GPRS inside. Part 4.1
This is the final part of a series of articles on GPRS / EDGE technologies, which we began in the previous three narrations: 1 , 2 , 3 . This time we will look behind the door mash. halls and see what actually provides the ability to transmit and receive data over the air using a mobile phone - we will talk about hardware under SGSNs and GGSNs.
As we already know from previous articles on packet technologies in mobile networks, currently 2G networks are the most widely distributed with the prospect of transition to the next generation of architectures and, naturally, SGSN 's and GGSN ' are the main network elements for such networks. s.
I’ll just say that the article is not an advertisement for a certain vendor, I’m just an opportunity to share the experience of the implementation of the packet-based network (PS Core Network) based on this vendor, in particular, we’ll discuss NSN products: Flexi ISN , which is a GGSN implementation and CombiSGSN , which is naturally the SGSN implementation for the PS Core Network.
')
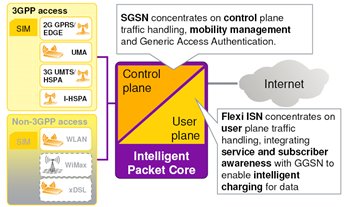
In almost any packet network there is a division into so-called. subscriber data transmission area (User plane) and the area of transmission of service information necessary to establish communication, correctly interrupt it, track subscriber movement over the network, etc. Moreover, in realizations of more and more modern technologies of the core network (GPRS / EDGE -> UMTS -> HSDPA -> LTE), this division is becoming more pronounced, separate network elements are distinguished for serving each of the planes, while in previous technologies the functions of controlling both the planes could be “engaged” by the same network element, for example SGSN.
In the 2G packet network, the division into the maintenance of the above planes can be conditionally applied to SGSN and GGSN (see the figure below).
We will begin our acquaintance with the GGSN implementation in the packet network - the Flexi ISN [Intelligent Service Node], and in the second part of this article we will take a closer look at the implementations of one of the most basic network elements - SGSN 'ohm.

Naturally, the needs of various mobile operators, providing the opportunity to use services and services based on packet networks, vendors create implementations of various network elements. No exception and packet network, almost all large telecommunications vendors provide their solutions in the "segment" GGSN'ov, and since In fact, GGSN is a multifunctional router / gateway, then monsters such as Cisco , Juniper Networks , not to mention NSN , Huawei and Ericsson , as well as the recently purchased Motorola division, come to the scene.
In order to slightly refresh the knowledge of the main network interfaces with which we familiarized in 3 parts , let me remind you the key interfaces with which the implementation of the GGSN from NSN - Flexi ISN works, which is shown in the figure above:

With a detailed description and purpose of each of the interfaces, you can learn from the articles above, and we will begin to consider the capabilities of the Flexi ISN.
In fact, Flexi ISN is a GGSN server, the main tasks of which include establishing and maintaining subscriber traffic, servicing APN on the operator’s packet network, providing access to various packet networks - internet, intranet. The main characteristics of GGSN'ov usually include the number of simultaneously raised PDP Context'ov and maximum throughput for access to external channels.

