Mission MESSENGER
For a long time on Habré there were no posts on space subjects. However, space articles are often quite interesting for the habrasoobshchestvo. The word MESSENGER in the title may be at first perceived as “Instant Messenger”, and the article as another news about the brainchild from Microsoft. But it will be a little about the other.

Attention readers are invited to a small article on the space project MESSENGER.
MESSENGER is a scientific study of the planet Mercury by launching a spacecraft to it.
The name of the mission MESSENGER is composed of English phrases:
ME rcury S urface (Surface of Mercury)
S pace en vironment (Outer space)
GE ochemistry (Geochemistry)
R anging (Classification).
Mercury himself, by the way, is named after the mythical messenger (eng. Messenger) of the gods.
Under the cut information about the project and interesting photos.
All images are clickable.

The spacecraft was launched on August 3, 2004 at Cape Canaveral (Florida, USA).
The journey of the ship MESSENGER will take more than 6.5 years before it takes its place in the orbit of Mercury in March 2011. The path includes a passage above the Earth (August 2005), two flights near Venus (October 2006 and June 2007) and three flights over Mercury (January 2008, October 2008 and September 2009). The overall path, the upcoming MESSENGER is more than 7.9 billion kilometers, the average speed of the “traveler” is about 38 km / s.
')
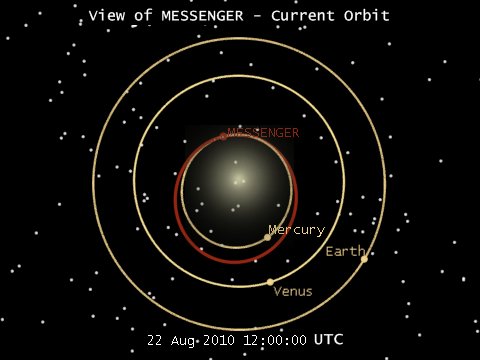
The current position of the spacecraft can always be viewed in the Solar System Simulator on the NASA website.
During the flight over the Earth (August 2, 2005), MESSENGER took several pictures of our planet in the visible and infrared spectrum.

In the course of two orbits over Venus, a whole series of images of its surface was taken. In particular, on June 5, 2005 MESSENGER camera MDIS filmed the surface of the planet, covered with a thick layer of clouds.

However, as a result of processing the images, scientists were able to see the surface of Venus.

Having reached the goal of his long journey - Mercury, MESSENGER for the first time captured the previously invisible side of the planet.

On January 22, 2008, color photographs of Mercury were taken.


Then images of the surface of Mercury were obtained from the apparatus, where the craters on the surface were given names, among them Picasso and Kipling.

At the moment, scientists MESSENGER are searching for the so-called volcanoids (eng. Vulcanoids) - asteroids orbiting around Solonts inside the orbit of Mercury. So far, no such objects have been found.
On August 17, 2010, an interesting photo was taken by the MESSENGER device, depicting the Earth and the Moon from a distance of 183 million kilometers. For comparison, the distance between the Earth and the Sun is 150 million kilometers.

The main questions to be answered by scientists as a result of the study:
- What is the geological history of Mercury?
- Why is the density of the planet so high?
- What is the nature of the Mercury magnetic field?
- What is the structure of the core of the planet?
- What kind of unusual substance is located on the poles of Mercury?
- What is the nature of changes on the planet?

The equipment with which the spacecraft is equipped:
- Dual shooting system MDIS (camera with a wide and narrow viewing angle).
- Spectrometer of neutrons and gamma rays (GRNS) for mapping the elemental composition of the bark of Mercury.
- A gamma-ray spectrometer (XRS) for studying the chemical composition of the components of the planet's crust.
- Magnetometer (MAG) for studying the detailed structure and dynamics of the magnetic field of Marcury.
As well as an altimeter to study the relief of the planet, a spectrometer to study the atmosphere and a device to study the composition of charged particles inside and around Mercury's magnetosphere.
Useful links:
1. The site of the project MESSENGER
2. MESSENGER on the NASA website

Attention readers are invited to a small article on the space project MESSENGER.
MESSENGER is a scientific study of the planet Mercury by launching a spacecraft to it.
The name of the mission MESSENGER is composed of English phrases:
ME rcury S urface (Surface of Mercury)
S pace en vironment (Outer space)
GE ochemistry (Geochemistry)
R anging (Classification).
Mercury himself, by the way, is named after the mythical messenger (eng. Messenger) of the gods.
Under the cut information about the project and interesting photos.
All images are clickable.

The spacecraft was launched on August 3, 2004 at Cape Canaveral (Florida, USA).
The journey of the ship MESSENGER will take more than 6.5 years before it takes its place in the orbit of Mercury in March 2011. The path includes a passage above the Earth (August 2005), two flights near Venus (October 2006 and June 2007) and three flights over Mercury (January 2008, October 2008 and September 2009). The overall path, the upcoming MESSENGER is more than 7.9 billion kilometers, the average speed of the “traveler” is about 38 km / s.
')

The current position of the spacecraft can always be viewed in the Solar System Simulator on the NASA website.
During the flight over the Earth (August 2, 2005), MESSENGER took several pictures of our planet in the visible and infrared spectrum.

In the course of two orbits over Venus, a whole series of images of its surface was taken. In particular, on June 5, 2005 MESSENGER camera MDIS filmed the surface of the planet, covered with a thick layer of clouds.

However, as a result of processing the images, scientists were able to see the surface of Venus.

Having reached the goal of his long journey - Mercury, MESSENGER for the first time captured the previously invisible side of the planet.

On January 22, 2008, color photographs of Mercury were taken.


Then images of the surface of Mercury were obtained from the apparatus, where the craters on the surface were given names, among them Picasso and Kipling.

At the moment, scientists MESSENGER are searching for the so-called volcanoids (eng. Vulcanoids) - asteroids orbiting around Solonts inside the orbit of Mercury. So far, no such objects have been found.
On August 17, 2010, an interesting photo was taken by the MESSENGER device, depicting the Earth and the Moon from a distance of 183 million kilometers. For comparison, the distance between the Earth and the Sun is 150 million kilometers.

The main questions to be answered by scientists as a result of the study:
- What is the geological history of Mercury?
- Why is the density of the planet so high?
- What is the nature of the Mercury magnetic field?
- What is the structure of the core of the planet?
- What kind of unusual substance is located on the poles of Mercury?
- What is the nature of changes on the planet?

The equipment with which the spacecraft is equipped:
- Dual shooting system MDIS (camera with a wide and narrow viewing angle).
- Spectrometer of neutrons and gamma rays (GRNS) for mapping the elemental composition of the bark of Mercury.
- A gamma-ray spectrometer (XRS) for studying the chemical composition of the components of the planet's crust.
- Magnetometer (MAG) for studying the detailed structure and dynamics of the magnetic field of Marcury.
As well as an altimeter to study the relief of the planet, a spectrometer to study the atmosphere and a device to study the composition of charged particles inside and around Mercury's magnetosphere.
Useful links:
1. The site of the project MESSENGER
2. MESSENGER on the NASA website
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/102372/
All Articles