How to start work on a startup?
The topic was inspired by the impressions of the reports on the swpiter and the post on how not to sell the car :)
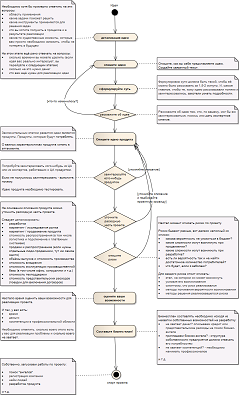
The point is, there is a certain portion of work that needs to be done before you start spending your money. I tried to describe the sequence of these actions.
The picture on the left is clickable, and below is a text description in 12 steps of how to initiate a startup and always win.
')
And so, it all starts with an idea that somehow came to your mind. The idea looks interesting and seductive. She motivates you.
The most important thing in the idea is not to lose motivation up to 10 steps and then in any case you will get the benefit for yourself.
It is necessary at least approximately to answer these questions:
Describe how you imagine the idea. Put thoughts on paper. Create linked text.
The formulation of the essence of the idea should be such that it can be told in 1.5-2 minutes. And, most importantly, those who were told the idea understood and interested, want to know the details.
Do not let the idea lie down! Tell about the idea to those who, in your opinion, could be interested in it, help or give an expert opinion.
In the process of conversations, the idea will mutate, be enriched with details, describe them, as in paragraph (3).
The final stage in the development of an idea is products. Products that will consume.
Important product features are:
Try to interest someone from Central Asia or from experts who worked with Central Asia product.
If you are not interested, find out why.
The idea of the product must be tested on hamsters.
The idea will continue to mutate, go back to point (6) and make a change to the product description!
In the process of conversations do not forget to find out the expert opinion on the cost of product development. Based on the description, such conclusions can already be made.
In the expenditure part should be detailed:
The time has come to describe the risks of the project.
The risks are different, here is an incomplete list of them:
For each risk it is worth describing:
It may turn out that previously unrecorded risks will affect the product idea. In this case, it is worth going back to point (6), making changes and testing the product again.
Up to this point you have worked for yourself and spent only your time (well, and, a little, the time of interlocutors). During the study of issues relating to the idea and the product, you have gained expertise in this area, some contacts began. It is time to assess your ability to implement the project.
It is at this stage that it is sometimes worth refusing to implement the idea. On the other hand, the work already done will be a good reward for the effort! :)
And so, you have:
It is necessary to answer how much of this you have for the implementation of the problem and how much is missing.
It is necessary to make a business plan based on the lack of own development capabilities:
Actually, we start work on the project:
Let me draw your attention: most of the time, work on launching a project does not require any additional efforts from you, you just walk, communicate on occasion, remember what was said.
Stages when you need to sit down and do at least something out of 6 out of 13: this is (2), (4), (6), (8), (9) and (11).
Once again, read the description - it looks monstrous. In fact, everything is much simpler and clearer, many items are minimized to the state of checking “aha, everything is ok with that”. In general, you just have to try, nothing terrible (except for wasting time) is not in it.
The text has grown due to an attempt to indicate important points that are worth paying attention to. These points are taken from my own experience and from observations of the projects of friends. And, let's say, before I begin to risk my own money, I always go over the list to find out that I have not forgotten anything. Download the text along with the chart here .
Do not keep ideas in yourself. Start working on them. Even if the idea turns out to be unrealizable in the current situation, dozens of new ideas will appear during the work on it, contacts will appear, and opportunities will emerge.

How to work on a startup and always win?
The point is, there is a certain portion of work that needs to be done before you start spending your money. I tried to describe the sequence of these actions.
The picture on the left is clickable, and below is a text description in 12 steps of how to initiate a startup and always win.
')
1. Idea!
And so, it all starts with an idea that somehow came to your mind. The idea looks interesting and seductive. She motivates you.
The most important thing in the idea is not to lose motivation up to 10 steps and then in any case you will get the benefit for yourself.
2. Detailed ideas
It is necessary at least approximately to answer these questions:
- application area
- what tasks will help solve
- what tools are used to solve problems
- what do you want to get in the process and as a result of the implementation
- any significant points that you just need to set out so as not to lose in the future
- how much time you can spend (if the idea really interests you, you will proceed to the next steps)
- how much money do you need?
- who else do you need to implement the idea
3. Describe the idea
Describe how you imagine the idea. Put thoughts on paper. Create linked text.
4. Formulate the essence
The formulation of the essence of the idea should be such that it can be told in 1.5-2 minutes. And, most importantly, those who were told the idea understood and interested, want to know the details.
5. Tell us about the idea
Do not let the idea lie down! Tell about the idea to those who, in your opinion, could be interested in it, help or give an expert opinion.
In the process of conversations, the idea will mutate, be enriched with details, describe them, as in paragraph (3).
6. Describe the product idea
The final stage in the development of an idea is products. Products that will consume.
Important product features are:
- the target audience
- who is it?
- What do they need this product for?
- Why do they need such a product?
- Why would they be interested in such a product?
- What benefits will they get?
- target segmentation
- it is possible to segment by any significant attribute:
- by product use
- by industry
- profit generation (remember the Pareto principle: 80% of profits bring 20% of buyers)
- by age, gender, etc.
- select groups of at least 5% of the characteristic you are interested in and describe them
- imagine a typical representative of this group
- who is he?
- his name, gender, income, age, nationality?
- his methods of doing business?
- his habits?
- his needs?
- his weaknesses?
- it is possible to segment by any significant attribute:
- consumption method
- What are the targeted uses?
- what non-target uses can be?
- monetization
- How will the product bring you income?