In this regard, the Flexi ISN has the following performance characteristics :
Naturally, Flexi ISN supports the basic functionality of providing a service in a packet network for the requested APN by the subscriber:
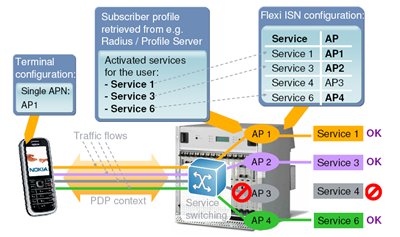
The main features include: Peer-to-Peer Detection & Control, Per Service Access Control, QoS, Charging, Bandwidth Management, as well as:
On the basis of Flexi ISNs, you can also implement a so-called. Multiple Charging Models , i.e. Carry out billing based on various events committed by the subscriber.
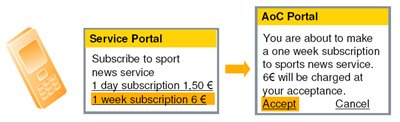
One of the useful functionalities provided by Flexi ISN is the so-called. Advice of Charge (AoC), which allows you to get acquainted with the price for the future use of the service, before starting its pricing, i.e. Before opening a certain HTTP / WAP session, the subscriber is redirected to the AoC server, which notifies him of the cost of the requested service and the subscriber can either accept the pricing conditions for using the service, or refuse. In the case of so-called. Non-HTTP / WAP traffic, notifications using WAP Push are used . This functionality can be widely used with subscription-based services.
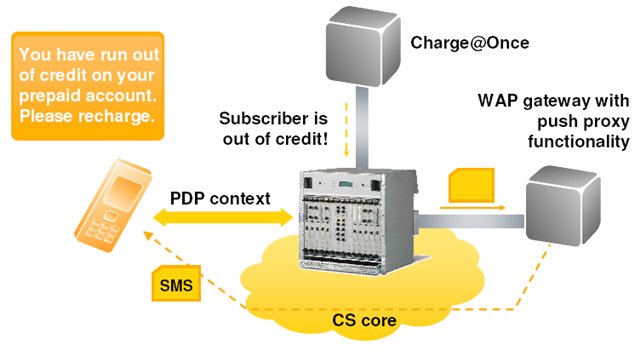
Another rather convenient functionality that can be provided by Flexi ISN and which is simply necessary for the realities of mobile operators in the CIS, in my opinion, is the ability to notify a subscriber that their cash balance has been exceeded for using packet services. Such notifications are also possible along with the Push message, which will redirect the subscriber to the operator’s site / portal.
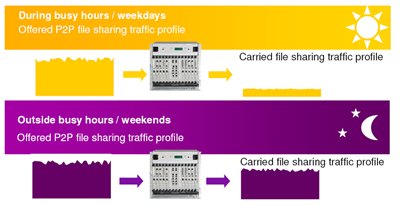
Operators consider one of their many “troubles” to be the transfer of data through peer-to-peer networks, and they are trying to oppress the presence of various services based on such networks in order not to lose their precious data. In particular, this also applies to mobile telephony based on peer-to-peer technology, the same Skype, various instant messengers: ICQ, Jabber, etc., not to mention transferring files through different trackers.
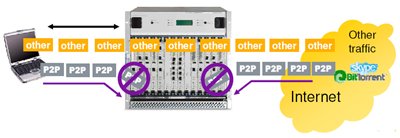
And in this case, the Flexi ISN is quite a significant “ assistant ” for operators, since provides quite extensive opportunities in terms of controlling and blocking Peer-To-Peer traffic, in particular:
At the same time, it is possible not only to block the selected type of Peer-To-Peer traffic, but to significantly reduce its quality. Traffic blocking can be based on the following criteria:
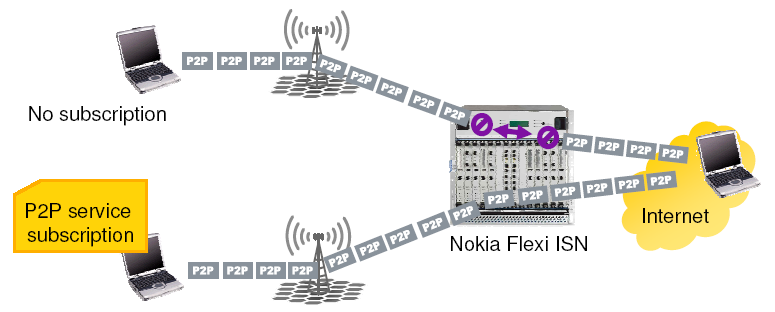
But it is also possible options for peer-to-peer traffic as an additional service, which can be separately provided to subscribers for a separate fee. For example, it is possible to provide access to peering networks by subscription, the same Skype, Bittorrent, etc.
Or form tariff plans based on the time of day, for example, provide access to the ability to transfer data through peer-to-peer networks only at night, because At this time, the total load on the operator’s network is reduced.
