;
- Use the abbr attribute to specify short caption names;
- Do not allow nesting of tables. If the nested table is simple, replace it with a list. Otherwise, the screen-reader will be difficult to associate nested cells.
Event handlers
- Try to avoid “narrow” handlers such as onMouseOver and onMouseOut . The user will not be able to work with them through the keyboard only. In this case, add additional handlers:
| current handler | additional |
|---|---|
| onClick | onKeyPress |
| onMouseDown | onKeyDown |
| onMouseUp | onKeyUp |
| onMouseOver | onFocus |
| onMouseOut | onBlur |
| onDblClick | onKeyDown |
- It should be noted that most browsers raise an onClick event for some items when you press Enter. Therefore, adding an additional handler will trigger the event twice. For these elements - A, INPUT, AREA, BUTTON it is enough to leave only onClick ;
- Element A must always contain the href attribute with just #. Otherwise, the link does not receive focus when tabbing;
- If you use not reference elements for navigation, but DIV is acceptable block, then to get the focus you should provide it with the tabindex attribute;
- We should not forget about the logical tabulation system. If there is not enough time for this, and you don’t want to pull up the navigation element from the general tabulation flow - just set the tabindex value to 0.
Navigation
It is recommended at the beginning of the menu to put a link to go directly to the content. This will make it possible not to follow the same links on each page.
Form elements
- Each form element must have a clear label (LABEL) which stands nearby. Basically on the left, and for checkbox and radio button elements on the right;
- In exceptional cases, if there is nowhere to place a label, one should add a title attribute to the form element with a description that the user must enter;
- The use of the title attribute and tags at the same time is extremely undesirable - this causes conflict in many auxiliary reading devices;
- For complex forms it is necessary to apply the FIELDSET grouping element with the LEGEND element.
For an example of not applying tags correctly, I’ll give the form of a habrahabr sandbox:

As you can see from the screenshot, three tags are associated with the same input form. Of course, this is most likely a mechanical typo, which will soon be fixed, but this example brings us to an equally important issue of interface testing.
Utilities to facilitate development
These are the WAVE plug-ins for Firefox and InFocus Toolbar for IE from the SSB Bart Group. Both plugins are free.
There is also a very convenient screen reader JAWS . However, it is paid and it is not so easy to buy it.
Links
- What is Web accessibility? - en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_accessibility
- Web Content Accessibility Guidelines Standard - www.w3.org/TR/WAI-WEBCONTENT
- Accessibility Standards by Country www.w3.org/WAI/Policy
- Many utilities for developers - training, certification www.webaim.org
PS And most importantly, if you do not know such people, this does not mean that they do not use the Internet. But tomorrow you yourself may be limited in opportunities.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/110600/
All Articles