- What form will this income be? There are many types of income, this is not a complete list:
- salary as a company employee
- payments from the sale of the product
- increase in the value of a share in a company (what investors are guided by)
- increase your value in the labor market by
- acquisition of expertise
- business acquisitions
- increasing personal awareness and popularity
- enhance personal reputation
- What form of income are you interested in?
- What absolute income (minus all costs) interests you?
- product instance life cycle: there is a product, but there is a product instance
- How is each product manufactured?
- What stages of consumption does it go through?
- end of life of a product instance: all product instances either end or deteriorate; for example, the program may lose its relevance with the release of the new version, the account in the forum may be lost, and the service life will end
- What will happen to the product instance after the end of the life cycle?
- ways to extend the life cycle
- ways of proposing another instance
- ways to offer a different copy, but better or worse (paid version, free version, new version)
- product life cycle: product instances live and die, but the same can be said about the product as a whole, it can lose relevance, deteriorate or become unpopular
- development
- development materials
- developers
- production creation
- production
- instance cost?
- materials?
- packaging? (for programs, this may be the installer and serial number)
- cost of delivery?
- copy value for the consumer?
- instance cost?
- setting up production of copies
- How do consumers know about the product?
- What are the methods to convey information about the product to the consumer?
- What are the distribution methods?
- How to get product opinions from consumers?
- scenarios of how a particular consumer learns about a product
- other marketing issues
- delivery of copies: in order to use the product, the copy must be delivered to the consumer
- What are the delivery methods for the instance?
- What forms / formats can I deliver?
- introduction: so that the product can begin to use, the consumer must be able to use this product
- What are the options for customizing the product for the consumer?
- How to teach the use of the product?
- How can a consumer take advantage of technical support?
- cost of training and technical support for the consumer?
- development
- retention: so that the consumer wants to use the product again, it is necessary for the consumer to be reminded all the time that the product is cool and he needs it
- how to do it?
- How to recognize consumer sensations and needs from a product?
- How to control the consumer's feelings from the product?
- How to make changes to the product at the request of users?
- exploitation
- product use scenarios: scripts should be written for each segment of the target audience of more than 5%
- operating cost
- electricity
- spending on technical support
- payments for services
- death: the product will die sooner or later, eternity does not exist
- what are the death scenarios?
- divide the death scenarios into negative and positive:
- positive death scenarios: the product is outdated because a new version has been released
- negative death scenarios: the product has not gained popularity, the cost price is expensive, it is necessary to turn off production
- describe ways out of positive and negative scenarios
7. Get someone interested in the product.
Try to interest someone from Central Asia or from experts who worked with Central Asia product.
If you are not interested, find out why.
The idea of the product must be tested on hamsters.
The idea will continue to mutate, go back to point (6) and make a change to the product description!
8. Specify the cost of the project
In the process of conversations do not forget to find out the expert opinion on the cost of product development. Based on the description, such conclusions can already be made.
In the expenditure part should be detailed:
- development
- marketing / market research
- marketing / product promotion
- distribution cost (including logistics and connection to payment systems)
- sales and distribution (if you need individual sales people, this is where they belong)
- production volumes and production costs
- implementation cost
- the cost of operating the production base (including office, staff, etc.)
- cost of technical support
- cost of hospitality (travel for contracts)
9. Describe the risks
The time has come to describe the risks of the project.
The risks are different, here is an incomplete list of them:
- What is the probability not to meet the budget?
- What difficulties may arise during the promotion?
- what difficulties may arise during the development?
- Is there any chance of not finding enough consumers?
- What happens if I get sick?
For each risk it is worth describing:
- the stage at which it may arise
- conditions of its occurrence
- symptoms that the risk is realized
- methods of reducing the probability of occurrence
- methods of solving realized risk
It may turn out that previously unrecorded risks will affect the product idea. In this case, it is worth going back to point (6), making changes and testing the product again.
10. Evaluate your options.
Up to this point you have worked for yourself and spent only your time (well, and, a little, the time of interlocutors). During the study of issues relating to the idea and the product, you have gained expertise in this area, some contacts began. It is time to assess your ability to implement the project.
It is at this stage that it is sometimes worth refusing to implement the idea. On the other hand, the work already done will be a good reward for the effort! :)
And so, you have:
- time
- money
- professional competences
It is necessary to answer how much of this you have for the implementation of the problem and how much is missing.
11. Make a business plan!
It is necessary to make a business plan based on the lack of own development capabilities:
- not enough money? we describe a loan or representation expenses for a business angel search
- invite business angel? - the ownership structure of the enterprise must meet its needs
- not enough competences? - you need to hire professionals
12. Project launch
Actually, we start work on the project:
- investor search
- Company registration
- hiring people
- product development
Afterword
Let me draw your attention: most of the time, work on launching a project does not require any additional efforts from you, you just walk, communicate on occasion, remember what was said.
Stages when you need to sit down and do at least something out of 6 out of 13: this is (2), (4), (6), (8), (9) and (11).
PS
Once again, read the description - it looks monstrous. In fact, everything is much simpler and clearer, many items are minimized to the state of checking “aha, everything is ok with that”. In general, you just have to try, nothing terrible (except for wasting time) is not in it.
The text has grown due to an attempt to indicate important points that are worth paying attention to. These points are taken from my own experience and from observations of the projects of friends. And, let's say, before I begin to risk my own money, I always go over the list to find out that I have not forgotten anything. Download the text along with the chart here .
Pps
Do not keep ideas in yourself. Start working on them. Even if the idea turns out to be unrealizable in the current situation, dozens of new ideas will appear during the work on it, contacts will appear, and opportunities will emerge.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/107380/
All Articles