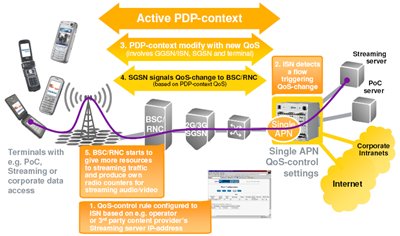
Quite significant attention is paid to the QoS profiles used to serve various services.
Moreover, the influence of QoS profiles can be extended both to subscribers using PoC services, and so-called services. Streaming services (VoIP, Video broadcasting, etc.), as well as corporate users.
Flexi ISN has quite flexible approaches to organizing access to corporate networks through mobile packet services:
The Flexi ISN itself mounted in a rack rack has the following appearance:
In the photo above, it is clear that only two Flexi ISN modules were installed, but it is possible to expand up to 4 such modules to realize maximum configuration.
This is the end of our acquaintance with the structure and main possibilities of implementing GGSN from NSN. In the second part of this article we will meet with SGSN'om from the same vendor ...
A small assistant:
APN - Access Point Name
CDR - Call-Data Record
EDGE - Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution
GGSN - Gateway GPRS Support Node
GPRS - General Packet Radio Service
GRE - Generic Routing Encapsulation
GTP - GPRS Tunneling Protocol
HSDPA - High-Speed Downlink Packet Access
HSUPA - High-Speed Uplink Packet Access
IMS - IP Multimedia System
LTE - Long Term Evolution
NSN - Nokia Siemens Networks
PDP - Packet Data Protocol
PS - Packet Switched
QoS - Quality of Service
SGSN - Serving GPRS Support Node
SIP - Session Initiation Protocol
UMTS - Universal Mobile Telecommunications System
WAP - Wireless Application Protocol
As we already know from previous articles on packet technologies in mobile networks, currently 2G networks are the most widely distributed with the prospect of transition to the next generation of architectures and, naturally, SGSN 's and GGSN ' are the main network elements for such networks. s.
I’ll just say that the article is not an advertisement for a certain vendor, I’m just an opportunity to share the experience of the implementation of the packet-based network (PS Core Network) based on this vendor, in particular, we’ll discuss NSN products: Flexi ISN , which is a GGSN implementation and CombiSGSN , which is naturally the SGSN implementation for the PS Core Network.
')
In almost any packet network there is a division into so-called. subscriber data transmission area (User plane) and the area of transmission of service information necessary to establish communication, correctly interrupt it, track subscriber movement over the network, etc. Moreover, in realizations of more and more modern technologies of the core network (GPRS / EDGE -> UMTS -> HSDPA -> LTE), this division is becoming more pronounced, separate network elements are distinguished for serving each of the planes, while in previous technologies the functions of controlling both the planes could be “engaged” by the same network element, for example SGSN.
In the 2G packet network, the division into the maintenance of the above planes can be conditionally applied to SGSN and GGSN (see the figure below).

We will begin our acquaintance with the GGSN implementation in the packet network - the Flexi ISN [Intelligent Service Node], and in the second part of this article we will take a closer look at the implementations of one of the most basic network elements - SGSN 'ohm.
NSN Flexi ISN

Naturally, the needs of various mobile operators, providing the opportunity to use services and services based on packet networks, vendors create implementations of various network elements. No exception and packet network, almost all large telecommunications vendors provide their solutions in the "segment" GGSN'ov, and since In fact, GGSN is a multifunctional router / gateway, then monsters such as Cisco , Juniper Networks , not to mention NSN , Huawei and Ericsson , as well as the recently purchased Motorola division, come to the scene.
In order to slightly refresh the knowledge of the main network interfaces with which we familiarized in 3 parts , let me remind you the key interfaces with which the implementation of the GGSN from NSN - Flexi ISN works, which is shown in the figure above:

With a detailed description and purpose of each of the interfaces, you can learn from the articles above, and we will begin to consider the capabilities of the Flexi ISN.
In fact, Flexi ISN is a GGSN server, the main tasks of which include establishing and maintaining subscriber traffic, servicing APN on the operator’s packet network, providing access to various packet networks - internet, intranet. The main characteristics of GGSN'ov usually include the number of simultaneously raised PDP Context'ov and maximum throughput for access to external channels.

In this regard, the Flexi ISN has the following performance characteristics :
- Capasity:
- about 1M simultaneous PDP Context'ov in the basic configuration, with the possibility of expanding to 4M simultaneous PDP Context'ov.
- 1Gbps bandwidth in the basic configuration, with the ability to expand up to 5Gbps bandwidth from one rack.
- Up to 5500 PDP Context Processing per second.
- Service up to 1000 different APN.
- Multi-Access level supports:
- Different Alias APN, i.e. the ability to combine different APNs under a specific service.
- Wildcard APN - the ability to support any existing APN operator’s network for subscribers who have * in HLR instead of APN (For more information, it doesn’t matter who you are ... it’s important what APN is! ).
- HSDPA support (16Mbps).
- HSUPA support (8Mbps).
- GGSN's networking capabilities provide the following features:
- The allocation of IP addresses in the following schemes: Static, Radius, DHCP, Internal Pool
- Supports Overlapping IP Addresses, i.e. "Overlapping networks" for VPN access.
- Policy Based Routing
- Multiple Routing Instances
- L2TP (LAC), GRE, IP-in-IP
- VLAN With QoS Mapping
- IPv6 User Layer
- IPv6 Routing
- WAP GW Redirection (WAP 1.x)
- Traffic redirection
- Load balancing
- Header Modification (HTTP) feature
- Service capabilities of the following services:
- L3 / L4 Analyzes
- L7 Inspection For: HTTP, WAP1.x, WAP2.0, RTSP, MMS (WAP 1.x), P2P
- Personal firewall
- Charging:
- Real-Time DCCA Based Charging
- Offline Charging GTP` (TLV, XML) (a form of GTP protocol).
- Radius Online Charging
- Temporary storage of CDR files
- Volume, Time & Hit Charging
- Time step charging
- Redundant CG Connection
- PoC Prepaid Charging Support (see article: Mobile Walkie-Talkie )
- MMS Transaction Based Charging
- Self-Contained CDR Format
- End User Notifications (ability to notify the subscriber using various Push messages, for example, via the Gc interface).
- Comply with the following requirements regarding various security policies:
- 3GPP QoS, IMS Support
- User Profile Downloading With: Radius or LDAP
- Radius Disconnect Support
- Service Authorization Based On: Roaming, Location, Access Type
- Service Based QoS, which allows to significantly increase the level of services provided, see the article GPRS QoS - myth or reality?
- IPv4 / IPv6 traffic controlled over go interface

Naturally, Flexi ISN supports the basic functionality of providing a service in a packet network for the requested APN by the subscriber:

The main features include: Peer-to-Peer Detection & Control, Per Service Access Control, QoS, Charging, Bandwidth Management, as well as:
- Lawful Interception (with IPSec), which by the way, is a strict requirement from law enforcement agencies when entering such equipment on the operator’s network.
- RoHS Compliance
- Command Line Interface (CLI)
- Service Level Statistics
- Multiple Deployment Options (NAS)
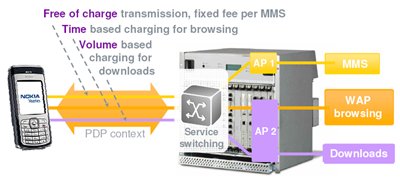
On the basis of Flexi ISNs, you can also implement a so-called. Multiple Charging Models , i.e. Carry out billing based on various events committed by the subscriber.
- Deep Packet Inspection [ DPI ] allows you to define and control various types of traffic (see the article)
- Different services can be charged differently even within the same PDP session.
- Tariff plans based on various protocols, services and levels: FTP, HTTP, WAPv1 / v2, MMS, L3 / L4, P2P, etc.

One of the useful functionalities provided by Flexi ISN is the so-called. Advice of Charge (AoC), which allows you to get acquainted with the price for the future use of the service, before starting its pricing, i.e. Before opening a certain HTTP / WAP session, the subscriber is redirected to the AoC server, which notifies him of the cost of the requested service and the subscriber can either accept the pricing conditions for using the service, or refuse. In the case of so-called. Non-HTTP / WAP traffic, notifications using WAP Push are used . This functionality can be widely used with subscription-based services.
Another rather convenient functionality that can be provided by Flexi ISN and which is simply necessary for the realities of mobile operators in the CIS, in my opinion, is the ability to notify a subscriber that their cash balance has been exceeded for using packet services. Such notifications are also possible along with the Push message, which will redirect the subscriber to the operator’s site / portal.
Peer-to-peer networks
Operators consider one of their many “troubles” to be the transfer of data through peer-to-peer networks, and they are trying to oppress the presence of various services based on such networks in order not to lose their precious data. In particular, this also applies to mobile telephony based on peer-to-peer technology, the same Skype, various instant messengers: ICQ, Jabber, etc., not to mention transferring files through different trackers.
And in this case, the Flexi ISN is quite a significant “ assistant ” for operators, since provides quite extensive opportunities in terms of controlling and blocking Peer-To-Peer traffic, in particular:
- ability to analyze the following protocols and services:
- Ability to analyze P2P tracking protocols:
At the same time, it is possible not only to block the selected type of Peer-To-Peer traffic, but to significantly reduce its quality. Traffic blocking can be based on the following criteria:
- type of service Peer-to-Peer network
- network access type or subscriber location
- subscription to certain services
But it is also possible options for peer-to-peer traffic as an additional service, which can be separately provided to subscribers for a separate fee. For example, it is possible to provide access to peering networks by subscription, the same Skype, Bittorrent, etc.
Or form tariff plans based on the time of day, for example, provide access to the ability to transfer data through peer-to-peer networks only at night, because At this time, the total load on the operator’s network is reduced.
Service Based QoS
Quite significant attention is paid to the QoS profiles used to serve various services.
Moreover, the influence of QoS profiles can be extended both to subscribers using PoC services, and so-called services. Streaming services (VoIP, Video broadcasting, etc.), as well as corporate users.
Corporate Access Points
Flexi ISN has quite flexible approaches to organizing access to corporate networks through mobile packet services:
- The ability to allocate a separate APN for corporate access.
- Providing virtual networks (VLAN, Separate Routing Instances).
- Allocation of IP addresses from the address space of the corporate network.
- Using Overlapping IP Addresses, i.e. "Overlapping networks".
- Additional authentication mechanisms in corporate networks (Radius)
- IP tunnel support (IP-in-IP, GRE, L2TP).
- The use of the same APN as for access to the corporate segment, and for other packet services from the operator.
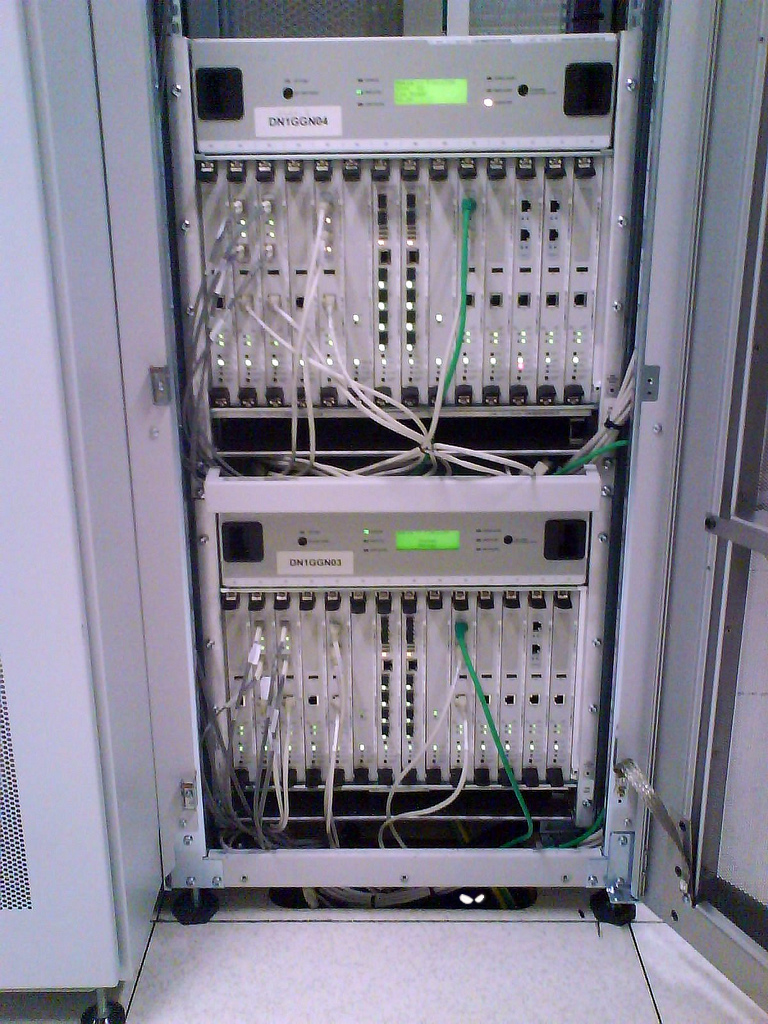
GGSN Rack
The Flexi ISN itself mounted in a rack rack has the following appearance:
In the photo above, it is clear that only two Flexi ISN modules were installed, but it is possible to expand up to 4 such modules to realize maximum configuration.
This is the end of our acquaintance with the structure and main possibilities of implementing GGSN from NSN. In the second part of this article we will meet with SGSN'om from the same vendor ...
A small assistant:
APN - Access Point Name
CDR - Call-Data Record
EDGE - Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution
GGSN - Gateway GPRS Support Node
GPRS - General Packet Radio Service
GRE - Generic Routing Encapsulation
GTP - GPRS Tunneling Protocol
HSDPA - High-Speed Downlink Packet Access
HSUPA - High-Speed Uplink Packet Access
IMS - IP Multimedia System
LTE - Long Term Evolution
NSN - Nokia Siemens Networks
PDP - Packet Data Protocol
PS - Packet Switched
QoS - Quality of Service
SGSN - Serving GPRS Support Node
SIP - Session Initiation Protocol
UMTS - Universal Mobile Telecommunications System
WAP - Wireless Application Protocol
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/105794/
All Articles